Waxing provides a protective layer that enhances shine and repels water temporarily, but it requires frequent reapplication to maintain effectiveness. Sealing, on the other hand, penetrates surfaces to create a longer-lasting barrier against stains and wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Choosing between waxing and sealing depends on the surface type and desired durability of maintenance.
Table of Comparison
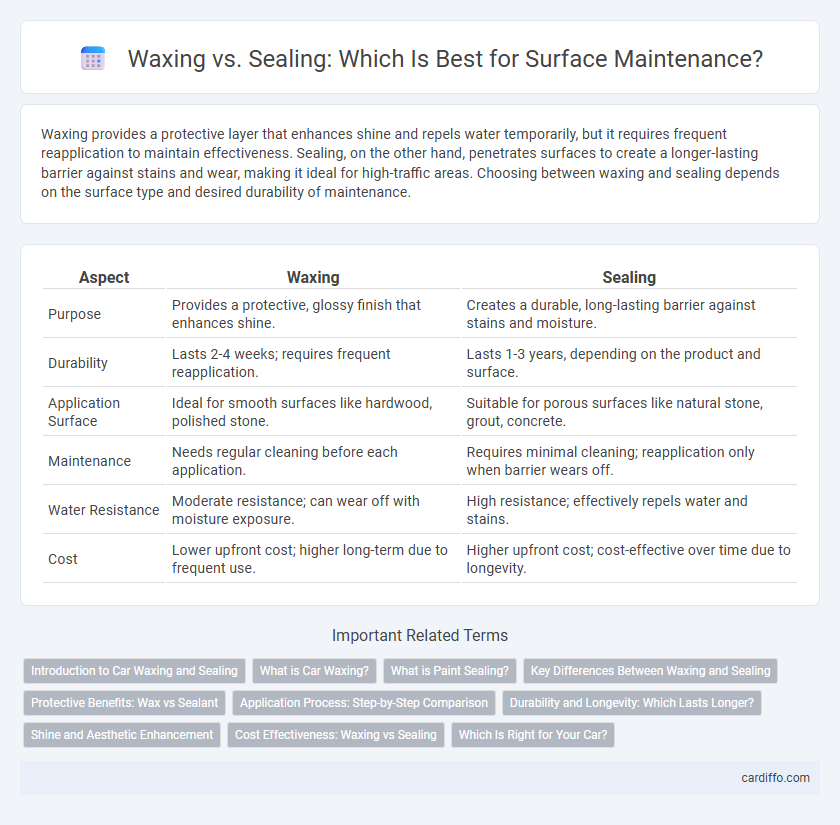
| Aspect | Waxing | Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides a protective, glossy finish that enhances shine. | Creates a durable, long-lasting barrier against stains and moisture. |
| Durability | Lasts 2-4 weeks; requires frequent reapplication. | Lasts 1-3 years, depending on the product and surface. |
| Application Surface | Ideal for smooth surfaces like hardwood, polished stone. | Suitable for porous surfaces like natural stone, grout, concrete. |
| Maintenance | Needs regular cleaning before each application. | Requires minimal cleaning; reapplication only when barrier wears off. |
| Water Resistance | Moderate resistance; can wear off with moisture exposure. | High resistance; effectively repels water and stains. |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost; higher long-term due to frequent use. | Higher upfront cost; cost-effective over time due to longevity. |
Introduction to Car Waxing and Sealing
Car waxing creates a protective layer that enhances shine and repels water, prolonging paint life through natural oils and synthetic polymers. Sealing uses advanced polymer or ceramic compounds to offer longer-lasting protection and stronger resistance to contaminants like UV rays, dirt, and road salts. Both methods require regular maintenance, but sealing provides a more durable shield, making it ideal for harsh environments and extended coverage.
What is Car Waxing?
Car waxing involves applying a thin layer of wax made from natural or synthetic ingredients to the vehicle's paint surface to enhance shine and provide a protective barrier against environmental elements such as UV rays, dirt, and water. This process helps to fill in minor scratches and smooth the paint, resulting in a glossy, polished finish that can last several weeks depending on the wax type and driving conditions. Regular waxing reduces the risk of paint oxidation and contributes to maintaining the car's aesthetic appeal and resale value.
What is Paint Sealing?
Paint sealing is a protective process that applies a synthetic polymer layer to a vehicle's exterior, forming a durable barrier against environmental contaminants like UV rays, dirt, and water. Unlike waxing, which is typically made from natural oils and offers temporary shine, sealants provide longer-lasting protection, enhancing the paint's resistance to oxidation and fading. Professional-grade paint sealers can extend the lifespan of a car's finish by several months, making them ideal for maintaining optimal gloss and durability.
Key Differences Between Waxing and Sealing
Waxing creates a protective layer on surfaces by applying a thin coat of wax that enhances shine and repels water but requires regular reapplication, while sealing involves penetrating the surface with a chemical barrier that provides longer-lasting protection against stains and moisture. Wax typically suits polished wood and car exteriors for aesthetic gloss, whereas sealants are ideal for porous materials like concrete, stone, and grout due to their deep penetration and durability. The key difference lies in the application method and longevity, with sealing offering more robust, long-term maintenance benefits compared to the temporary surface-level protection of waxing.
Protective Benefits: Wax vs Sealant
Wax creates a hydrophobic barrier that repels water and enhances shine but requires frequent reapplication to maintain protection. Sealants form a durable, chemical-resistant layer that offers long-lasting defense against UV rays, dirt, and contaminants. The choice between waxing and sealing depends on desired maintenance frequency and the level of environmental protection needed for the surface.
Application Process: Step-by-Step Comparison
Waxing involves cleaning the surface, applying a thin layer of wax with a cloth or applicator, allowing it to haze, and buffing it to a shine, typically requiring reapplication every few months. Sealing requires thorough cleaning and drying of the surface, applying the sealer with a brush, roller, or sprayer in a thin, even layer, and curing it for 24 to 48 hours to form a durable protective barrier. The waxing process is quicker but less durable, while sealing takes longer but provides extended protection against stains and damage.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Sealing provides superior durability and longevity compared to waxing, as sealants penetrate the surface to create a protective barrier against moisture, stains, and wear. Wax typically lasts a few weeks, requiring frequent reapplication, while quality sealers can endure for months or even years, significantly reducing maintenance frequency. For high-traffic or outdoor areas, sealing offers a more robust, long-lasting solution that preserves the surface integrity over time.
Shine and Aesthetic Enhancement
Waxing enhances shine by creating a smooth, reflective surface that highlights a vehicle's paint depth and gloss. Sealing provides longer-lasting protection with a sleek finish that maintains aesthetic appeal by preventing oxidation and environmental damage. Both improve appearance, but waxing delivers a richer shine while sealing offers durable, polished protection.
Cost Effectiveness: Waxing vs Sealing
Sealing offers a longer-lasting protective barrier on surfaces, reducing the frequency of reapplications and lowering overall maintenance costs compared to waxing. Waxing requires more frequent upkeep, which increases labor and material expenses over time. For large areas or high-traffic environments, sealing provides a more cost-effective solution by extending surface durability and minimizing repetitive treatments.
Which Is Right for Your Car?
Waxing enhances your car's paint by providing a glossy finish and temporary protection against UV rays, dirt, and water. Sealing uses synthetic polymers to create a durable barrier that lasts longer, offering stronger resistance to environmental contaminants and chemical stains. Choosing between waxing and sealing depends on your car's exposure to elements and desired maintenance frequency: wax suits occasional protection and shine, while sealant is ideal for long-lasting defense.
Waxing vs Sealing Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com