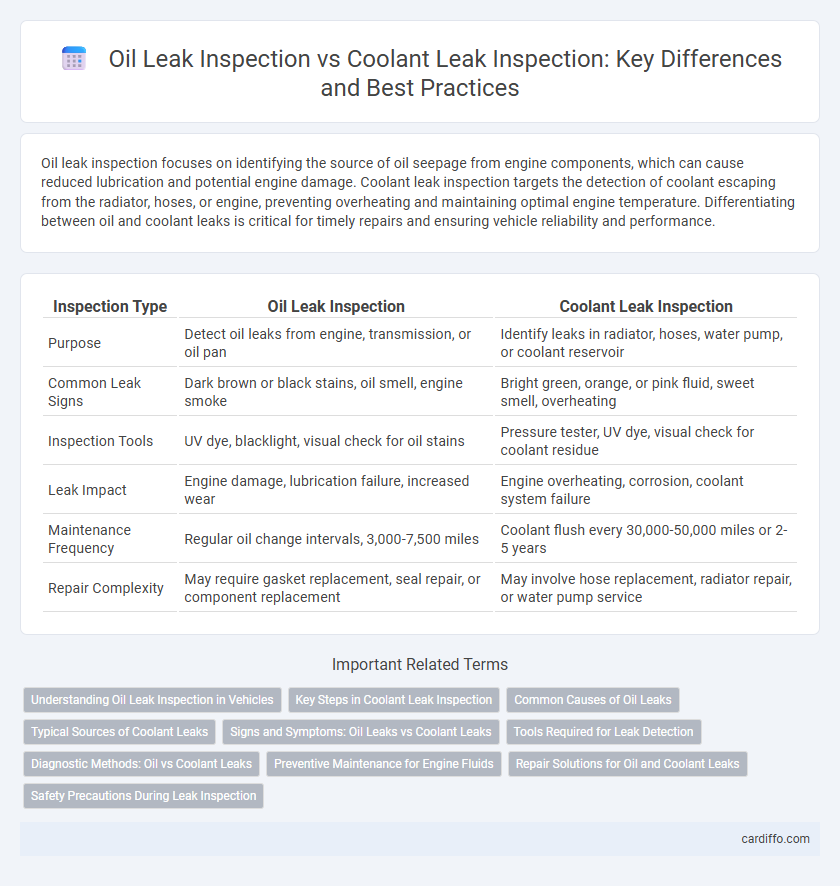
Oil leak inspection focuses on identifying the source of oil seepage from engine components, which can cause reduced lubrication and potential engine damage. Coolant leak inspection targets the detection of coolant escaping from the radiator, hoses, or engine, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal engine temperature. Differentiating between oil and coolant leaks is critical for timely repairs and ensuring vehicle reliability and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Inspection Type | Oil Leak Inspection | Coolant Leak Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect oil leaks from engine, transmission, or oil pan | Identify leaks in radiator, hoses, water pump, or coolant reservoir |
| Common Leak Signs | Dark brown or black stains, oil smell, engine smoke | Bright green, orange, or pink fluid, sweet smell, overheating |
| Inspection Tools | UV dye, blacklight, visual check for oil stains | Pressure tester, UV dye, visual check for coolant residue |
| Leak Impact | Engine damage, lubrication failure, increased wear | Engine overheating, corrosion, coolant system failure |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular oil change intervals, 3,000-7,500 miles | Coolant flush every 30,000-50,000 miles or 2-5 years |
| Repair Complexity | May require gasket replacement, seal repair, or component replacement | May involve hose replacement, radiator repair, or water pump service |
Understanding Oil Leak Inspection in Vehicles
Oil leak inspection in vehicles involves carefully examining the engine, gaskets, seals, and oil pan for signs of oil seepage or drips that could indicate wear or damage. This process uses techniques like visual checks, UV dye tracing, and pressure testing to accurately locate and assess oil leaks, which can lead to engine performance issues or mechanical failure if untreated. Identifying oil leaks early helps maintain engine lubrication, prevent contamination, and reduce costly repairs compared to coolant leak inspections that prioritize the radiator, hoses, and reservoir for fluid loss affecting engine temperature regulation.
Key Steps in Coolant Leak Inspection
Coolant leak inspection involves checking hose connections, radiator, water pump, and coolant reservoir for visible cracks or damage. Pressure testing the cooling system helps identify hidden leaks by forcing coolant out of weak points. Monitoring coolant levels and examining for discoloration or contamination offers critical data for pinpointing leak sources effectively.
Common Causes of Oil Leaks
Common causes of oil leaks include worn gaskets, damaged seals, and loose or cracked oil pans, which often lead to oil seeping from the engine. Faulty valve cover gaskets and degraded oil filter seals also contribute significantly to oil leakage issues. Identifying these sources during oil leak inspections is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and preventing further engine damage.
Typical Sources of Coolant Leaks
Typical sources of coolant leaks include radiator hoses, water pump seals, heater core, and the radiator itself, which often exhibit cracks or wear. Coolant leaks can also occur from the thermostat housing gasket and cylinder head gasket, leading to significant engine overheating risks. Identifying these common leak points during inspection helps prevent engine damage and maintains vehicle cooling system efficiency.
Signs and Symptoms: Oil Leaks vs Coolant Leaks
Oil leaks typically present as dark, greasy spots on engine components or the ground beneath the vehicle, with a distinctive burnt oil smell and smoke from the engine bay in severe cases. Coolant leaks often manifest as brightly colored fluid puddles, usually green, orange, or pink, accompanied by a sweet smell, engine overheating, and low coolant levels on the reservoir. Recognizing these signs ensures timely maintenance, preventing engine damage and maintaining vehicle performance.
Tools Required for Leak Detection
Oil leak inspection requires tools such as UV dye kits, digital scope cameras, and oil pressure gauges to accurately detect and pinpoint leaks in engine components. Coolant leak detection involves using pressure testers, infrared thermometers, and chemical test kits designed to identify coolant fluid presence and system pressure issues. Both inspections benefit from handheld flashlights and electronic leak detectors, but the specific tools vary based on the fluid type and system requirements.
Diagnostic Methods: Oil vs Coolant Leaks
Diagnostic methods for oil leaks primarily involve visual inspections, UV dye tests, and pressure testing to identify the source and severity of the leak. Coolant leak diagnostics often rely on pressure testing the cooling system, infrared thermography, and chemical test kits to detect even small leaks or cracks in hoses and radiators. Both inspection types use specialized equipment, but oil leak detection emphasizes contamination patterns, while coolant leak inspection focuses on maintaining optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating.
Preventive Maintenance for Engine Fluids
Oil leak inspection targets engine oil seals, gaskets, and pan areas to prevent contamination and loss of lubrication, preserving engine performance and preventing costly repairs. Coolant leak inspection focuses on radiator, hoses, and water pump integrity to maintain optimal temperature regulation and avoid engine overheating or corrosion damage. Regular preventive maintenance of these engine fluids ensures reliability, extends engine life, and reduces downtime caused by fluid-related failures.
Repair Solutions for Oil and Coolant Leaks
Effective repair solutions for oil leaks involve replacing worn gaskets, seals, or damaged oil pans to restore engine integrity and prevent contamination. Coolant leak repairs typically require tightening or replacing hoses, fixing radiator cracks, or servicing the water pump to maintain optimal engine temperature and avoid overheating. Both inspections prioritize identifying leak sources accurately to implement targeted fixes that enhance vehicle performance and reliability.
Safety Precautions During Leak Inspection
Safety precautions during oil leak inspection emphasize avoiding ignition sources and ensuring proper ventilation due to the flammable nature of oil. Coolant leak inspection prioritizes handling chemicals carefully to prevent skin irritation and inhalation hazards, using gloves and masks as protective gear. Both inspections require wearing eye protection and securing the vehicle to prevent accidental movement, minimizing injury risks.
Oil leak inspection vs coolant leak inspection Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com