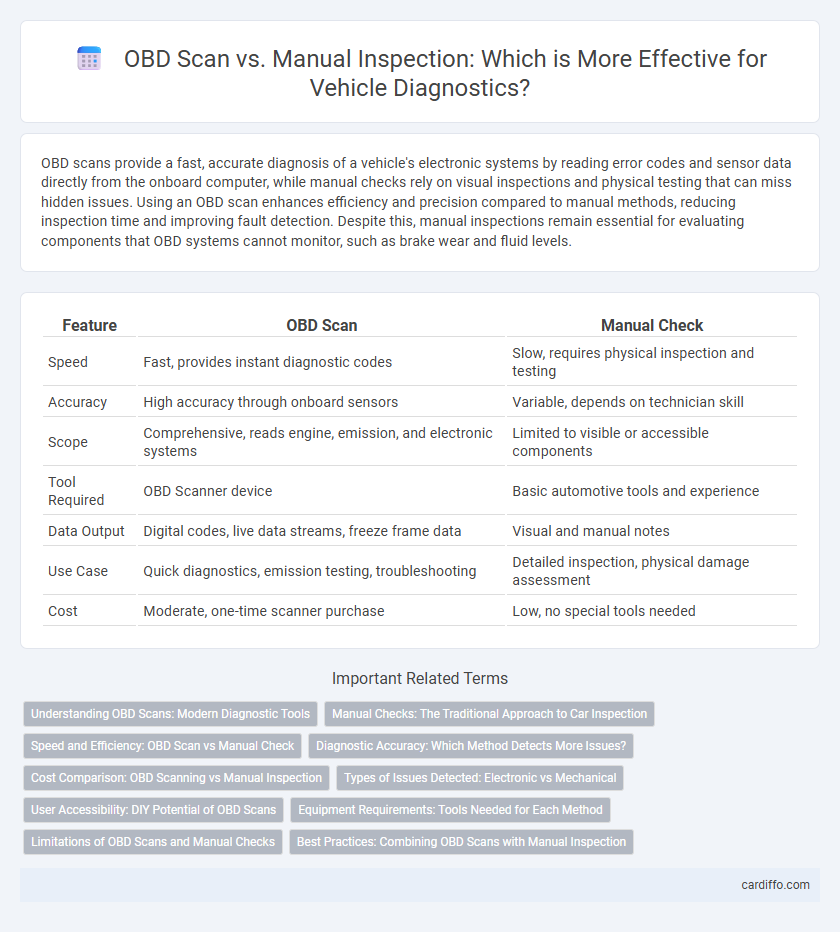
OBD scans provide a fast, accurate diagnosis of a vehicle's electronic systems by reading error codes and sensor data directly from the onboard computer, while manual checks rely on visual inspections and physical testing that can miss hidden issues. Using an OBD scan enhances efficiency and precision compared to manual methods, reducing inspection time and improving fault detection. Despite this, manual inspections remain essential for evaluating components that OBD systems cannot monitor, such as brake wear and fluid levels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | OBD Scan | Manual Check |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast, provides instant diagnostic codes | Slow, requires physical inspection and testing |
| Accuracy | High accuracy through onboard sensors | Variable, depends on technician skill |
| Scope | Comprehensive, reads engine, emission, and electronic systems | Limited to visible or accessible components |
| Tool Required | OBD Scanner device | Basic automotive tools and experience |
| Data Output | Digital codes, live data streams, freeze frame data | Visual and manual notes |
| Use Case | Quick diagnostics, emission testing, troubleshooting | Detailed inspection, physical damage assessment |
| Cost | Moderate, one-time scanner purchase | Low, no special tools needed |
Understanding OBD Scans: Modern Diagnostic Tools
OBD scans utilize onboard diagnostic systems to quickly retrieve error codes and system statuses, enabling precise identification of vehicle issues without dismantling components. Manual checks rely on physical inspection and traditional testing methods, often requiring more time and technical expertise to diagnose problems accurately. Understanding the capabilities of OBD scans enhances diagnostic efficiency, reduces human error, and supports preventative maintenance through real-time data analysis.
Manual Checks: The Traditional Approach to Car Inspection
Manual checks remain a crucial component of car inspection by allowing technicians to physically assess vehicle components such as brakes, tires, and suspension systems for wear and damage. This traditional approach provides tactile feedback and visual confirmation that OBD scans may overlook, especially concerning non-electronic systems. Skilled mechanics use manual inspections to detect subtle issues like fluid leaks, chassis integrity, and unusual noises that require hands-on evaluation beyond digital diagnostics.
Speed and Efficiency: OBD Scan vs Manual Check
OBD scans provide rapid diagnostics by quickly accessing real-time data from the vehicle's onboard computer, significantly reducing inspection time compared to manual checks. Manual inspections require a detailed physical examination, which can be time-consuming due to the need to visually inspect components and test functions individually. The efficiency of OBD scanning enables faster fault detection and streamlined maintenance processes, improving overall inspection productivity.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Which Method Detects More Issues?
OBD scans provide precise diagnostic accuracy by accessing real-time data and error codes directly from the vehicle's onboard computer, identifying a broader range of issues including hidden sensor faults and emissions problems. Manual inspections rely on visual and physical checks, which may miss internal electronic or software-related malfunctions but are essential for detecting wear and damage not yet triggering error codes. Combining both methods enhances overall diagnostic coverage, leveraging OBD's detailed system insights and manual checks' tactile assessments to ensure comprehensive fault detection.
Cost Comparison: OBD Scanning vs Manual Inspection
OBD scanning significantly reduces inspection costs by minimizing labor time and providing immediate diagnostics through electronic data retrieval, while manual inspection incurs higher expenses due to extensive hands-on labor and longer inspection durations. The average cost of an OBD scan ranges from $40 to $70, whereas manual inspections can exceed $100 depending on the complexity and time required. Cost-effectiveness makes OBD scans preferable for routine vehicle diagnostics and emission inspections compared to traditional manual methods.
Types of Issues Detected: Electronic vs Mechanical
OBD scans excel at detecting electronic and software-related issues such as engine misfires, sensor failures, and emission system faults through diagnostic trouble codes. Manual checks are essential for identifying mechanical problems like worn brake pads, leaking hoses, and physical damage that electronic scans cannot detect. Combining both methods ensures comprehensive vehicle inspection by covering electronic diagnostics and mechanical integrity.
User Accessibility: DIY Potential of OBD Scans
OBD scans offer enhanced user accessibility by allowing vehicle owners to perform diagnostics without specialized tools or advanced mechanical knowledge. Unlike manual checks that often require professional expertise and physical inspection, OBD scanners provide real-time error codes and system status via user-friendly interfaces. This DIY potential enables timely troubleshooting, reduces dependence on mechanics, and supports proactive vehicle maintenance for diverse users.
Equipment Requirements: Tools Needed for Each Method
OBD scans require an OBD-II scanner, compatible connectors, and software to read diagnostic trouble codes from the vehicle's computer system. Manual checks depend on traditional tools such as multimeters, pressure gauges, and specialized mechanical tools for physical inspection and testing. Each method demands specific equipment to ensure accurate and efficient diagnosis.
Limitations of OBD Scans and Manual Checks
OBD scans provide quick diagnostics by accessing real-time data from a vehicle's onboard computer but may miss issues not detected by sensors or software limitations. Manual checks offer a detailed visual and physical inspection that can identify mechanical wear, fluid leaks, or external damage, yet are prone to human error and can be time-consuming. Both methods have limitations, requiring a combined approach for comprehensive vehicle inspection and accurate fault diagnosis.
Best Practices: Combining OBD Scans with Manual Inspection
Combining OBD scans with manual inspections ensures a comprehensive vehicle diagnosis by detecting both electronic and mechanical issues. OBD scans efficiently identify fault codes related to engine performance and emissions, while manual checks assess physical components like brakes, tires, and suspension for wear or damage. Integrating both methods optimizes inspection accuracy, improves safety, and helps maintain regulatory compliance.
OBD scan vs manual check Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com