Winter blend gasoline contains more volatile compounds to improve engine starting and performance in cold temperatures, reducing emissions and preventing fuel line freeze. Summer blend gasoline is formulated to be less volatile, minimizing evaporation and smog formation during hot weather, which helps meet environmental regulations. Choosing the correct seasonal blend ensures optimal engine efficiency and environmental protection throughout the year.
Table of Comparison
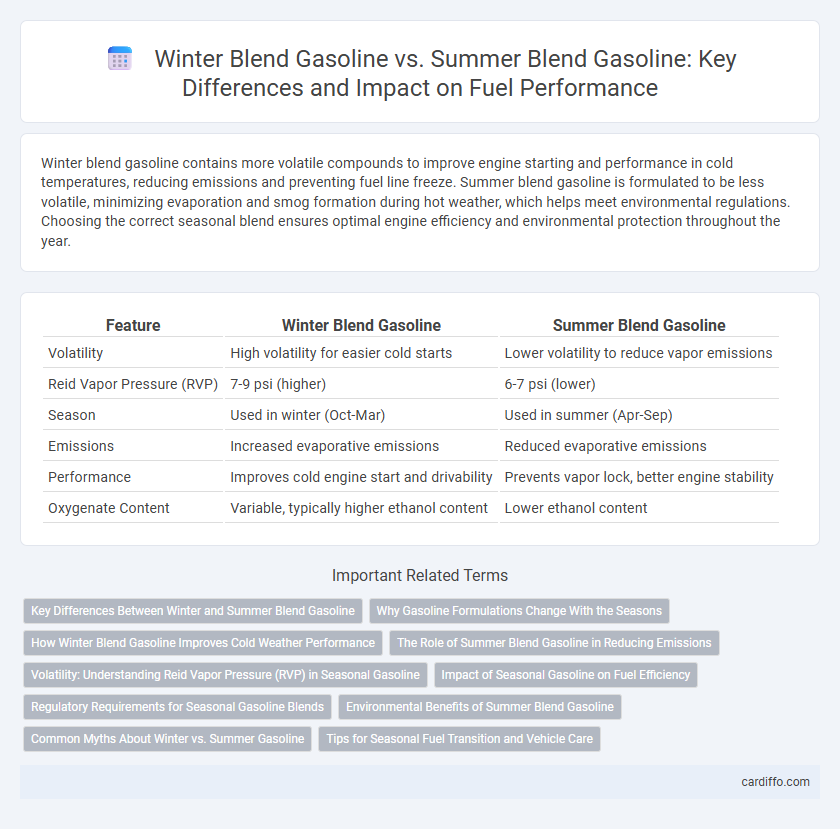
| Feature | Winter Blend Gasoline | Summer Blend Gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Volatility | High volatility for easier cold starts | Lower volatility to reduce vapor emissions |
| Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) | 7-9 psi (higher) | 6-7 psi (lower) |
| Season | Used in winter (Oct-Mar) | Used in summer (Apr-Sep) |
| Emissions | Increased evaporative emissions | Reduced evaporative emissions |
| Performance | Improves cold engine start and drivability | Prevents vapor lock, better engine stability |
| Oxygenate Content | Variable, typically higher ethanol content | Lower ethanol content |
Key Differences Between Winter and Summer Blend Gasoline
Winter blend gasoline contains higher volatility compounds to improve cold starting and reduce engine stalling in low temperatures, while summer blend gasoline has lower volatility to minimize evaporation and smog formation during hot weather. The oxygen content in winter blends is typically increased to enhance combustion and reduce emissions in cold climates, whereas summer blends prioritize lower evaporative emissions to comply with stricter environmental regulations. These seasonal formulations ensure optimal engine performance and environmental protection by adapting to temperature and air quality challenges unique to each season.
Why Gasoline Formulations Change With the Seasons
Gasoline formulations change with the seasons to optimize engine performance and reduce environmental impact. Winter blend gasoline contains more volatile hydrocarbons to improve cold-start performance and prevent fuel line freezing, while summer blend gasoline has lower volatility to minimize evaporative emissions and ozone formation during warmer temperatures. These adjustments ensure compliance with environmental regulations and maintain fuel efficiency across varying climate conditions.
How Winter Blend Gasoline Improves Cold Weather Performance
Winter blend gasoline contains higher levels of volatility and specific additives that prevent fuel line freezing and improve engine startup in cold temperatures. Its formulation includes increased butane and pentane content, which vaporize more easily to enhance combustion efficiency during cold starts. These properties reduce engine hesitation and emissions, ensuring reliable vehicle performance and fuel economy in winter conditions.
The Role of Summer Blend Gasoline in Reducing Emissions
Summer blend gasoline contains lower volatility compounds, which help reduce evaporative emissions during warmer months. Its formulation minimizes smog and ozone formation by controlling hydrocarbon vapor release, contributing significantly to improved air quality. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandates summer blends to meet strict VOC emission standards, ensuring cleaner combustion and reduced environmental impact.
Volatility: Understanding Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) in Seasonal Gasoline
Winter blend gasoline features higher Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) values, typically ranging from 7.0 to 9.0 psi, to enhance volatility and ensure easier engine starts and better combustion in cold temperatures. In contrast, summer blend gasoline has lower RVP levels, usually between 6.0 and 7.0 psi, to minimize evaporation and reduce smog formation during warmer months. Understanding these RVP differences is critical for optimizing fuel performance and meeting environmental regulations across seasonal variations.
Impact of Seasonal Gasoline on Fuel Efficiency
Winter blend gasoline contains higher volatility components to improve cold-start performance, which can lead to lower fuel efficiency compared to summer blend gasoline. Summer blend gasoline is formulated with lower volatility to reduce evaporation losses and improve combustion efficiency during warmer temperatures. These seasonal variations in gasoline composition directly affect engine performance and miles per gallon, with summer blends generally providing better fuel economy.
Regulatory Requirements for Seasonal Gasoline Blends
Winter blend gasoline and summer blend gasoline must comply with distinct Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulatory requirements to control volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and improve air quality. Winter blends have a lower Reid Vapor Pressure (RVP) limit, generally around 7.0 psi, to enhance cold-start performance and reduce evaporative emissions in colder temperatures. Summer blends are formulated with a reduced RVP, typically about 6.0 psi or lower, to minimize smog formation and meet state-specific air quality standards during warmer months.
Environmental Benefits of Summer Blend Gasoline
Summer blend gasoline contains lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), significantly reducing ground-level ozone formation and smog compared to winter blends. Its formulation limits evaporative emissions, which helps improve air quality and decreases harmful pollutants during warmer months. These environmental benefits contribute to better respiratory health and compliance with regulatory air standards.
Common Myths About Winter vs. Summer Gasoline
Winter blend gasoline contains higher volatility compounds to improve engine start-up and performance in cold temperatures, contrary to the myth that all gasoline is the same year-round. Some believe winter fuel damages engines, but it is formulated to prevent fuel line freezing and maintain efficiency without harm. Summer blend, designed to reduce evaporation and smog in hot weather, does not mean winter fuel lacks quality or causes increased emissions.
Tips for Seasonal Fuel Transition and Vehicle Care
Winter blend gasoline is formulated with higher volatility to improve cold-weather starting and reduce engine hesitation, while summer blend gasoline contains lower volatility to minimize evaporation and ozone formation. To ensure optimal performance during seasonal fuel transitions, drivers should consider refueling with the appropriate blend ahead of temperature changes and maintain regular vehicle tune-ups, including checking spark plugs and fuel filters. Proper tire pressure and battery health inspections are critical during these transitions to support reliable engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Winter Blend Gasoline vs Summer Blend Gasoline Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com