Octane boosters enhance gasoline's resistance to knocking by raising the octane rating for smoother combustion in spark-ignition engines. Cetane improvers increase the cetane number of diesel fuel, promoting faster ignition and more efficient combustion in compression-ignition engines. Both additives optimize engine performance but target different fuel types and combustion processes.
Table of Comparison
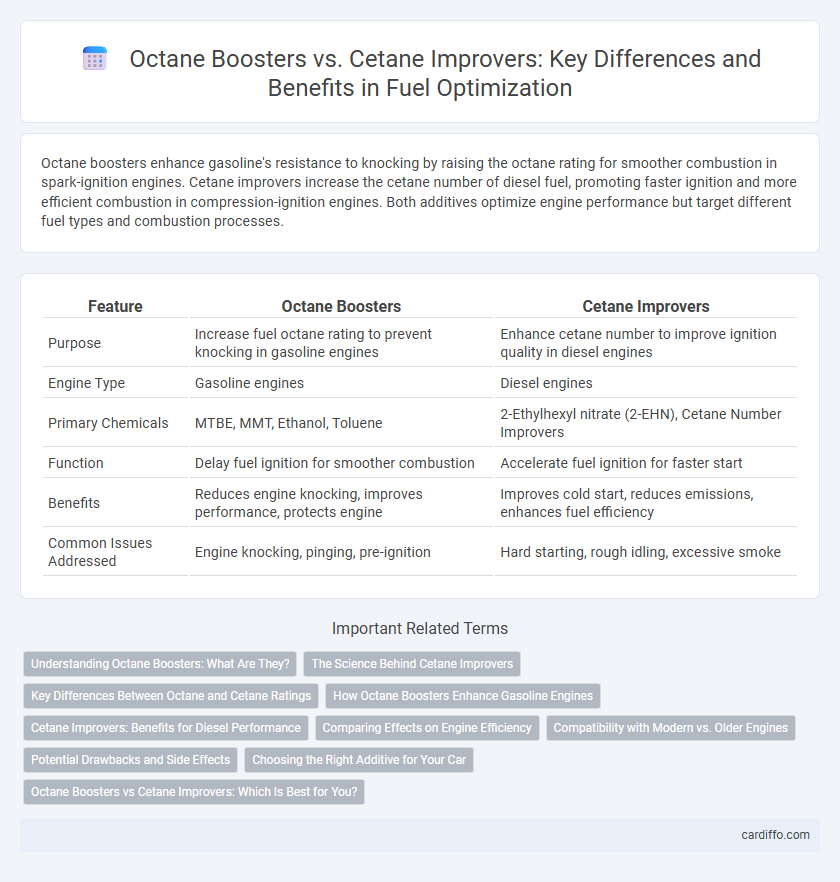
| Feature | Octane Boosters | Cetane Improvers |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Increase fuel octane rating to prevent knocking in gasoline engines | Enhance cetane number to improve ignition quality in diesel engines |
| Engine Type | Gasoline engines | Diesel engines |
| Primary Chemicals | MTBE, MMT, Ethanol, Toluene | 2-Ethylhexyl nitrate (2-EHN), Cetane Number Improvers |
| Function | Delay fuel ignition for smoother combustion | Accelerate fuel ignition for faster start |
| Benefits | Reduces engine knocking, improves performance, protects engine | Improves cold start, reduces emissions, enhances fuel efficiency |
| Common Issues Addressed | Engine knocking, pinging, pre-ignition | Hard starting, rough idling, excessive smoke |
Understanding Octane Boosters: What Are They?
Octane boosters are additives designed to increase a fuel's octane rating, which enhances its resistance to knocking and premature combustion in gasoline engines. Common compounds in octane boosters include toluene, ethanol, and MTBE, which promote smoother engine performance and improved power output. These additives are crucial for high-performance vehicles and can help maintain engine efficiency under demanding driving conditions.
The Science Behind Cetane Improvers
Cetane improvers enhance diesel fuel combustion by accelerating ignition delay, which increases cetane number and promotes more efficient atomization and combustion of fuel droplets. These additives typically contain organic nitrates or peroxides that decompose under combustion conditions to release radicals, facilitating faster fuel ignition and reducing engine knocking and emissions. Understanding the chemical mechanisms behind cetane improvement enables optimized fuel formulations that improve cold-start performance and overall engine efficiency in diesel-powered vehicles.
Key Differences Between Octane and Cetane Ratings
Octane boosters increase the octane rating of gasoline, enhancing its resistance to engine knocking by delaying ignition during the compression stroke, which is crucial for spark-ignited engines. Cetane improvers raise the cetane number of diesel fuel, promoting quicker ignition and smoother combustion in compression-ignited engines by shortening the ignition delay. The key difference lies in their application: octane ratings measure fuel's ability to resist premature ignition in petrol engines, while cetane ratings indicate the readiness of diesel fuel to ignite under pressure.
How Octane Boosters Enhance Gasoline Engines
Octane boosters increase the octane rating of gasoline, preventing engine knocking and allowing for higher compression ratios in gasoline engines. By enhancing fuel stability under high pressure, octane boosters improve combustion efficiency, leading to smoother engine performance and reduced emissions. These additives enable engines to operate with optimal timing and power output, particularly in high-performance or turbocharged gasoline vehicles.
Cetane Improvers: Benefits for Diesel Performance
Cetane improvers significantly enhance diesel engine performance by increasing the cetane number, leading to faster ignition and more efficient combustion. Improved ignition quality reduces engine knocking, lowers emissions, and enhances fuel economy. These additives are essential for cold start reliability and smoother engine operation under varying loads.
Comparing Effects on Engine Efficiency
Octane boosters increase the gasoline's resistance to knocking, enabling higher compression ratios and improved power output in spark-ignition engines. Cetane improvers enhance diesel fuel ignition quality by reducing ignition delay, resulting in smoother combustion and better cold-start performance in compression-ignition engines. Comparing engine efficiency, octane boosters primarily optimize performance under high load, while cetane improvers contribute to overall fuel economy and emission reduction in diesel engines.
Compatibility with Modern vs. Older Engines
Octane boosters enhance gasoline's resistance to knocking, making them ideal for modern high-compression engines designed to run on premium fuel. Cetane improvers increase the ignition quality of diesel, benefiting older diesel engines with harder starting issues and less refined combustion systems. Understanding the compatibility of these additives is crucial: octane boosters suit contemporary spark-ignition engines, while cetane improvers are tailored for older compression-ignition engines requiring improved cold starts and smoother performance.
Potential Drawbacks and Side Effects
Octane boosters, designed to increase gasoline's resistance to knocking, may cause engine deposits and damage catalytic converters if overused, leading to reduced engine efficiency and increased emissions. Cetane improvers, aimed at enhancing diesel fuel ignition quality, can raise combustion temperature, potentially increasing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions and accelerating engine wear with excessive use. Both additives require careful dosing to avoid negative impacts on engine performance and environmental compliance.
Choosing the Right Additive for Your Car
Octane boosters enhance gasoline performance by increasing the fuel's octane rating, preventing knocking in high-compression engines, while cetane improvers are designed for diesel engines, accelerating fuel ignition to improve combustion efficiency. Choosing the right additive depends on your vehicle's engine type: gasoline engines benefit from octane boosters, whereas diesel engines require cetane improvers to optimize power and fuel economy. Using the appropriate additive ensures smoother engine operation, better mileage, and reduced emissions tailored to your car's fuel system.
Octane Boosters vs Cetane Improvers: Which Is Best for You?
Octane boosters enhance gasoline's resistance to knocking by increasing the octane rating, making them ideal for high-performance gasoline engines. Cetane improvers elevate diesel fuel's ignition quality by raising the cetane number, leading to smoother combustion and reduced emissions in diesel engines. Choosing between octane boosters and cetane improvers depends on your vehicle's fuel type--gasoline engines benefit from octane boosters, while diesel engines require cetane improvers for optimal performance.
Octane Boosters vs Cetane Improvers Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com