Locked brakes occur when the brake system fails to release pressure, causing the wheels to stop spinning and leading to loss of control, while worn brake pads result from excessive friction material wear that reduces braking efficiency and increases stopping distance. Locked brakes often indicate hydraulic or mechanical issues within the braking system, requiring immediate inspection to prevent accidents. Worn brake pads produce squealing noises and diminished responsiveness, signaling the need for timely replacement to maintain optimal vehicle safety.
Table of Comparison
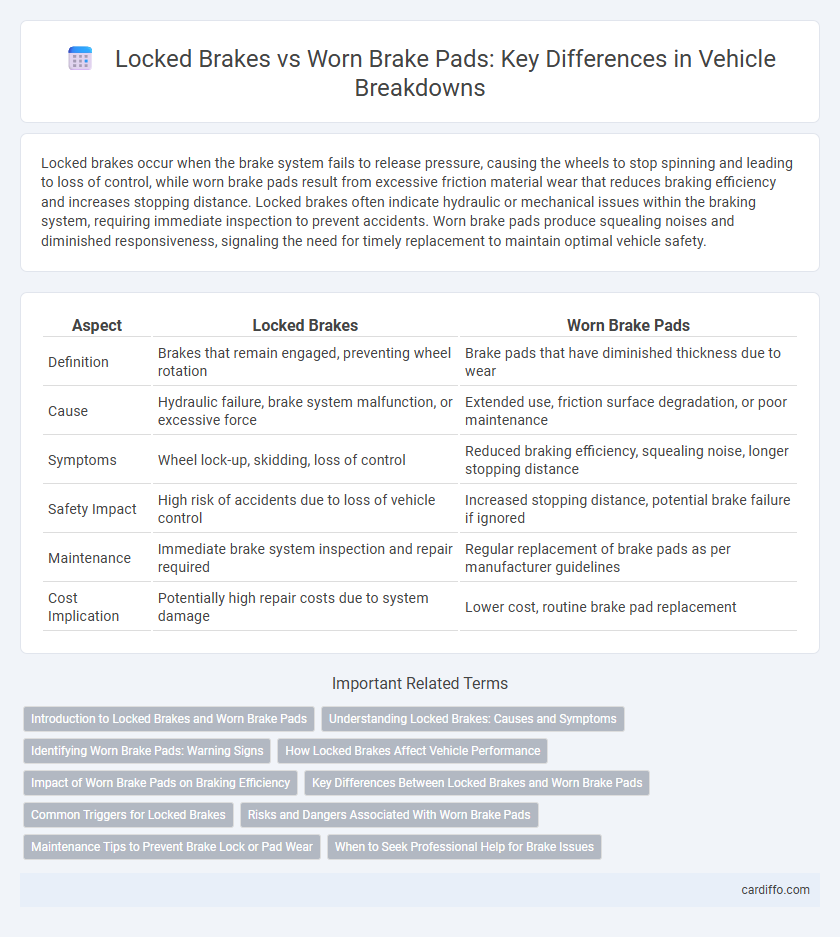
| Aspect | Locked Brakes | Worn Brake Pads |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Brakes that remain engaged, preventing wheel rotation | Brake pads that have diminished thickness due to wear |
| Cause | Hydraulic failure, brake system malfunction, or excessive force | Extended use, friction surface degradation, or poor maintenance |
| Symptoms | Wheel lock-up, skidding, loss of control | Reduced braking efficiency, squealing noise, longer stopping distance |
| Safety Impact | High risk of accidents due to loss of vehicle control | Increased stopping distance, potential brake failure if ignored |
| Maintenance | Immediate brake system inspection and repair required | Regular replacement of brake pads as per manufacturer guidelines |
| Cost Implication | Potentially high repair costs due to system damage | Lower cost, routine brake pad replacement |
Introduction to Locked Brakes and Worn Brake Pads
Locked brakes occur when the braking system fails to release, causing wheels to stop rotating and leading to loss of control. Worn brake pads result from prolonged friction, causing reduced braking efficiency and increased stopping distances. Both conditions compromise vehicle safety but stem from different mechanical issues requiring distinct maintenance approaches.
Understanding Locked Brakes: Causes and Symptoms
Locked brakes often result from hydraulic system failures, such as a malfunctioning master cylinder or brake caliper, causing wheels to stop rotating suddenly. Symptoms include a hard brake pedal, overheating wheels, and a noticeable loss of vehicle control during braking. Recognizing these signs early helps differentiate locked brakes from worn brake pads, which typically produce squealing noises and reduced braking efficiency instead.
Identifying Worn Brake Pads: Warning Signs
Worn brake pads often cause a high-pitched squealing noise when braking, signaling the embedded wear indicator is contacting the rotor. Identifying reduced braking responsiveness or a spongy brake pedal can also indicate brake pad deterioration, increasing stopping distance and safety risks. Visual inspection reveals brake pads thinner than 3 millimeters, a critical threshold for replacement to prevent rotor damage and maintain optimal braking performance.
How Locked Brakes Affect Vehicle Performance
Locked brakes cause significant reduction in vehicle control and increase stopping distance, posing a severe safety risk during driving. Unlike worn brake pads that gradually diminish braking efficiency, locked brakes prevent wheel rotation, leading to skidding and uneven tire wear. This sudden loss of traction can compromise steering response and cause the vehicle to lose stability, especially on slippery surfaces.
Impact of Worn Brake Pads on Braking Efficiency
Worn brake pads significantly reduce braking efficiency by decreasing friction between the pad and the rotor, leading to longer stopping distances. This wear compromises vehicle safety by increasing the risk of brake fade under repeated use or emergency braking. Maintaining adequate brake pad thickness is crucial to ensure optimal braking performance and prevent costly breakdowns.
Key Differences Between Locked Brakes and Worn Brake Pads
Locked brakes occur when the braking system fails to release pressure, causing the wheels to stop rotating and potentially skid, often due to hydraulic or mechanical malfunction. Worn brake pads result in decreased friction material, leading to reduced braking efficiency, longer stopping distances, and noise such as squealing or grinding. Key differences include the cause--locked brakes stem from system failure, while worn brake pads arise from material degradation--and the symptoms, with locked brakes causing wheel lockup and worn pads causing diminished braking performance.
Common Triggers for Locked Brakes
Common triggers for locked brakes include hydraulic system failures, such as a malfunctioning brake master cylinder or caliper, which cause uneven pressure distribution. Contaminated brake fluid, excessive heat buildup from prolonged braking, and seized brake calipers due to corrosion also contribute significantly to brake lockup. Worn brake pads, while affecting braking efficiency, typically do not cause brakes to lock but may increase stopping distances and brake noise.
Risks and Dangers Associated With Worn Brake Pads
Worn brake pads significantly increase the risk of brake failure, leading to longer stopping distances and reduced vehicle control in emergency situations. As the pads wear down, heat dissipation becomes less effective, causing brake overheating and potential warping of rotors, which can result in brake lockup or unpredictable braking performance. Ignoring worn brake pads heightens the danger of accidents, especially in high-traffic or slippery road conditions, where immediate and reliable braking is crucial for safety.
Maintenance Tips to Prevent Brake Lock or Pad Wear
Regularly inspecting brake pads for thickness and replacing them before they wear below 3mm prevents premature pad wear and brake lock. Flushing brake fluid every 2 years removes moisture buildup that can cause caliper seizing and locked brakes. Ensuring proper caliper lubrication and avoiding aggressive braking habits extend brake component life and maintain optimal braking performance.
When to Seek Professional Help for Brake Issues
Seek professional help for brake issues immediately if you experience locked brakes, as this can indicate a serious hydraulic or mechanical failure risking complete brake loss. Worn brake pads may initially cause noise or reduced braking efficiency, but if you notice persistent squealing, longer stopping distances, or dashboard brake warnings, visit a mechanic promptly to prevent further damage or unsafe driving conditions. Timely diagnosis and repair by a certified brake specialist ensure safe and reliable vehicle operation.
Locked brakes vs worn brake pads Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com