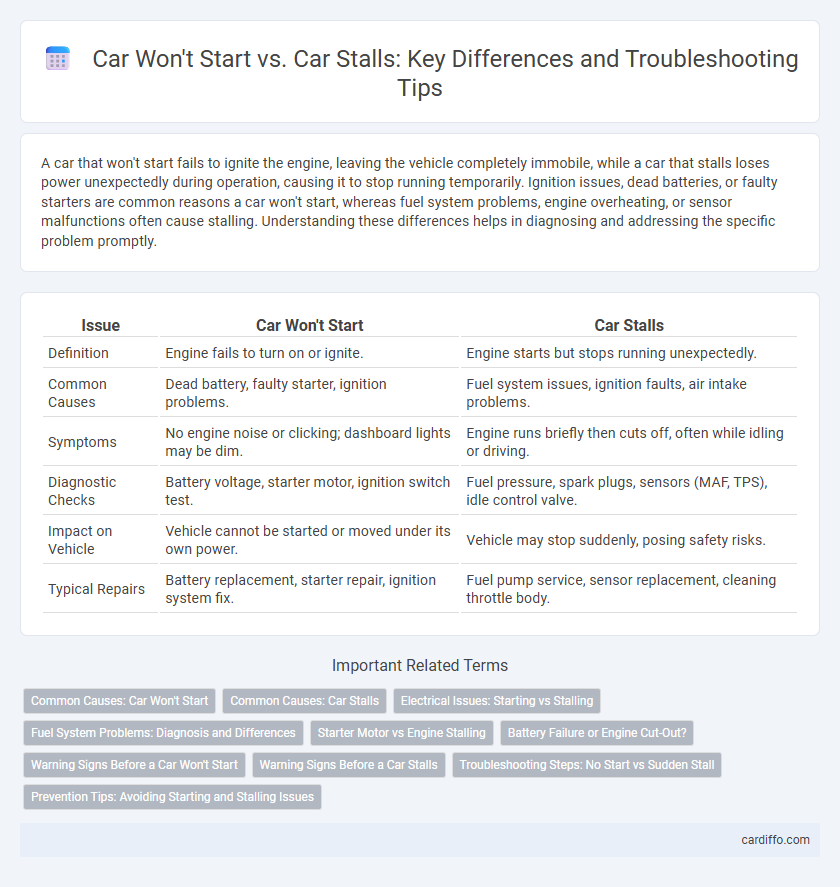
A car that won't start fails to ignite the engine, leaving the vehicle completely immobile, while a car that stalls loses power unexpectedly during operation, causing it to stop running temporarily. Ignition issues, dead batteries, or faulty starters are common reasons a car won't start, whereas fuel system problems, engine overheating, or sensor malfunctions often cause stalling. Understanding these differences helps in diagnosing and addressing the specific problem promptly.
Table of Comparison
| Issue | Car Won't Start | Car Stalls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engine fails to turn on or ignite. | Engine starts but stops running unexpectedly. |
| Common Causes | Dead battery, faulty starter, ignition problems. | Fuel system issues, ignition faults, air intake problems. |
| Symptoms | No engine noise or clicking; dashboard lights may be dim. | Engine runs briefly then cuts off, often while idling or driving. |
| Diagnostic Checks | Battery voltage, starter motor, ignition switch test. | Fuel pressure, spark plugs, sensors (MAF, TPS), idle control valve. |
| Impact on Vehicle | Vehicle cannot be started or moved under its own power. | Vehicle may stop suddenly, posing safety risks. |
| Typical Repairs | Battery replacement, starter repair, ignition system fix. | Fuel pump service, sensor replacement, cleaning throttle body. |
Common Causes: Car Won't Start
Common causes for a car that won't start include a dead or weak battery, faulty starter motor, and fuel delivery issues such as an empty gas tank or clogged fuel filter. Ignition system problems like worn spark plugs or a malfunctioning ignition switch can also prevent the engine from turning over. Electrical issues such as a blown fuse or damaged wiring may disrupt the necessary power flow to start the vehicle.
Common Causes: Car Stalls
Engine misfires, clogged fuel filters, or a faulty ignition system often cause a car to stall unexpectedly while driving. Low fuel pressure or an overheating engine can disrupt combustion, leading to sudden engine shutdowns. Electrical issues such as a weak battery or malfunctioning sensors also contribute to frequent car stalls.
Electrical Issues: Starting vs Stalling
Electrical issues causing a car not to start often involve a dead battery, faulty starter motor, or corroded wiring disrupting the ignition process. In contrast, electrical problems leading to stalling usually stem from a malfunctioning ignition coil, failing crankshaft sensor, or intermittent alternator faults that cut power while driving. Diagnosing these issues requires thorough testing of the electrical system components to distinguish between startup failure and in-motion stalling.
Fuel System Problems: Diagnosis and Differences
Fuel system problems causing a car not to start often involve a completely blocked fuel line, faulty fuel pump, or empty fuel tank preventing fuel delivery to the engine. In contrast, a car that stalls usually experiences intermittent fuel supply issues such as a malfunctioning fuel injector, clogged fuel filter, or inconsistent fuel pressure. Diagnosing these issues typically requires checking fuel pressure, testing pump operation, and inspecting filter condition to distinguish between a no-start fuel failure and a stall triggered by unstable fuel flow.
Starter Motor vs Engine Stalling
A car that won't start typically signals an issue with the starter motor, which fails to engage the engine despite turning the key or pushing the start button. In contrast, engine stalling occurs when the engine starts but then unexpectedly shuts off due to problems such as fuel delivery issues or sensor malfunctions. Diagnosing starter motor faults often involves inspecting electrical connections and battery health, whereas engine stalling requires evaluation of fuel injectors, ignition systems, and air intake sensors.
Battery Failure or Engine Cut-Out?
Car won't start issues often stem from battery failure, indicated by dim lights or clicking sounds when turning the key, whereas car stalls during driving typically result from engine cut-out caused by fuel delivery or ignition system problems. Battery failure prevents the engine from cranking, blocking initial ignition, while engine cut-out interrupts running combustion, causing sudden power loss. Diagnosing electrical system voltage and fuel pump functionality helps distinguish between a dead battery and engine stall scenarios.
Warning Signs Before a Car Won't Start
Warning signs before a car won't start include a slow engine crank, dimming headlights, and unusual clicking noises when turning the key. Battery issues, such as corrosion on terminals or a weak charge, often precede starting problems. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to complete failure to start, distinguishing it from a car that stalls unexpectedly while running.
Warning Signs Before a Car Stalls
Warning signs before a car stalls often include engine hesitation, rough idling, and sudden loss of power, which differ from a car that simply won't start. A car that won't start typically shows no engine turnover or cranking, whereas stalling happens while driving or at idle. Recognizing symptoms like fluctuating RPMs or warning lights can prevent breakdowns and costly repairs.
Troubleshooting Steps: No Start vs Sudden Stall
When a car won't start, begin troubleshooting by checking the battery charge, ignition switch, and fuel delivery system to identify power or fuel issues. In contrast, if a car suddenly stalls while running, inspect the fuel pump, sensors, and engine control unit (ECU) for intermittent failures or sensor malfunctions. Diagnostic tools such as an OBD-II scanner can quickly pinpoint error codes, streamlining the repair process for both no-start and sudden stall conditions.
Prevention Tips: Avoiding Starting and Stalling Issues
Regular maintenance, including timely oil changes and battery checks, significantly reduces the risk of a car failing to start or stalling unexpectedly. Ensuring fuel system cleanliness by using high-quality gasoline and replacing fuel filters prevents common issues related to engine performance. Monitoring spark plugs and ignition components helps maintain consistent engine ignition, minimizing breakdowns caused by starting and stalling problems.
Car Won't Start vs Car Stalls Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com