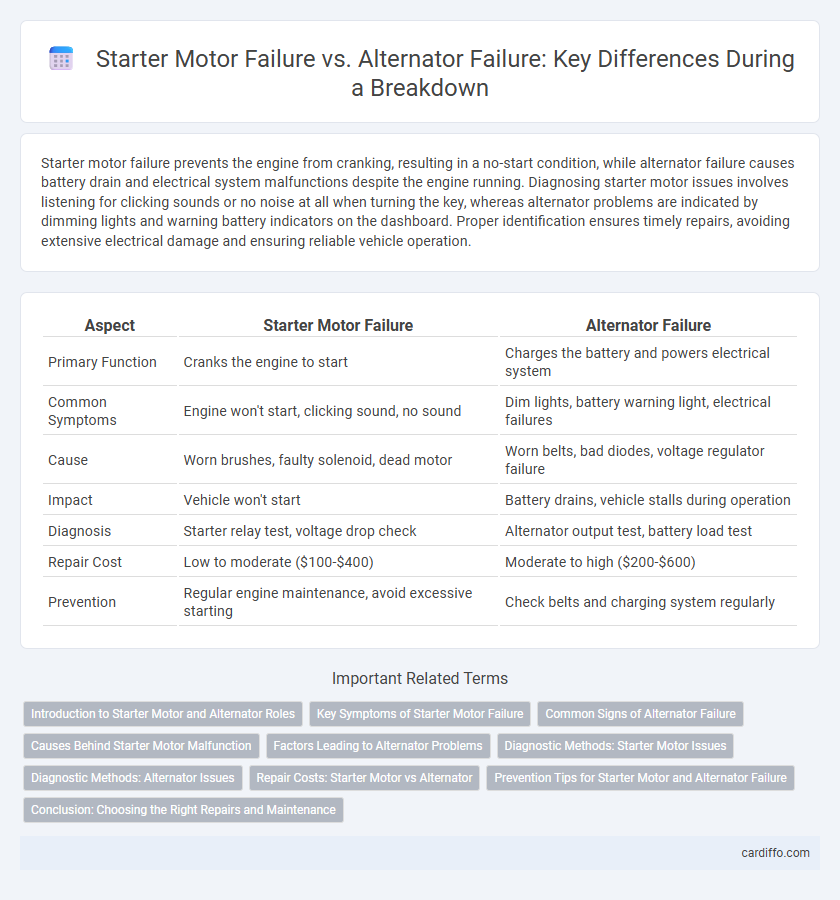
Starter motor failure prevents the engine from cranking, resulting in a no-start condition, while alternator failure causes battery drain and electrical system malfunctions despite the engine running. Diagnosing starter motor issues involves listening for clicking sounds or no noise at all when turning the key, whereas alternator problems are indicated by dimming lights and warning battery indicators on the dashboard. Proper identification ensures timely repairs, avoiding extensive electrical damage and ensuring reliable vehicle operation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Starter Motor Failure | Alternator Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Cranks the engine to start | Charges the battery and powers electrical system |
| Common Symptoms | Engine won't start, clicking sound, no sound | Dim lights, battery warning light, electrical failures |
| Cause | Worn brushes, faulty solenoid, dead motor | Worn belts, bad diodes, voltage regulator failure |
| Impact | Vehicle won't start | Battery drains, vehicle stalls during operation |
| Diagnosis | Starter relay test, voltage drop check | Alternator output test, battery load test |
| Repair Cost | Low to moderate ($100-$400) | Moderate to high ($200-$600) |
| Prevention | Regular engine maintenance, avoid excessive starting | Check belts and charging system regularly |
Introduction to Starter Motor and Alternator Roles
The starter motor is crucial for initiating engine combustion by turning the engine over during ignition, while the alternator generates electrical power to recharge the battery and sustain vehicle electrical systems during operation. Starter motor failure typically results in the engine not cranking, preventing the vehicle from starting, whereas alternator failure leads to battery drain and electrical component malfunction while driving. Understanding the distinct roles of the starter motor and alternator helps diagnose breakdown causes and prioritize repairs effectively.
Key Symptoms of Starter Motor Failure
Key symptoms of starter motor failure include a clicking noise when turning the ignition key, the engine failing to crank, and dim dashboard lights during startup attempts. Unlike alternator failure, which often causes battery drainage and electrical issues while the engine runs, starter motor issues prevent the engine from starting. A dead starter motor typically results in no response at all when turning the key, indicating an immediate need for diagnosis and replacement.
Common Signs of Alternator Failure
Common signs of alternator failure include dim or flickering headlights, a dead battery despite recent charging, and electrical accessories malfunctioning or operating inconsistently. Drivers may notice warning lights on the dashboard, such as the battery or check engine light, which indicate charging system issues. Alternator failure often leads to difficulty starting the vehicle, as the battery loses charge without proper alternator function.
Causes Behind Starter Motor Malfunction
Starter motor failure primarily occurs due to electrical issues such as a worn-out solenoid, corroded battery terminals, or a dead battery that prevents sufficient current from reaching the motor. Mechanical wear and tear, including damaged brushes or a faulty armature, can also lead to starter motor malfunction by hindering the motor's ability to engage or spin the engine. Unlike alternator failure, which often stems from belt problems or diode failure affecting battery charging, starter motor issues are mainly rooted in direct starting system components.
Factors Leading to Alternator Problems
Alternator problems often arise from worn-out brushes, a slipping or broken drive belt, and faulty voltage regulators impairing the electrical system's performance. Excessive heat and exposure to dirt or moisture accelerate alternator component degradation, increasing failure risk. Corroded or loose wiring connections further contribute to charging inefficiencies and intermittent electrical issues in vehicles.
Diagnostic Methods: Starter Motor Issues
Starter motor failure is commonly diagnosed by testing for a clicking sound when turning the ignition key, indicating insufficient electrical current reaching the starter solenoid. Voltage drop tests across starter terminals help identify poor connections or a faulty starter motor. Using a multimeter to measure battery voltage during start attempts can distinguish starter motor issues from battery-related problems.
Diagnostic Methods: Alternator Issues
Diagnostic methods for alternator issues include measuring voltage output with a multimeter, which should typically read between 13.8 to 14.4 volts when the engine is running. Inspecting the alternator belt for wear and tension is crucial, as a loose or damaged belt can cause charging problems. Conducting a diode test on the alternator can identify internal electrical faults that lead to intermittent power failures.
Repair Costs: Starter Motor vs Alternator
Repair costs for starter motor failure typically range from $200 to $500, depending on the vehicle model and labor rates. Alternator replacement generally costs between $300 and $700, largely influenced by the alternator type and installation complexity. Understanding these cost differences helps prioritize repairs based on budget and vehicle reliability needs.
Prevention Tips for Starter Motor and Alternator Failure
Regular maintenance of the starter motor, including checking electrical connections and ensuring battery health, helps prevent starter motor failure by avoiding strain during engine startup. For alternator failure prevention, it is crucial to inspect and replace worn-out drive belts, keep the alternator clean from debris, and monitor charging system voltage to ensure proper power generation. Timely diagnosis and addressing warning signs such as dimming lights or slow engine cranking significantly reduce the risk of breakdowns related to starter motor and alternator malfunctions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Repairs and Maintenance
Starter motor failure typically demands immediate replacement or repair to restore engine ignition functionality, while alternator failure affects battery charging and electrical systems, often requiring alternator replacement or regulator repair. Accurate diagnosis using voltage and current tests ensures appropriate intervention, preventing recurrent breakdowns and costly repairs. Selecting targeted repairs based on component-specific symptoms optimizes vehicle reliability and extends electrical system longevity.
Starter motor failure vs alternator failure Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com