Power steering failure significantly increases the effort required to turn the steering wheel, making maneuvering at low speeds challenging and potentially dangerous. Manual steering difficulty, while also demanding more physical strength, results from the absence of hydraulic or electric assistance, requiring drivers to rely solely on their own power and control. Understanding the distinction between these issues helps diagnose steering problems accurately and ensures timely vehicle maintenance.
Table of Comparison
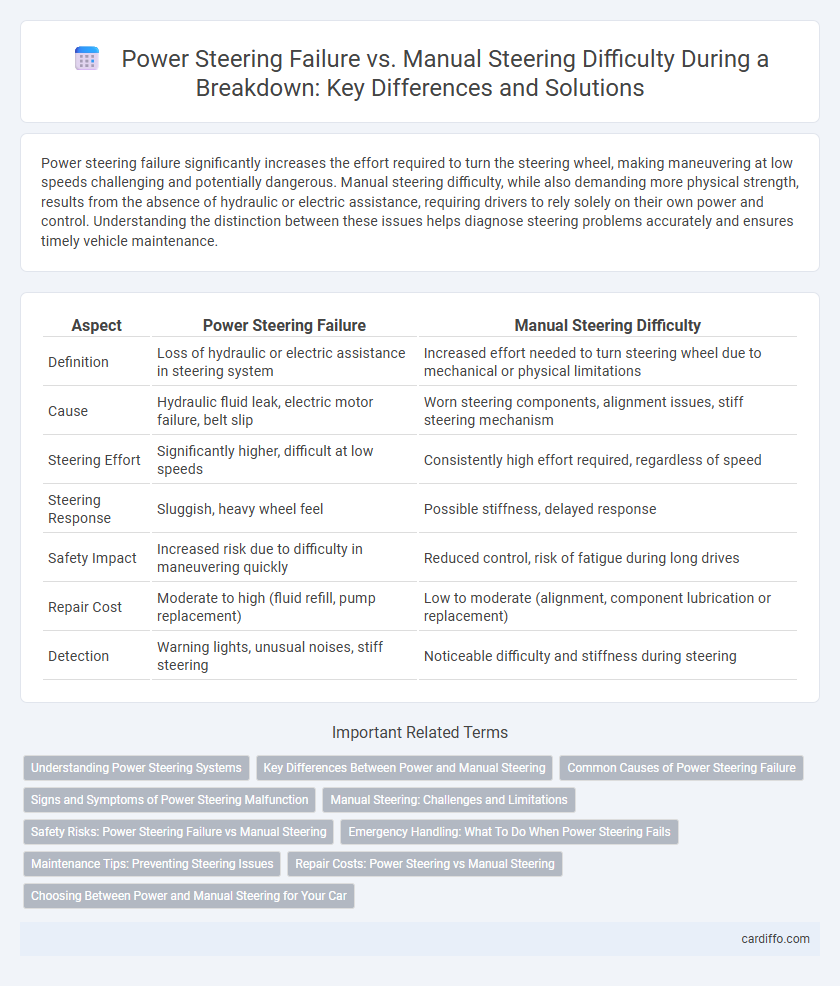
| Aspect | Power Steering Failure | Manual Steering Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of hydraulic or electric assistance in steering system | Increased effort needed to turn steering wheel due to mechanical or physical limitations |
| Cause | Hydraulic fluid leak, electric motor failure, belt slip | Worn steering components, alignment issues, stiff steering mechanism |
| Steering Effort | Significantly higher, difficult at low speeds | Consistently high effort required, regardless of speed |
| Steering Response | Sluggish, heavy wheel feel | Possible stiffness, delayed response |
| Safety Impact | Increased risk due to difficulty in maneuvering quickly | Reduced control, risk of fatigue during long drives |
| Repair Cost | Moderate to high (fluid refill, pump replacement) | Low to moderate (alignment, component lubrication or replacement) |
| Detection | Warning lights, unusual noises, stiff steering | Noticeable difficulty and stiffness during steering |
Understanding Power Steering Systems
Power steering systems use hydraulic or electric mechanisms to reduce the effort required for steering, making vehicle control smoother and less physically demanding compared to manual steering. When power steering fails, the steering wheel becomes significantly harder to turn, resembling the high effort needed in manual steering systems, especially at low speeds or during parking maneuvers. Understanding the components such as the power steering pump, fluid, control valves, and electric motors helps diagnose issues and differentiate power steering failure from inherent manual steering difficulty.
Key Differences Between Power and Manual Steering
Power steering uses hydraulic or electric assistance to reduce the effort needed to turn the steering wheel, making it easier to maneuver the vehicle compared to manual steering, which relies solely on the driver's physical strength. In case of power steering failure, the lack of assistive force significantly increases steering effort, often making low-speed turns and parking much harder, whereas manual steering systems maintain consistent difficulty regardless of mechanical issues. Key differences include the presence of a power assist mechanism in power steering systems, varying ease of steering under failure conditions, and the mechanical simplicity and reliability of manual steering.
Common Causes of Power Steering Failure
Power steering failure often results from leaks in the power steering fluid reservoir, damaged hoses, or a malfunctioning power steering pump, causing increased steering effort and reduced vehicle control. Worn-out belts or contaminated fluid can further exacerbate the problem by impairing the hydraulic system's efficiency. Unlike manual steering, where difficulty arises solely from physical resistance in the steering mechanism, power steering failure involves hydraulic or electronic system breakdowns that significantly affect steering responsiveness.
Signs and Symptoms of Power Steering Malfunction
Power steering failure typically presents with increased steering effort, especially at low speeds or while parking, along with unusual whining or groaning noises originating from the power steering pump. Drivers may notice vibrations or jerky steering response, indicating hydraulic fluid leaks or belt issues within the power steering system. Manual steering difficulty, by contrast, manifests as heavy, unassisted steering requiring significant physical force, but lacks the accompanying noise and fluid-related symptoms characteristic of power steering malfunctions.
Manual Steering: Challenges and Limitations
Manual steering requires significantly more physical effort compared to power steering, especially at low speeds or during parking maneuvers, leading to driver fatigue. The absence of hydraulic or electric assistance limits responsiveness and precision, making steering heavier and less fluid. This increased difficulty can reduce control in emergency situations, posing safety risks and requiring greater skill to manage vehicle direction.
Safety Risks: Power Steering Failure vs Manual Steering
Power steering failure significantly increases steering effort, especially at low speeds, which can lead to delayed reaction times and compromised vehicle control, heightening the risk of accidents. Manual steering, while requiring consistent physical effort, offers predictable feedback and control without sudden loss of assistive power, reducing unexpected handling challenges. Safety risks escalate sharply with power steering failure due to the abrupt change in steering dynamics, demanding immediate driver adaptation to maintain vehicle stability.
Emergency Handling: What To Do When Power Steering Fails
Power steering failure drastically increases steering effort, making maneuvering difficult, especially at low speeds or during emergency situations. Drivers should maintain a firm grip on the wheel, reduce speed gradually, and avoid sudden turns to retain control. In such emergencies, safely pulling over and shutting off the engine helps prevent further damage and allows for calling roadside assistance.
Maintenance Tips: Preventing Steering Issues
Regularly inspect power steering fluid levels and replace fluid every 50,000 miles to prevent failure and ensure smooth steering response. Check for leaks in hoses and seals, as deteriorated components can cause power steering loss and increase manual steering difficulty. Maintain alignment and tire pressure to reduce strain on the steering system and avoid premature wear, enhancing overall vehicle control and safety.
Repair Costs: Power Steering vs Manual Steering
Repair costs for power steering failures typically exceed those for manual steering issues due to the complexity of components such as the power steering pump, rack and pinion, and hydraulic or electric systems. Manual steering repairs are generally less expensive, often involving simpler mechanical adjustments or replacements of the steering linkage without hydraulic fluid or electronic sensors. Labor costs for power steering repairs can also be higher because of the specialized tools and expertise required compared to manual steering maintenance.
Choosing Between Power and Manual Steering for Your Car
Power steering significantly reduces steering effort, making it easier to maneuver, especially at low speeds or during parking, while manual steering demands more physical strength but offers direct road feedback and simpler mechanics. Power steering failures can lead to increased steering effort and potential safety concerns, requiring timely repairs, whereas manual steering, though harder to handle, is less prone to sudden breakdowns. Choosing between power and manual steering depends on driver preference, vehicle type, and maintenance considerations, balancing ease of use against reliability.
Power steering failure vs manual steering difficulty Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com