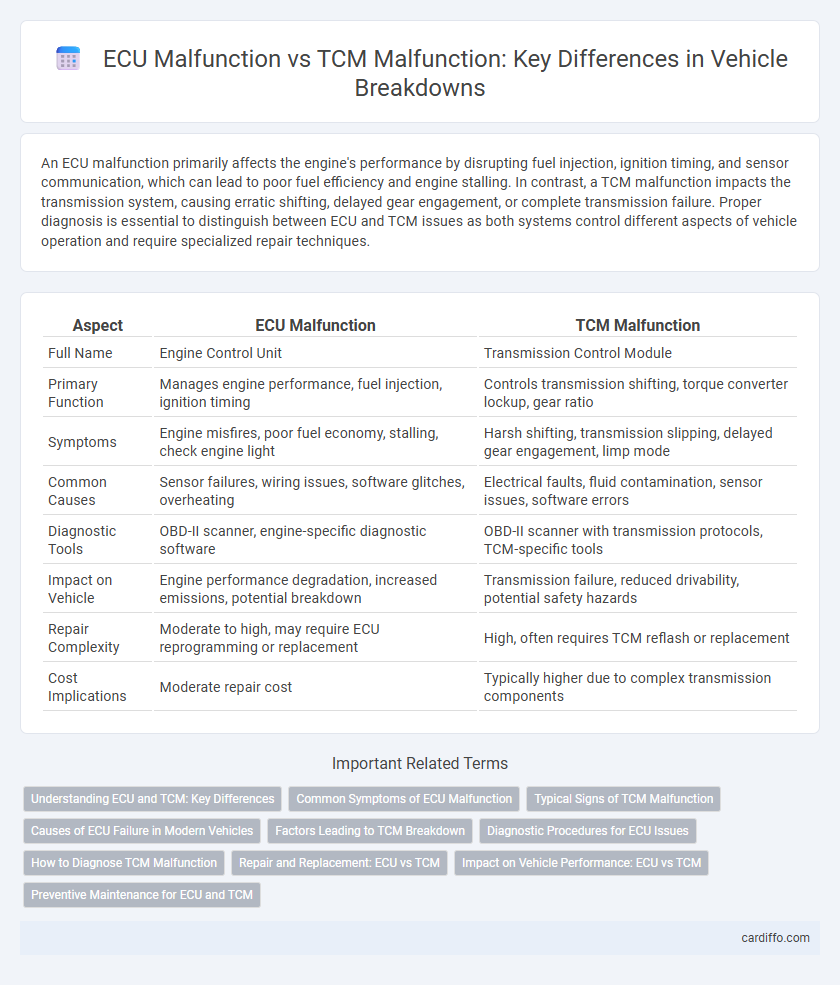
An ECU malfunction primarily affects the engine's performance by disrupting fuel injection, ignition timing, and sensor communication, which can lead to poor fuel efficiency and engine stalling. In contrast, a TCM malfunction impacts the transmission system, causing erratic shifting, delayed gear engagement, or complete transmission failure. Proper diagnosis is essential to distinguish between ECU and TCM issues as both systems control different aspects of vehicle operation and require specialized repair techniques.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ECU Malfunction | TCM Malfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Engine Control Unit | Transmission Control Module |
| Primary Function | Manages engine performance, fuel injection, ignition timing | Controls transmission shifting, torque converter lockup, gear ratio |
| Symptoms | Engine misfires, poor fuel economy, stalling, check engine light | Harsh shifting, transmission slipping, delayed gear engagement, limp mode |
| Common Causes | Sensor failures, wiring issues, software glitches, overheating | Electrical faults, fluid contamination, sensor issues, software errors |
| Diagnostic Tools | OBD-II scanner, engine-specific diagnostic software | OBD-II scanner with transmission protocols, TCM-specific tools |
| Impact on Vehicle | Engine performance degradation, increased emissions, potential breakdown | Transmission failure, reduced drivability, potential safety hazards |
| Repair Complexity | Moderate to high, may require ECU reprogramming or replacement | High, often requires TCM reflash or replacement |
| Cost Implications | Moderate repair cost | Typically higher due to complex transmission components |
Understanding ECU and TCM: Key Differences
ECU (Engine Control Unit) and TCM (Transmission Control Module) both regulate vehicle performance but control distinct systems; the ECU manages engine functions such as fuel injection and ignition timing, while the TCM oversees transmission operations including gear shifts and clutch engagement. Malfunctions in the ECU typically result in engine-related issues like poor fuel efficiency or stalling, whereas TCM failures cause transmission problems such as erratic shifting or failure to change gears. Diagnosing breakdowns requires understanding these differences to target repairs accurately and prevent further damage.
Common Symptoms of ECU Malfunction
Common symptoms of ECU malfunction include engine misfires, poor fuel efficiency, and difficulty starting the vehicle. Unlike TCM malfunctions, which primarily affect transmission shifting and cause gear slip or harsh shifts, ECU issues often trigger the check engine light and result in erratic engine behavior. Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to ignition, fuel injection, or sensor failures frequently indicate ECU problems.
Typical Signs of TCM Malfunction
Typical signs of TCM malfunction include erratic shifting, delayed gear engagement, and transmission slipping. Drivers may experience harsh or inappropriate gear changes and warning lights such as the check engine or transmission warning light illuminating on the dashboard. These symptoms indicate that the Transmission Control Module is failing to correctly manage transmission operations, differentiating it from ECU malfunction which primarily affects engine performance and fuel management.
Causes of ECU Failure in Modern Vehicles
ECU failure in modern vehicles commonly results from electrical issues such as short circuits, voltage spikes, or water damage, leading to disrupted engine control functions. In contrast, TCM malfunctions often arise from transmission fluid contamination, sensor failures, or internal component wear, impacting gear shifting performance. Understanding the distinct causes of ECU versus TCM failure is essential for accurate diagnostics and effective repair in automotive electronic control systems.
Factors Leading to TCM Breakdown
Factors leading to TCM (Transmission Control Module) breakdown include electrical issues such as faulty wiring, voltage spikes, and poor grounding. Environmental conditions like extreme temperatures and moisture intrusion can corrode internal components, accelerating failure. Software bugs or outdated firmware also contribute to TCM malfunctions, affecting transmission performance and vehicle drivability.
Diagnostic Procedures for ECU Issues
Diagnostic procedures for ECU issues typically involve connecting a professional OBD-II scanner to read error codes related to the engine control unit, helping identify faults such as sensor malfunctions or software glitches. Technicians perform voltage and continuity tests on ECU wiring harnesses to ensure proper electrical connections and isolate potential shorts or open circuits. Firmware updates and ECU reprogramming may be necessary to resolve communication errors or restore optimal engine performance after identifying ECU-specific malfunctions.
How to Diagnose TCM Malfunction
Diagnosing a Transmission Control Module (TCM) malfunction involves scanning the vehicle's onboard diagnostic system for specific trouble codes related to shifting issues and sensor failures. Checking transmission fluid levels and condition can help differentiate TCM problems from Engine Control Unit (ECU) malfunctions, which typically affect engine performance rather than gear changes. Performing a visual inspection of the TCM wiring harness and connectors ensures proper electrical connections, as loose or corroded contacts frequently cause transmission control errors.
Repair and Replacement: ECU vs TCM
ECU malfunction repair often involves advanced diagnostic tools to reprogram or replace the engine control unit, as it manages critical engine functions. TCM malfunction repair requires specialized software to recalibrate or replace the transmission control module, which controls gear shifting and transmission performance. Replacement of ECU or TCM depends on the severity of the fault, with ECU repairs focusing on sensor and wiring checks, while TCM replacements prioritize resolving transmission errors for optimal vehicle operation.
Impact on Vehicle Performance: ECU vs TCM
ECU malfunction disrupts engine control parameters such as fuel injection and ignition timing, leading to poor acceleration, stalling, and reduced fuel efficiency, while TCM malfunction affects transmission shift timing and gear engagement, causing rough shifting, transmission slipping, and potential drivetrain damage. Both ECUs and TCMs are critical for optimal vehicle performance, with ECU issues primarily impacting engine operation and TCM problems specifically degrading transmission response. Diagnostics targeting error codes from the ECU or TCM can pinpoint malfunctions, enabling timely repairs and preventing extensive vehicle breakdowns.
Preventive Maintenance for ECU and TCM
ECU malfunction often results from electrical faults or software glitches, requiring regular diagnostics and firmware updates to prevent failures. TCM malfunctions typically stem from hydraulic issues or sensor malfunctions, making routine fluid checks and sensor calibrations critical for maintenance. Implementing preventive maintenance schedules for both ECU and TCM enhances vehicle reliability and minimizes costly breakdowns.
ECU malfunction vs TCM malfunction Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com