Standard charging extends battery lifespan by delivering a steady current, reducing heat generation and minimizing wear on battery cells. Fast charging provides rapid power replenishment but can increase battery temperature and stress, potentially shortening overall battery life. Choosing between standard and fast charging depends on balancing convenience with long-term battery health.
Table of Comparison
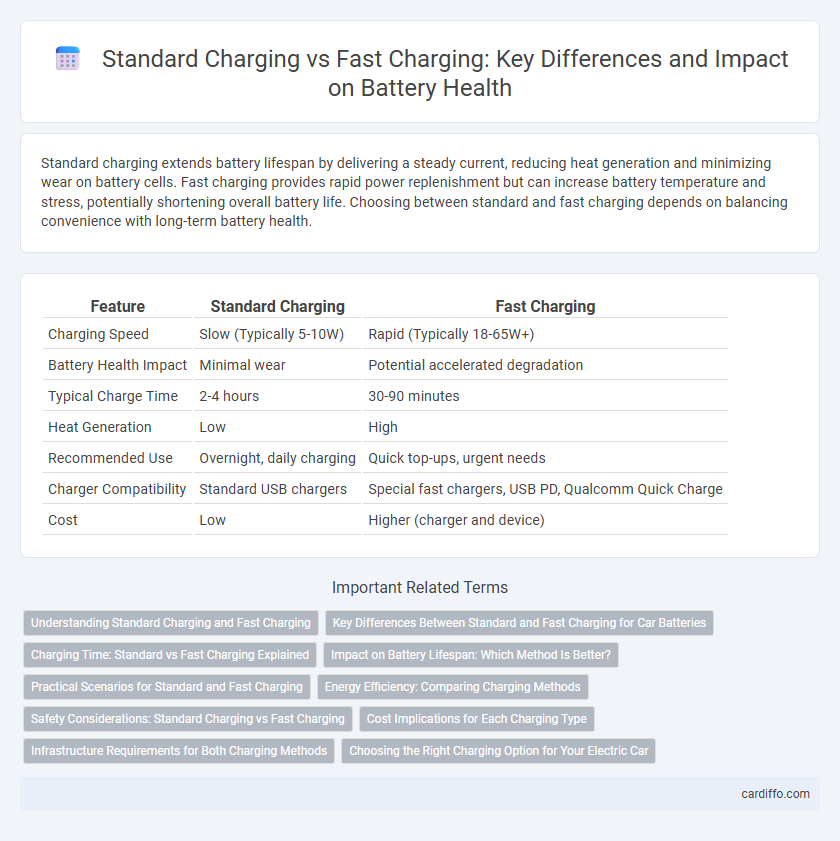
| Feature | Standard Charging | Fast Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Slow (Typically 5-10W) | Rapid (Typically 18-65W+) |
| Battery Health Impact | Minimal wear | Potential accelerated degradation |
| Typical Charge Time | 2-4 hours | 30-90 minutes |
| Heat Generation | Low | High |
| Recommended Use | Overnight, daily charging | Quick top-ups, urgent needs |
| Charger Compatibility | Standard USB chargers | Special fast chargers, USB PD, Qualcomm Quick Charge |
| Cost | Low | Higher (charger and device) |
Understanding Standard Charging and Fast Charging
Standard charging typically delivers a lower current, allowing the battery to charge safely and preserve its overall lifespan through controlled heat generation. Fast charging increases the current and voltage to significantly reduce charging time but may lead to higher battery temperature and potential capacity degradation over time. Understanding the specific battery chemistry, such as lithium-ion or lithium-polymer, is essential to optimize charging strategies that balance speed and longevity.
Key Differences Between Standard and Fast Charging for Car Batteries
Standard charging for car batteries typically operates at a lower current, ensuring a slower yet safer and more controlled energy transfer that reduces heat generation and prolongs battery lifespan. Fast charging utilizes higher current levels to significantly reduce charging time but may increase the risk of battery degradation and heat-related damage if not properly managed. Vehicle manufacturers often recommend standard charging for routine use, reserving fast charging for emergency situations to balance convenience with battery health preservation.
Charging Time: Standard vs Fast Charging Explained
Standard charging typically takes several hours to fully recharge a battery, often ranging from 3 to 8 hours depending on the battery capacity and charger power. Fast charging technology significantly reduces this time, delivering up to 80% battery capacity in as little as 30 minutes by increasing the charge current and voltage safely. The trade-off includes potential heat generation and long-term battery health impact, but advancements in battery management systems help mitigate these risks.
Impact on Battery Lifespan: Which Method Is Better?
Standard charging preserves battery lifespan more effectively by minimizing heat generation and reducing stress on battery cells, leading to slower degradation over time. Fast charging, while convenient, accelerates battery aging due to increased thermal buildup and higher charge currents, which can shorten overall battery health. Choosing standard charging extends battery longevity, making it a better option for users prioritizing durability over quick recharge times.
Practical Scenarios for Standard and Fast Charging
Standard charging suits overnight or extended periods when device usage is low, preserving battery health and ensuring full capacity over time. Fast charging is ideal during short breaks or urgent situations, quickly replenishing battery levels but potentially generating more heat and accelerating battery wear. Choosing between standard and fast charging depends on balancing convenience with maintaining long-term battery lifespan in practical daily use.
Energy Efficiency: Comparing Charging Methods
Standard charging offers higher energy efficiency by minimizing heat generation and power loss during the charging process, preserving battery lifespan. Fast charging increases energy consumption due to rapid current flow, leading to more heat dissipation and reduced overall efficiency. Optimizing charging methods involves balancing speed with energy efficiency to maintain battery health and performance.
Safety Considerations: Standard Charging vs Fast Charging
Standard charging typically generates less heat and reduces stress on battery cells, significantly lowering the risk of thermal runaway and prolonging battery lifespan. Fast charging, while convenient, increases internal temperature and pressure, which can accelerate degradation and elevate safety risks if not managed by advanced cooling and monitoring systems. Properly designed fast-charging protocols incorporate thermal management and voltage regulation to maintain safety standards comparable to standard charging.
Cost Implications for Each Charging Type
Standard charging generally incurs lower electricity costs due to slower energy transfer rates, leading to more efficient power use and reduced strain on the battery, which extends its lifespan and delays replacement expenses. Fast charging demands higher power output, increasing electricity costs and accelerating battery degradation, potentially resulting in more frequent battery replacements and higher long-term expenses. Evaluating the trade-off between upfront charging speed and overall battery health is essential for minimizing total cost of ownership in electric vehicle and device charging.
Infrastructure Requirements for Both Charging Methods
Standard charging typically requires lower power output and can be supported by common electrical outlets, minimizing the need for specialized infrastructure, making it more accessible for residential and public use. Fast charging demands advanced infrastructure with high-capacity power delivery systems, including dedicated charging stations equipped with robust cooling mechanisms and upgraded electrical grids to ensure safety and efficiency. The significant difference in infrastructure requirements influences deployment costs and scalability for electric vehicle charging networks.
Choosing the Right Charging Option for Your Electric Car
Selecting the appropriate charging option for your electric car depends on balancing convenience, battery health, and driving needs. Standard charging, typically offering 3-7 kW power, preserves battery longevity by providing a steady and moderate charge, ideal for overnight or extended stops. Fast charging, delivering 50 kW or more through DC fast chargers, rapidly replenishes battery capacity, making it suitable for long trips but may increase battery degradation if used frequently.
Standard Charging vs Fast Charging Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com