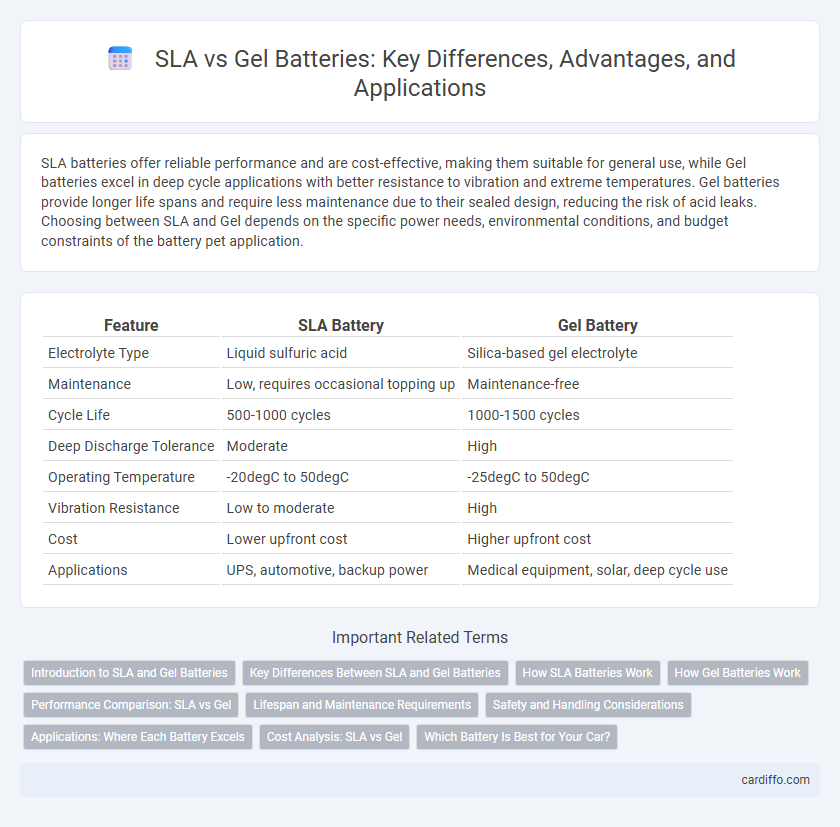
SLA batteries offer reliable performance and are cost-effective, making them suitable for general use, while Gel batteries excel in deep cycle applications with better resistance to vibration and extreme temperatures. Gel batteries provide longer life spans and require less maintenance due to their sealed design, reducing the risk of acid leaks. Choosing between SLA and Gel depends on the specific power needs, environmental conditions, and budget constraints of the battery pet application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SLA Battery | Gel Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Liquid sulfuric acid | Silica-based gel electrolyte |
| Maintenance | Low, requires occasional topping up | Maintenance-free |
| Cycle Life | 500-1000 cycles | 1000-1500 cycles |
| Deep Discharge Tolerance | Moderate | High |
| Operating Temperature | -20degC to 50degC | -25degC to 50degC |
| Vibration Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Applications | UPS, automotive, backup power | Medical equipment, solar, deep cycle use |
Introduction to SLA and Gel Batteries
SLA (Sealed Lead Acid) batteries feature a sealed design with absorbed electrolyte, offering maintenance-free operation and widespread use in backup power systems. Gel batteries utilize silica to suspend electrolyte, enhancing deep cycling capabilities and resistance to vibration. Both types provide reliable energy storage but differ in construction and application suitability.
Key Differences Between SLA and Gel Batteries
SLA (Sealed Lead Acid) batteries use a liquid electrolyte absorbed in a fiberglass mat, providing reliable performance but requiring maintenance to prevent acid leakage. Gel batteries contain a silica-based gel electrolyte, offering enhanced resistance to vibration, deeper discharge cycles, and reduced risk of acid stratification. SLA batteries excel in cost-effectiveness and high discharge rates, while gel batteries deliver superior longevity and suitability for extreme temperatures in renewable energy and deep cycle applications.
How SLA Batteries Work
SLA (Sealed Lead Acid) batteries operate through a chemical reaction between lead plates and sulfuric acid electrolyte contained within a sealed casing, preventing leakage and allowing maintenance-free operation. The electrolyte is immobilized using a gel or absorbed glass mat to enhance stability and reduce acid stratification. This design ensures reliable power delivery with minimal gas emissions, making SLA batteries suitable for backup power and renewable energy applications.
How Gel Batteries Work
Gel batteries use a silica-based gel electrolyte that immobilizes the acid, preventing spillage and reducing the risk of leaks. This gel electrolyte enhances battery performance by providing stability during operation and allowing for deeper discharge cycles compared to SLA batteries. The design of gel batteries supports better heat resistance and longevity, making them suitable for applications requiring reliable and maintenance-free energy storage.
Performance Comparison: SLA vs Gel
SLA batteries offer high discharge rates and are ideal for applications requiring quick bursts of power, while Gel batteries excel in deep cycle performance with longer service life and superior resistance to vibration. Gel batteries provide better performance in extreme temperatures and minimal maintenance due to their sealed design, whereas SLA batteries are more cost-effective for general use. Both types maintain reliable voltage output, but Gel batteries generally outperform SLA in terms of longevity and durability under heavy use.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) batteries typically offer a lifespan of 3 to 5 years, requiring regular maintenance such as checking electrolyte levels and ensuring proper charging cycles. Gel batteries, with a lifespan extending up to 7 years, demand lower maintenance due to their sealed design and gelled electrolyte, which reduces the risk of leakage and sulfation. Choosing between SLA and Gel batteries depends on balancing longer lifespan benefits with lower maintenance needs for specific applications.
Safety and Handling Considerations
SLA batteries feature a liquid electrolyte that requires careful handling to avoid spills and corrosion, while gel batteries use a silica-thickened electrolyte, greatly reducing leakage risks and enhancing safety. Gel batteries perform reliably under extreme temperatures and are less prone to acid stratification, making them safer for transport and storage. Proper ventilation must be ensured for SLA batteries due to their potential hydrogen gas emission during charging, whereas gel batteries emit minimal gases, reducing the need for specialized ventilation.
Applications: Where Each Battery Excels
SLA batteries excel in automotive starting and backup power applications due to their high discharge rates and reliability under heavy load. Gel batteries are preferred in deep cycle applications such as solar energy storage and marine use because of their superior resistance to vibration and ability to perform well in extreme temperatures. Each battery type offers unique advantages tailored to specific operational demands and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: SLA vs Gel
Absorbent Glass Mat (SLA) batteries typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to Gel batteries, making them more economical for budget-conscious applications. Gel batteries, while higher in initial price, provide longer service life and better deep-cycle performance, which can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals Gel batteries may deliver improved value in high-demand environments despite higher initial investment.
Which Battery Is Best for Your Car?
Sealed Lead Acid (SLA) batteries offer reliable performance and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for standard vehicle applications. Gel batteries provide superior deep-cycle capabilities, longer lifespan, and enhanced resistance to vibration, ideal for demanding car systems and off-road conditions. Choosing between SLA and Gel batteries depends on your car's power needs, usage patterns, and environmental exposure.
SLA vs Gel Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com