Battery pets perform more efficiently in cold weather as lower temperatures reduce the risk of overheating and slow down internal chemical reactions, thus extending battery life. In hot weather, elevated temperatures accelerate chemical reactions inside the battery, causing faster degradation and reduced overall capacity. Proper temperature management is essential to optimize battery pet performance and longevity in varying climate conditions.
Table of Comparison
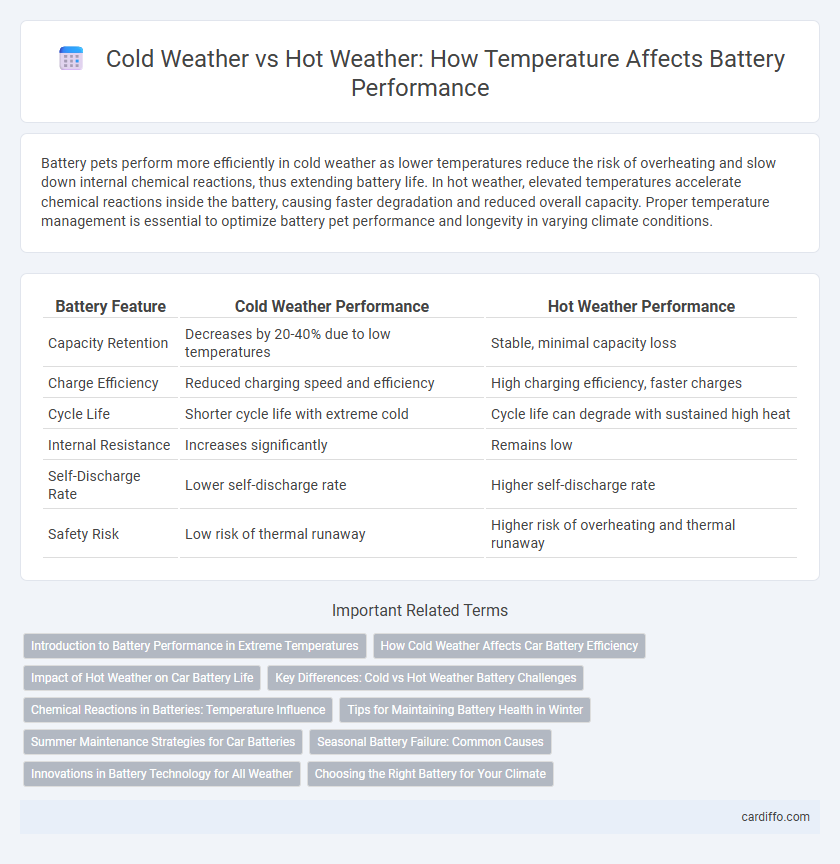
| Battery Feature | Cold Weather Performance | Hot Weather Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity Retention | Decreases by 20-40% due to low temperatures | Stable, minimal capacity loss |
| Charge Efficiency | Reduced charging speed and efficiency | High charging efficiency, faster charges |
| Cycle Life | Shorter cycle life with extreme cold | Cycle life can degrade with sustained high heat |
| Internal Resistance | Increases significantly | Remains low |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Lower self-discharge rate | Higher self-discharge rate |
| Safety Risk | Low risk of thermal runaway | Higher risk of overheating and thermal runaway |
Introduction to Battery Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Battery performance in extreme temperatures is significantly influenced by environmental conditions, with cold weather often reducing battery capacity and efficiency due to slowed chemical reactions. Conversely, hot weather can accelerate chemical activity but increases the risk of overheating and accelerated degradation of battery components. Understanding these temperature-induced effects is crucial for optimizing battery life and ensuring reliable operation in both cold and hot climates.
How Cold Weather Affects Car Battery Efficiency
Cold weather significantly reduces car battery efficiency by decreasing the chemical reaction rates inside the battery, leading to reduced voltage output and slower engine cranking. Low temperatures cause the electrolyte to thicken, which increases internal resistance and diminishes the battery's ability to deliver peak power. In contrast, hot weather can accelerate battery degradation due to higher rates of corrosion and evaporation of electrolyte fluid, but cold weather primarily impacts immediate performance and starting power.
Impact of Hot Weather on Car Battery Life
Hot weather significantly accelerates the chemical reactions inside car batteries, leading to increased corrosion and faster degradation of battery components. High temperatures cause the battery fluid to evaporate, reducing the electrolyte level and impairing the battery's ability to hold a charge effectively. This thermal stress shortens the overall lifespan of the battery compared to cold weather conditions, where performance primarily decreases due to reduced chemical activity rather than permanent damage.
Key Differences: Cold vs Hot Weather Battery Challenges
Cold weather causes reduced battery capacity and slower chemical reactions, leading to decreased performance and longer charging times, while hot weather accelerates chemical degradation, increasing the risk of overheating and shortening battery lifespan. Low temperatures result in higher internal resistance, limiting power output, whereas high temperatures cause electrolyte evaporation and increased self-discharge rates. Managing thermal conditions is essential to optimize battery efficiency and longevity under extreme weather scenarios.
Chemical Reactions in Batteries: Temperature Influence
Battery chemical reactions accelerate in hot weather, increasing ion movement and improving initial performance but causing faster electrolyte degradation and capacity loss. In cold weather, slowed chemical reactions reduce ion flow, resulting in diminished battery capacity and longer charge times. Temperature extremes impact battery electrolyte viscosity and electrode kinetics, directly influencing efficiency and lifespan.
Tips for Maintaining Battery Health in Winter
To maintain battery health in winter, keep the battery fully charged as low temperatures reduce its capacity and slow chemical reactions. Use an insulated battery blanket to protect against extreme cold and prevent electrolyte freezing. Regularly clean battery terminals to avoid corrosion, which can be exacerbated by moisture and salt during winter months.
Summer Maintenance Strategies for Car Batteries
Car batteries tend to perform optimally in cold weather by retaining charge but can overheat and degrade faster in hot summer conditions. To extend battery life during summer, regularly check electrolyte levels, clean corrosion from terminals, and ensure proper ventilation to prevent heat buildup. Using heat shields and parking in shaded areas further reduces thermal stress, enhancing battery reliability under high temperatures.
Seasonal Battery Failure: Common Causes
Battery failure during cold weather often results from reduced chemical reactions inside the cells, causing decreased capacity and slower cranking power. In hot weather, elevated temperatures accelerate electrolyte evaporation and increase the risk of internal corrosion, leading to premature battery degradation. Seasonal battery failure commonly arises from temperature extremes that stress battery components, emphasizing the need for temperature-adapted maintenance strategies.
Innovations in Battery Technology for All Weather
Innovations in battery technology have significantly enhanced performance across extreme temperatures, using advanced materials such as lithium iron phosphate and solid-state electrolytes to maintain capacity and efficiency in cold and hot weather. Thermal management systems, including phase change materials and integrated cooling/heating modules, ensure optimal battery temperatures, preventing degradation and extending lifespan. These advancements contribute to consistent energy density, faster charging rates, and improved safety in varying climatic conditions.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Climate
Cold weather performance in batteries demands high cold cranking amps (CCA) to ensure reliable engine starts, while hot weather performance emphasizes heat tolerance and resistance to evaporation and corrosion. Selecting a battery with a temperature-appropriate design, such as enhanced plate construction and robust electrolyte formulas, extends lifespan and maintains optimal power output under specific climate stresses. Understanding the climate-specific battery ratings, including reserve capacity and cycle durability, helps consumers choose the right battery that balances performance and longevity for cold or hot environments.
Cold Weather Performance vs Hot Weather Performance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com