The crank test evaluates a battery's ability to start an engine by measuring voltage drop during cranking, ensuring reliable power delivery under high current. The load test simulates real operating conditions by applying a controlled load to assess overall battery performance and capacity over time. Comparing both tests helps diagnose battery health accurately and determine whether replacement or maintenance is required.
Table of Comparison
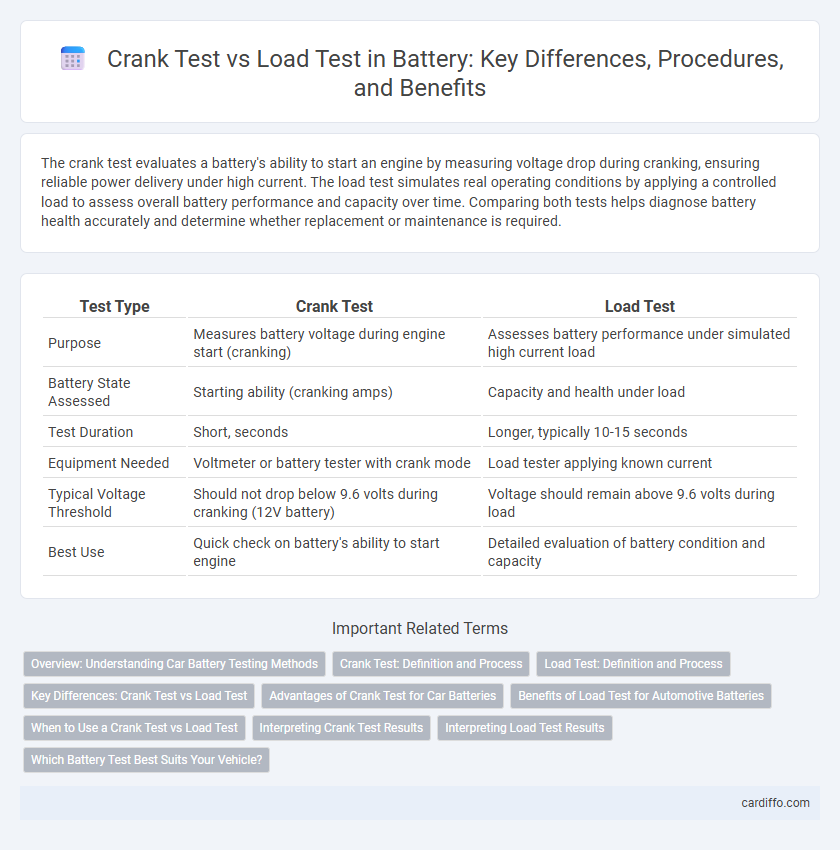
| Test Type | Crank Test | Load Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures battery voltage during engine start (cranking) | Assesses battery performance under simulated high current load |
| Battery State Assessed | Starting ability (cranking amps) | Capacity and health under load |
| Test Duration | Short, seconds | Longer, typically 10-15 seconds |
| Equipment Needed | Voltmeter or battery tester with crank mode | Load tester applying known current |
| Typical Voltage Threshold | Should not drop below 9.6 volts during cranking (12V battery) | Voltage should remain above 9.6 volts during load |
| Best Use | Quick check on battery's ability to start engine | Detailed evaluation of battery condition and capacity |
Overview: Understanding Car Battery Testing Methods
Crank test measures a car battery's ability to provide cold cranking amps (CCA) crucial for engine start-up, while load test evaluates the battery's overall capacity to sustain electrical loads under real operating conditions. Both tests assess different performance aspects, with crank test focusing on short-term power output and load test on long-term reliability. Accurate battery diagnostics rely on combining these methods to ensure optimal vehicle starting and electrical system functionality.
Crank Test: Definition and Process
The Crank Test measures a battery's ability to deliver current during engine startup by simulating cold cranking conditions. It assesses the Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), providing critical data on the battery's performance under high load demands in low temperature environments. The process involves applying a high current load for a short duration while monitoring voltage drop to evaluate the battery's health and starting capability.
Load Test: Definition and Process
A load test evaluates a battery's ability to maintain voltage under a specified load, simulating real operating conditions. During the process, the battery is subjected to a discharge load for a set duration while monitoring voltage drop to detect weaknesses or potential failure. This method provides accurate insight into the battery's capacity and health compared to simple voltage measurements.
Key Differences: Crank Test vs Load Test
Crank tests measure a battery's ability to provide high current during engine starting, focusing on cold cranking amps (CCA) performance, while load tests assess overall battery health by applying a fixed electrical load to evaluate voltage stability under stress. Crank tests simulate real-world engine cranking conditions, emphasizing instant power delivery, whereas load tests determine the battery's capacity to maintain voltage during prolonged load application. The key difference lies in crank tests targeting starting power effectiveness and load tests evaluating sustained battery performance and health.
Advantages of Crank Test for Car Batteries
Crank Test offers a quick and accurate assessment of a car battery's ability to deliver sufficient starting power by measuring voltage during engine startup conditions. It requires minimal equipment and can be performed without fully discharging the battery, preserving battery life. This method is ideal for early detection of starting issues, preventing unexpected battery failures on the road.
Benefits of Load Test for Automotive Batteries
Load testing automotive batteries accurately measures their real-world performance by applying controlled electrical loads that simulate actual engine starting conditions. This method identifies weak cells and assesses battery capacity, providing a more reliable indicator of battery health compared to crank tests, which only measure voltage response. As a result, load tests help prevent unexpected battery failures and extend vehicle reliability by ensuring batteries maintain appropriate power output under demand.
When to Use a Crank Test vs Load Test
A crank test is ideal for assessing a battery's ability to deliver high current needed for engine starting, making it essential during cold weather or when diagnosing starting problems. Load tests measure overall battery capacity and performance under simulated operating conditions, providing a complete evaluation of battery health during routine maintenance. Use a crank test when immediate starting power is in question and a load test for comprehensive assessment of battery endurance and charge retention.
Interpreting Crank Test Results
Crank test results measure a battery's ability to deliver sufficient current during engine startup, typically expressed in cold cranking amps (CCA). A low CCA value or a voltage drop below 9.6 volts during the crank test indicates inadequate battery performance or potential failure. Comparing these results with load test outcomes helps confirm battery health and diagnose starting system issues accurately.
Interpreting Load Test Results
Load test results indicate the battery's ability to deliver current under a specified load, reflecting its true capacity and health. Crank tests measure voltage drop during engine start, showing immediate performance but may not reveal overall battery condition. Interpreting load test outcomes involves comparing voltage readings against standard thresholds to assess potential issues like sulfation or capacity loss.
Which Battery Test Best Suits Your Vehicle?
Crank tests measure a battery's ability to deliver the required cold cranking amps (CCA) for engine starting, making them ideal for evaluating starting power in cold conditions. Load tests assess overall battery performance by applying a simulated electrical load, providing insight into capacity and health under typical driving conditions. Choosing between a crank test and a load test depends on whether you need to verify your vehicle's starting power or gauge long-term battery reliability during normal operation.
Crank Test vs Load Test Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com