The CCA rating measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, indicating its performance at 0degF. The CA rating, or cranking amps, reflects the battery's starting power at 32degF, showing how well it performs in milder conditions. Comparing CCA vs CA ratings helps select the right battery based on climate and starting power requirements.
Table of Comparison
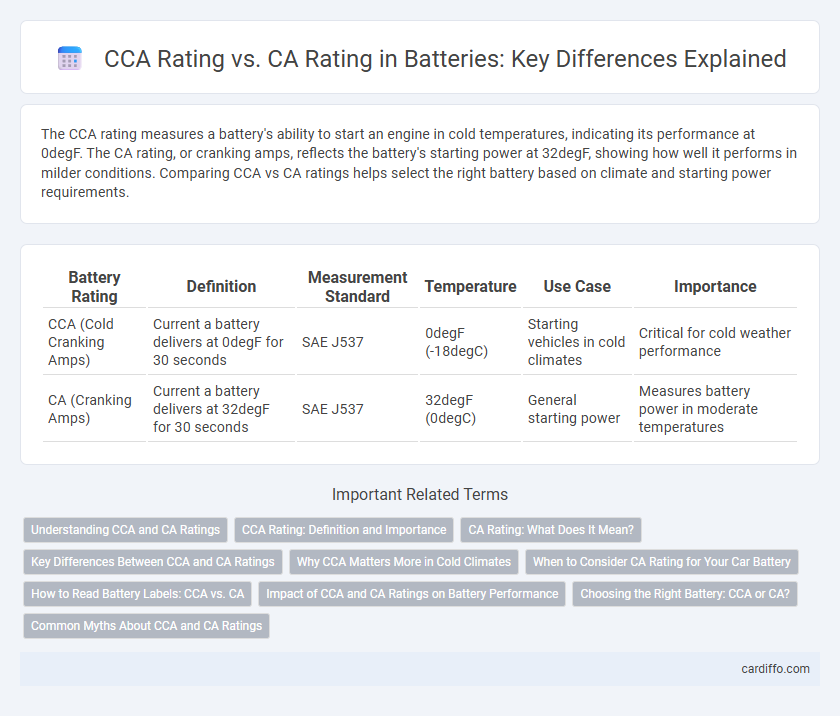
| Battery Rating | Definition | Measurement Standard | Temperature | Use Case | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA (Cold Cranking Amps) | Current a battery delivers at 0degF for 30 seconds | SAE J537 | 0degF (-18degC) | Starting vehicles in cold climates | Critical for cold weather performance |
| CA (Cranking Amps) | Current a battery delivers at 32degF for 30 seconds | SAE J537 | 32degF (0degC) | General starting power | Measures battery power in moderate temperatures |
Understanding CCA and CA Ratings
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by indicating the maximum current it can deliver for 30 seconds at 0degF (-18degC). Cranking Amps (CA) rating, also known as Marine Cranking Amps (MCA), assesses the battery's performance at 32degF (0degC), reflecting higher values since batteries perform better at warmer temperatures. Understanding both CCA and CA ratings is essential for selecting the right battery, ensuring reliable engine starts under varying temperature conditions.
CCA Rating: Definition and Importance
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by indicating the number of amps a battery can deliver at 0degF for 30 seconds while maintaining at least 7.2 volts. This rating is crucial for vehicles operating in cold climates, ensuring reliable engine starts under harsh conditions. Higher CCA ratings correlate with better cold-weather performance and overall battery durability.
CA Rating: What Does It Mean?
The CA Rating, or Cranking Amps rating, measures a battery's ability to deliver a certain amount of current at 32degF (0degC) for 30 seconds while maintaining a minimum voltage of 7.2 volts for a 12-volt battery. This rating reflects the battery's starting power in moderate temperature conditions, providing a more realistic indication of performance in typical environments compared to the Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating, which is measured at 0degF (-18degC). Understanding the CA rating helps consumers select batteries optimized for reliable engine starts during average climate conditions.
Key Differences Between CCA and CA Ratings
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Cranking Amps (CA) both measure a battery's ability to start an engine, with CCA indicating performance at 0degF (-18degC) and CA at 32degF (0degC). The CCA rating is critical for vehicles operating in cold climates as it reflects battery capacity under extreme cold conditions, while the CA rating applies to milder temperatures and is generally higher due to less stress on the battery. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the appropriate battery, ensuring reliable engine starts under varying temperature conditions.
Why CCA Matters More in Cold Climates
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) rating measures a battery's ability to start an engine in freezing temperatures, making it crucial for cold climates where low temperatures increase engine resistance. Cranking Amps (CA) rating indicates performance at 32degF but does not reflect battery capacity under extreme cold conditions. High CCA values ensure reliable starting power in winter, preventing battery failure when temperatures drop below freezing.
When to Consider CA Rating for Your Car Battery
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, while Cranking Amps (CA) indicate performance at 32degF. Consider the CA rating for your car battery when operating in moderate climates where cold starts are less frequent, as it reflects the battery's capacity under normal temperature conditions. Choosing a battery with a suitable CA rating ensures reliable starts and optimal power delivery during typical weather scenarios.
How to Read Battery Labels: CCA vs. CA
Battery labels display Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Cranking Amps (CA) to indicate starting power at different temperatures, with CCA measuring performance at 0degF (-18degC) and CA at 32degF (0degC). Higher CCA ratings signify better cold-weather starting ability, while CA ratings reflect the battery's cranking power in warmer conditions. Understanding both CCA and CA ratings helps choose the right battery for climate and vehicle requirements, ensuring reliable engine starts.
Impact of CCA and CA Ratings on Battery Performance
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, directly impacting performance in low-temperature environments by ensuring reliable power delivery during ignition. Cranking Amps (CA) indicate the current a battery can provide at 32degF, reflecting its overall power capacity under moderate temperature conditions. Both CCA and CA ratings are critical for evaluating a battery's starting power and operational efficiency, influencing vehicle reliability and engine responsiveness in varying climates.
Choosing the Right Battery: CCA or CA?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making it crucial for winter climates, while Cranking Amps (CA) indicates starting power at 32degF, reflecting performance in moderate conditions. Choosing the right battery depends on the typical environment; high CCA ratings are essential for cold regions to ensure reliable starts, whereas CA ratings suffice in milder temperatures. Understanding the difference between CCA and CA helps optimize battery selection for engine starting reliability and overall vehicle performance.
Common Myths About CCA and CA Ratings
Common myths about CCA (Cold Cranking Amps) and CA (Cranking Amps) ratings often confuse their true significance in battery performance; CCA measures a battery's ability to start engines in cold temperatures at 0degF (-18degC), while CA is rated at 32degF (0degC), indicating higher amp delivery under milder conditions. Many believe a higher CA rating means better cold-weather starting, but CCA is the critical rating for cold climates as it reflects battery power under severe cold stress. Understanding the temperature-specific nature of these ratings helps consumers select batteries suited to their environment, debunking misconceptions that CA ratings alone determine battery starting strength.
CCA Rating vs CA Rating Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com