Front-end alignment adjusts the angles of the front wheels to ensure proper steering and reduce tire wear, ideal for vehicles with a solid rear axle. All-wheel alignment calibrates all four wheels, enhancing overall handling and traction, especially for all-wheel-drive vehicles. Choosing the right alignment improves vehicle stability, extends tire life, and optimizes fuel efficiency.
Table of Comparison
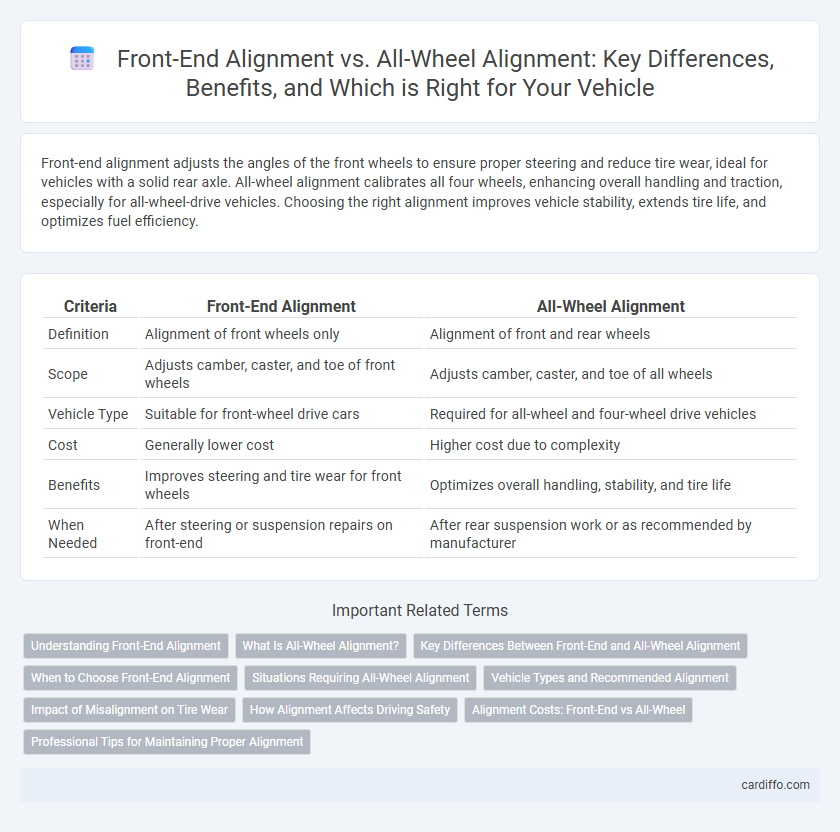
| Criteria | Front-End Alignment | All-Wheel Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alignment of front wheels only | Alignment of front and rear wheels |
| Scope | Adjusts camber, caster, and toe of front wheels | Adjusts camber, caster, and toe of all wheels |
| Vehicle Type | Suitable for front-wheel drive cars | Required for all-wheel and four-wheel drive vehicles |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Benefits | Improves steering and tire wear for front wheels | Optimizes overall handling, stability, and tire life |
| When Needed | After steering or suspension repairs on front-end | After rear suspension work or as recommended by manufacturer |
Understanding Front-End Alignment
Front-end alignment adjusts the angle of the front wheels to ensure proper steering response and tire wear, primarily focusing on camber, caster, and toe settings. This type of alignment is essential for vehicles with front-wheel drive or those without independent rear suspension, where only the front wheels steer and bear most of the driving force. Understanding front-end alignment helps maintain precise handling and extends tire lifetime by preventing uneven wear on the front tires.
What Is All-Wheel Alignment?
All-wheel alignment adjusts the suspension angles on all four wheels to optimize vehicle handling, prevent uneven tire wear, and improve fuel efficiency. Unlike front-end alignment, which services only the front wheels, all-wheel alignment ensures precise alignment across front and rear axles, enhancing overall vehicle stability. This comprehensive alignment is essential for modern vehicles with independent rear suspensions and all-wheel-drive systems.
Key Differences Between Front-End and All-Wheel Alignment
Front-End Alignment adjusts only the front wheels' camber, caster, and toe settings, primarily affecting steering and tire wear for vehicles with solid rear axles. All-Wheel Alignment involves aligning all four wheels, correcting the suspension geometry for vehicles with independent rear suspension to optimize handling and tire performance. The key difference lies in the scope of adjustment: front-end is limited to the front wheels, while all-wheel ensures comprehensive alignment for enhanced stability and even tire wear.
When to Choose Front-End Alignment
Front-end alignment is ideal for vehicles with a solid rear axle or those experiencing uneven tire wear primarily on the front tires, offering a cost-effective solution focused on adjusting the front wheels' camber and toe settings. This alignment type suits vehicles without independent rear suspension, where rear wheel alignment is fixed or factory-set, making front-end alignment sufficient for maintaining proper handling and tire performance. Choose front-end alignment when the manufacturer's specifications or vehicle condition do not require adjustments to the rear wheels, ensuring optimal steering response and tire longevity without the expense of a full all-wheel alignment.
Situations Requiring All-Wheel Alignment
Situations requiring all-wheel alignment typically involve vehicles with independent rear suspension systems or those experiencing uneven tire wear on both front and rear tires. All-wheel alignment ensures optimal handling, improved tire longevity, and alignment accuracy by adjusting camber, caster, and toe on both the front and rear wheels simultaneously. This service is crucial after collision repairs, suspension replacements, or when manufacturers specify rear alignment settings for precise vehicle control.
Vehicle Types and Recommended Alignment
Front-end alignment is typically recommended for front-wheel-drive vehicles, focusing on adjusting the camber and toe of the front wheels to ensure proper handling and tire wear. All-wheel alignment suits all-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive vehicles, addressing the alignment of all four wheels for balanced traction and improved stability. Selecting the correct alignment type depends on the drivetrain configuration and manufacturer specifications to maintain optimal vehicle performance.
Impact of Misalignment on Tire Wear
Front-end alignment primarily adjusts the angles of the front wheels, directly influencing the steering and handling characteristics, whereas all-wheel alignment ensures that all four wheels are properly aligned for optimal contact with the road. Misalignment in either can cause uneven tire wear, but all-wheel misalignment often leads to accelerated wear on rear tires, impacting vehicle stability and safety more significantly. Detecting and correcting misalignment prevents premature tire degradation, enhances fuel efficiency, and ensures balanced load distribution across all tires.
How Alignment Affects Driving Safety
Proper front-end alignment ensures that the vehicle's steering system is correctly adjusted, which directly enhances handling precision and reduces tire wear, thereby improving driving safety. All-wheel alignment involves adjusting all four wheels to manufacturer specifications, providing balanced traction and stability, especially in adverse conditions. Misalignment in either system can cause uneven tire wear, reduced control, and increased risk of accidents due to compromised vehicle stability.
Alignment Costs: Front-End vs All-Wheel
Front-end alignment typically costs between $50 and $75, while all-wheel alignment often ranges from $100 to $150 due to the more complex adjustments required. Front-end alignment adjusts only the front wheels, making it less expensive and quicker, whereas all-wheel alignment involves aligning all four wheels to factory specifications, ensuring better handling and tire longevity. Choosing the right alignment depends on vehicle type and wear patterns, with all-wheel alignment recommended for all-wheel-drive vehicles to maintain optimal performance.
Professional Tips for Maintaining Proper Alignment
Maintaining proper alignment requires regular inspections of both front-end and all-wheel alignment to ensure optimal tire wear and vehicle handling. Professional tips include checking alignment after suspension repairs and uneven tire wear, using precise alignment equipment that measures camber, caster, and toe angles accurately. Scheduling alignment services based on manufacturer recommendations improves fuel efficiency and extends tire life, preventing costly drivability issues.
Front-End Alignment vs All-Wheel Alignment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com