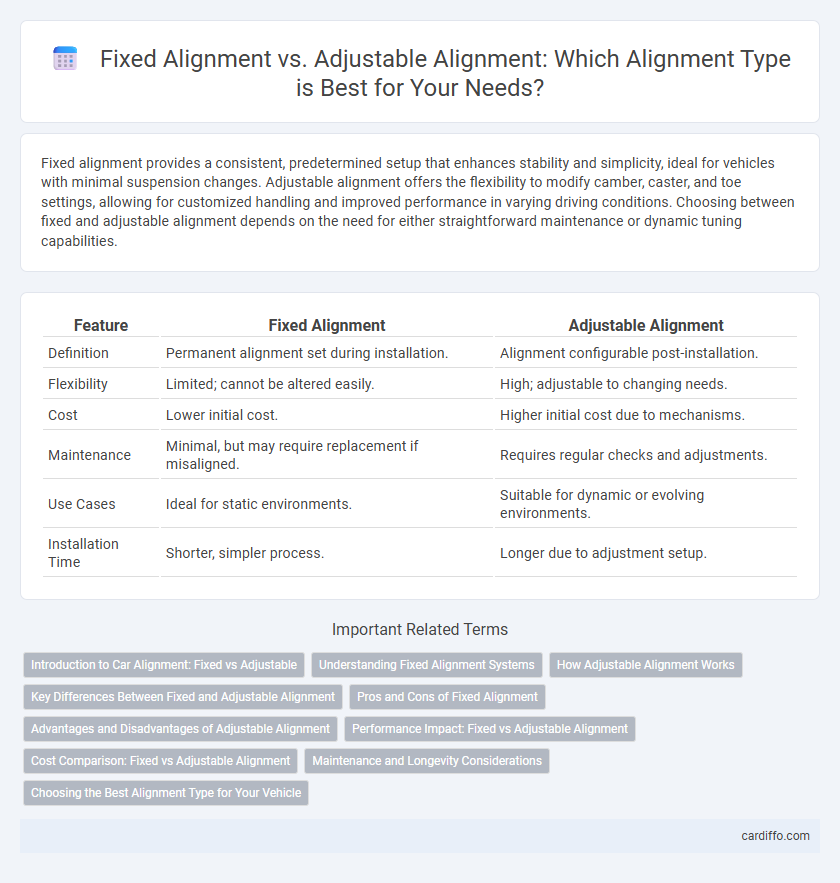
Fixed alignment provides a consistent, predetermined setup that enhances stability and simplicity, ideal for vehicles with minimal suspension changes. Adjustable alignment offers the flexibility to modify camber, caster, and toe settings, allowing for customized handling and improved performance in varying driving conditions. Choosing between fixed and adjustable alignment depends on the need for either straightforward maintenance or dynamic tuning capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fixed Alignment | Adjustable Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent alignment set during installation. | Alignment configurable post-installation. |
| Flexibility | Limited; cannot be altered easily. | High; adjustable to changing needs. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost. | Higher initial cost due to mechanisms. |
| Maintenance | Minimal, but may require replacement if misaligned. | Requires regular checks and adjustments. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for static environments. | Suitable for dynamic or evolving environments. |
| Installation Time | Shorter, simpler process. | Longer due to adjustment setup. |
Introduction to Car Alignment: Fixed vs Adjustable
Fixed alignment systems offer limited adjustment options, providing preset alignment angles ideal for standard vehicle setups and maintaining basic tire performance. Adjustable alignment systems enable precise tuning of camber, caster, and toe angles, improving handling, tire wear, and overall vehicle stability. Understanding the differences between fixed and adjustable alignment helps in selecting the appropriate system for specific driving conditions and vehicle requirements.
Understanding Fixed Alignment Systems
Fixed alignment systems maintain predetermined positions of components, ensuring consistent orientation without the need for manual adjustments. These systems are designed for stability and reliability in environments where alignment parameters remain constant over time. Understanding fixed alignment involves recognizing its advantages in reducing maintenance complexity and minimizing alignment errors in applications such as optical devices and mechanical assemblies.
How Adjustable Alignment Works
Adjustable alignment enables precise modification of alignment angles such as camber, caster, and toe through specialized hardware like eccentric bolts or adjustable control arms. This system allows for fine-tuning vehicle handling, tire wear, and overall performance by accommodating changes in suspension dynamics or load conditions. Technicians can make real-time alignment adjustments without disassembling suspension components, enhancing efficiency and customization.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Adjustable Alignment
Fixed alignment maintains a consistent position using predefined settings, offering stability and simplicity but limited customization. Adjustable alignment allows dynamic changes to position and angle, providing greater flexibility to optimize performance based on specific conditions. Key differences include the level of customization, ease of adjustments, and application suitability, with fixed alignment best for consistent environments and adjustable alignment ideal for variable or precise tuning needs.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Alignment
Fixed alignment offers consistent structural support and precise positioning, minimizing the risk of misalignment over time. However, its rigidity limits customization and adaptability to changing needs or anatomical variations. This inflexibility can lead to discomfort or suboptimal performance in situations requiring dynamic adjustments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Adjustable Alignment
Adjustable alignment offers the advantage of precise customization, allowing users to fine-tune settings for optimal performance and comfort across various applications such as optical devices, machinery, and software interfaces. This flexibility reduces the risk of misalignment-related issues and extends the lifespan of components by accommodating changes over time. However, adjustable alignment can introduce complexity and increase setup time, requiring specialized knowledge or tools, which may lead to higher initial costs and potential maintenance challenges.
Performance Impact: Fixed vs Adjustable Alignment
Fixed alignment offers consistent performance by maintaining a stable configuration that reduces latency and minimizes overhead during operation. Adjustable alignment provides flexibility to optimize system efficiency in varying conditions but may introduce slight delays due to real-time recalibration processes. Choosing between fixed and adjustable alignment depends on the specific performance demands and the need for adaptability in the operational environment.
Cost Comparison: Fixed vs Adjustable Alignment
Fixed alignment systems generally incur lower initial costs due to their simpler design and reduced component requirements compared to adjustable alignment systems. Adjustable alignment, however, involves higher upfront investment but offers long-term cost savings through increased precision and reduced maintenance expenses. Cost comparison reveals fixed alignment is more budget-friendly initially, while adjustable alignment provides better value in applications demanding frequent adjustments or high accuracy.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Fixed alignment offers low maintenance due to its permanent setting, reducing the need for frequent adjustments but may cause uneven tire wear if initial alignment is imperfect. Adjustable alignment allows for periodic realignment, enhancing longevity by correcting deviations caused by road conditions or mechanical wear, thereby extending tire and suspension life. Proper maintenance of adjustable alignment ensures optimal vehicle handling and prevents premature component damage, improving overall durability.
Choosing the Best Alignment Type for Your Vehicle
Fixed alignment offers a stable, factory-set configuration ideal for standard vehicles with predictable driving conditions, ensuring consistent tire wear and handling. Adjustable alignment provides flexibility to fine-tune camber, caster, and toe angles, making it suitable for performance vehicles or those frequently encountering varied terrains. Selecting the best alignment type depends on your vehicle's usage, suspension design, and the level of customization required for optimal tire performance and driving safety.
Fixed Alignment vs Adjustable Alignment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com