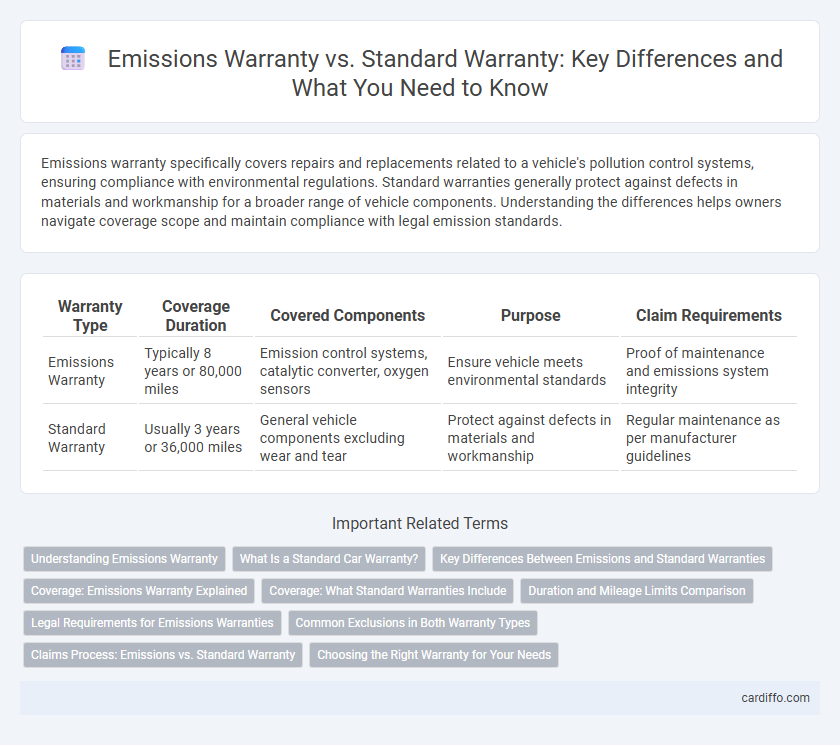
Emissions warranty specifically covers repairs and replacements related to a vehicle's pollution control systems, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Standard warranties generally protect against defects in materials and workmanship for a broader range of vehicle components. Understanding the differences helps owners navigate coverage scope and maintain compliance with legal emission standards.
Table of Comparison
| Warranty Type | Coverage Duration | Covered Components | Purpose | Claim Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emissions Warranty | Typically 8 years or 80,000 miles | Emission control systems, catalytic converter, oxygen sensors | Ensure vehicle meets environmental standards | Proof of maintenance and emissions system integrity |
| Standard Warranty | Usually 3 years or 36,000 miles | General vehicle components excluding wear and tear | Protect against defects in materials and workmanship | Regular maintenance as per manufacturer guidelines |
Understanding Emissions Warranty
Emissions Warranty specifically covers components related to a vehicle's emissions control system, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and onboard diagnostics, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. This warranty typically lasts longer than the standard warranty, often up to eight years or 80,000 miles, reflecting stricter government mandates. Understanding the Emissions Warranty is crucial for vehicle owners to maintain emissions compliance and avoid costly repairs related to pollution control equipment.
What Is a Standard Car Warranty?
A standard car warranty typically covers essential vehicle components such as the engine, transmission, and drivetrain against defects in materials or workmanship for a specified period, usually three years or 36,000 miles. Unlike an emissions warranty that specifically guarantees the performance and compliance of the vehicle's emissions control system, the standard warranty provides broader protection for general mechanical failures. Buyers should review the standard warranty terms carefully, as coverage limits, exclusions, and duration can vary significantly between manufacturers.
Key Differences Between Emissions and Standard Warranties
Emissions warranties specifically cover components related to a vehicle's pollution control system, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, while standard warranties provide broader protection against defects in materials and workmanship for general parts. Emissions warranties often have longer coverage periods mandated by government regulations, typically spanning 8 years or 80,000 miles for critical components like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors. Standard warranties usually cover a shorter timeframe, such as 3 years or 36,000 miles, focusing on overall vehicle reliability and performance rather than emission-related parts.
Coverage: Emissions Warranty Explained
Emissions warranties specifically cover the repair or replacement of components related to a vehicle's emissions control system, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control systems, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Standard warranties typically cover general vehicle components like the engine, transmission, and electrical systems, but may exclude emissions-related parts unless explicitly stated. Emissions warranties often have longer durations mandated by regulatory agencies, offering extended protection against costly repairs needed to maintain low emissions and pass state inspections.
Coverage: What Standard Warranties Include
Standard warranties typically cover defects in materials and workmanship for a specified period or mileage, including repairs and replacements for key vehicle components such as the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. These warranties often exclude wear-and-tear parts like brake pads and tires, focusing instead on mechanical reliability and manufacturing faults. Emissions warranties, by contrast, specifically cover components related to the vehicle's emissions control system, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Duration and Mileage Limits Comparison
Emissions warranties typically offer coverage ranging from 2 to 8 years or 24,000 to 80,000 miles, focusing specifically on components that affect vehicle emissions compliance. Standard warranties generally provide broader protection, often lasting 3 to 5 years or 36,000 to 60,000 miles, covering most vehicle parts and labor. The extended duration and mileage limits of emissions warranties address regulatory requirements to ensure long-term environmental standards are met.
Legal Requirements for Emissions Warranties
Emissions warranties are mandated by environmental laws such as the Clean Air Act, requiring manufacturers to cover repairs related to emissions control components for a longer period than standard warranties. Standard warranties typically protect against general defects in materials and workmanship for a limited time or mileage, often shorter and less specific than emissions coverage. Legal requirements for emissions warranties ensure compliance with federal and state regulations, safeguarding air quality and consumer rights over extended durations.
Common Exclusions in Both Warranty Types
Emissions warranties typically exclude coverage for damage caused by improper maintenance, use of incorrect fuel, or unauthorized modifications to the emission control system. Standard warranties often exclude wear-and-tear items such as brake pads, tires, and battery replacements. Both warranty types generally do not cover damages resulting from accidents, neglect, or environmental factors like flooding or corrosion.
Claims Process: Emissions vs. Standard Warranty
The claims process for emissions warranty typically involves stringent verification of emission-related components, requiring detailed diagnostic data and compliance with environmental standards, whereas the standard warranty claims focus broadly on general mechanical and electrical repairs. Emissions warranty claims must adhere to federally mandated guidelines, often necessitating manufacturer or regulatory approval before repairs or replacements are authorized. Standard warranty claims usually undergo a streamlined evaluation based on vehicle service records and warranty terms without the additional regulatory scrutiny seen in emissions-related issues.
Choosing the Right Warranty for Your Needs
Emissions warranties specifically cover defects affecting a vehicle's emission control system, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations for up to 8 years or 80,000 miles, while standard warranties generally cover broader repairs and parts for a shorter period, often 3 years or 36,000 miles. Choosing the right warranty depends on factors such as your vehicle's age, driving habits, and the importance of reducing environmental impact versus overall mechanical coverage. Prioritizing an emissions warranty can save costly repairs on emission components and avoid regulatory penalties, whereas a standard warranty offers more comprehensive protection for general vehicle issues.
Emissions Warranty vs Standard Warranty Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com