Interoperable toll systems enable seamless payments across multiple regions and toll operators, enhancing convenience for drivers and reducing administrative costs. Proprietary toll systems, restricted to specific networks, often require multiple accounts and devices, leading to inefficiencies and higher user frustration. Transitioning to interoperable solutions drives greater accessibility, streamlined operations, and improved traffic flow management.
Table of Comparison
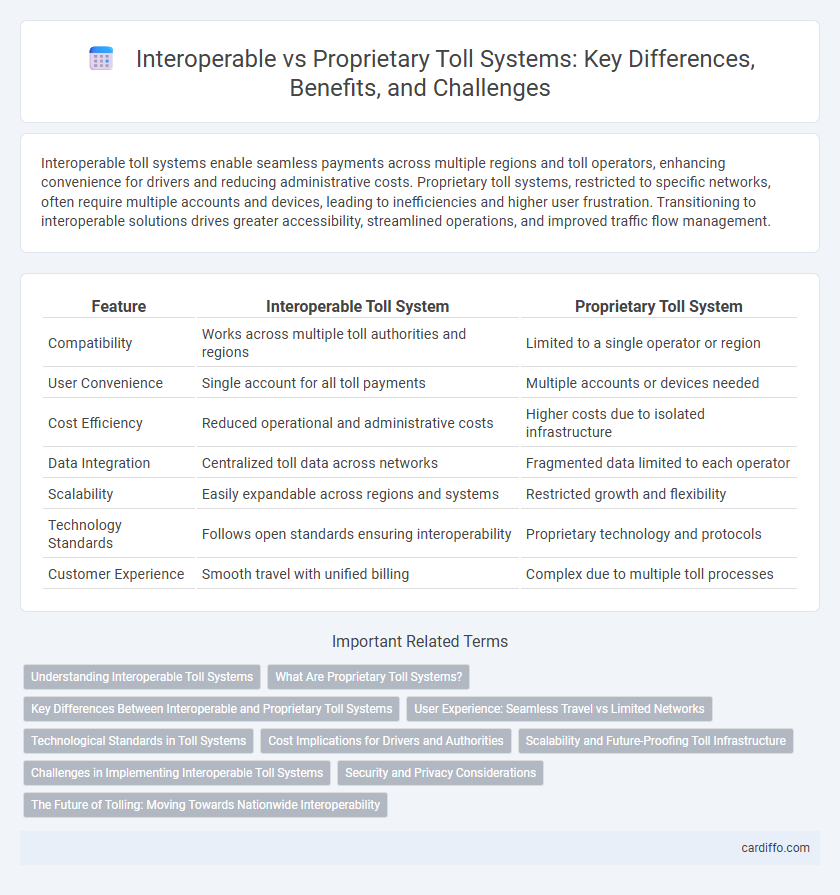
| Feature | Interoperable Toll System | Proprietary Toll System |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Works across multiple toll authorities and regions | Limited to a single operator or region |
| User Convenience | Single account for all toll payments | Multiple accounts or devices needed |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced operational and administrative costs | Higher costs due to isolated infrastructure |
| Data Integration | Centralized toll data across networks | Fragmented data limited to each operator |
| Scalability | Easily expandable across regions and systems | Restricted growth and flexibility |
| Technology Standards | Follows open standards ensuring interoperability | Proprietary technology and protocols |
| Customer Experience | Smooth travel with unified billing | Complex due to multiple toll processes |
Understanding Interoperable Toll Systems
Interoperable toll systems enable seamless vehicle toll payments across multiple jurisdictions by integrating diverse toll technologies and operators into a standardized platform. These systems utilize shared databases and unified communication protocols to ensure real-time transaction processing and accurate billing. Interoperability reduces administrative costs, enhances user convenience, and supports efficient traffic flow across interconnected toll networks.
What Are Proprietary Toll Systems?
Proprietary toll systems are closed-loop networks operated by a single agency or company, requiring users to have specific transponders or accounts tied exclusively to that operator. These systems limit interoperability, meaning toll payments and access are restricted to that vendor's infrastructure. This contrasts with interoperable toll systems, which allow seamless toll transactions across multiple regions and providers using standardized technology.
Key Differences Between Interoperable and Proprietary Toll Systems
Interoperable toll systems enable seamless payment across multiple toll facilities by using standardized technology and protocols, enhancing user convenience and reducing transaction complexities. Proprietary toll systems rely on vendor-specific hardware and software, limiting usage to single networks and often requiring multiple accounts or transponders. The key difference lies in interoperability scope, where interoperable systems support multi-agency collaboration and unified billing, while proprietary systems focus on localized control and restricted access.
User Experience: Seamless Travel vs Limited Networks
Interoperable toll systems enhance user experience by enabling seamless travel across multiple regions with a single payment method, reducing the need for multiple transponders or accounts. Proprietary toll systems often limit users to specific networks, causing inconvenience and delays due to incompatible payment methods and frequent stops. The broader coverage and simplified billing in interoperable systems significantly improve travel efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Technological Standards in Toll Systems
Interoperable toll systems adhere to international technological standards such as ISO 12855 and DSRC protocols, enabling seamless communication across diverse tolling infrastructures and enhancing cross-border travel efficiency. Proprietary toll systems rely on exclusive technologies and protocols, limiting compatibility and necessitating multiple devices or accounts for different toll operators. Standardized technologies promote data exchange, system integration, and broader acceptance, crucial for unified electronic toll collection on regional and global scales.
Cost Implications for Drivers and Authorities
Interoperable toll systems reduce costs for drivers by enabling seamless payment across multiple regions without the need for multiple transponders or accounts, lowering administrative expenses and enhancing user convenience. Authorities benefit from cost savings through streamlined operations, reduced infrastructure duplication, and simplified maintenance compared to proprietary systems. Proprietary toll systems often impose higher costs on both drivers and authorities due to limited compatibility, increased transaction fees, and the necessity for separate management platforms in each jurisdiction.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Toll Infrastructure
Interoperable toll systems enhance scalability by enabling seamless integration across diverse regional networks, facilitating nationwide coverage without infrastructure redundancies. Proprietary toll systems often limit expansion due to vendor-specific technologies that hinder compatibility and increase costs for upgrades. Emphasizing open standards ensures future-proofing toll infrastructure by supporting emerging technologies such as connected vehicles and smart city applications.
Challenges in Implementing Interoperable Toll Systems
Implementing interoperable toll systems faces significant challenges such as harmonizing technology standards and ensuring secure data exchange across diverse jurisdictions. Integration complexities arise from varying regional regulations, differing payment methods, and legacy infrastructure compatibility. Addressing concerns about data privacy, system reliability, and cross-border financial settlements remains critical for widespread adoption.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Interoperable toll systems enhance security by enabling standardized encryption protocols and secure data exchange across multiple jurisdictions, reducing vulnerabilities associated with data breaches. Proprietary toll systems, however, may concentrate security controls within a single vendor, which can limit transparency and increase risks of unauthorized access due to isolated security frameworks. Privacy considerations in interoperable systems benefit from uniform data protection policies, while proprietary systems often lack consistent privacy safeguards, increasing potential misuse of sensitive traveler information.
The Future of Tolling: Moving Towards Nationwide Interoperability
Nationwide interoperability in toll systems enables seamless vehicle passage across state lines without multiple transponders or accounts, enhancing user convenience and reducing congestion. Interoperable toll systems rely on standardized technology and data-sharing protocols, fostering collaboration among agencies and private operators. Proprietary toll systems, while offering customized solutions, often limit scalability and increase operational complexities compared to unified, nationwide frameworks designed for efficient revenue collection and improved traffic management.
Interoperable Toll System vs Proprietary Toll System Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com