Single-axle tolls charge vehicles based on a single set of wheels, making them ideal for smaller cars and motorcycles, often resulting in lower fees. Multi-axle tolls apply to larger vehicles like trucks and buses, calculating charges according to the number of axles, which reflects the greater wear and tear these vehicles cause to the road infrastructure. Choosing the correct toll category ensures accurate toll payments and helps maintain fair funding for road maintenance.
Table of Comparison
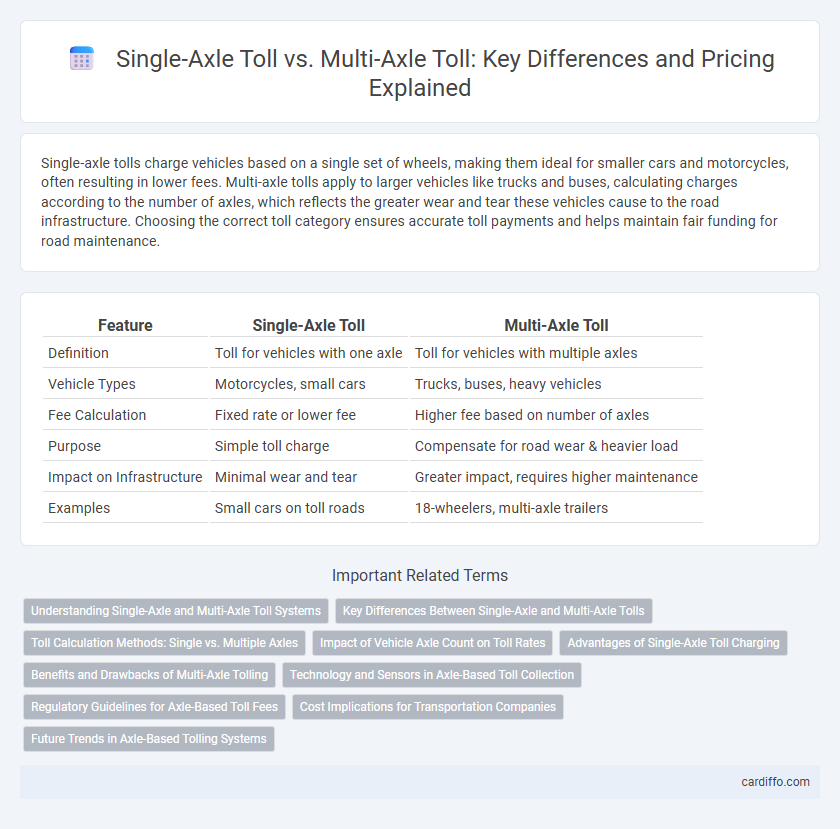
| Feature | Single-Axle Toll | Multi-Axle Toll |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toll for vehicles with one axle | Toll for vehicles with multiple axles |
| Vehicle Types | Motorcycles, small cars | Trucks, buses, heavy vehicles |
| Fee Calculation | Fixed rate or lower fee | Higher fee based on number of axles |
| Purpose | Simple toll charge | Compensate for road wear & heavier load |
| Impact on Infrastructure | Minimal wear and tear | Greater impact, requires higher maintenance |
| Examples | Small cars on toll roads | 18-wheelers, multi-axle trailers |
Understanding Single-Axle and Multi-Axle Toll Systems
Single-axle toll systems charge vehicles based on the toll rate applicable to vehicles with one axle, typically affecting motorcycles, cars, and light trucks, whereas multi-axle toll systems apply higher rates reflecting the increased wear and road usage caused by vehicles with multiple axles, such as buses and heavy trucks. Toll operators use axle count sensors and vehicle classification technology to differentiate between single-axle and multi-axle vehicles, ensuring accurate toll calculation and fair revenue distribution. Understanding these systems helps in optimizing traffic flow, reducing road damage costs, and enhancing infrastructure funding efficiency.
Key Differences Between Single-Axle and Multi-Axle Tolls
Single-axle tolls are typically lower due to the reduced weight and wear on infrastructure compared to multi-axle tolls, which accommodate heavier and larger vehicles such as trucks and buses. Multi-axle toll rates increase progressively with the number of axles, reflecting the greater road damage and maintenance costs caused by these vehicles. Differentiating tolls by axle count ensures fair pricing and efficient road usage, optimizing revenue for transportation authorities.
Toll Calculation Methods: Single vs. Multiple Axles
Toll calculation for single-axle vehicles typically involves a flat rate based on axle count, simplifying cost assessment and minimizing processing time. Multi-axle tolls are calculated by summing individual axle charges, often adjusted for vehicle weight and type, reflecting increased road wear and maintenance costs. Advanced tolling systems employ automated axle detection technologies to accurately determine toll fees and ensure fair pricing for both single and multi-axle vehicles.
Impact of Vehicle Axle Count on Toll Rates
Vehicle axle count significantly influences toll rates, with single-axle vehicles generally paying lower fees compared to multi-axle trucks due to reduced road wear and infrastructure strain. Multi-axle tolls are structured to reflect increased maintenance costs and traffic impact caused by heavier, longer vehicles. Toll authorities use axle-based pricing models to promote fair cost distribution and incentivize efficient vehicle design for highway sustainability.
Advantages of Single-Axle Toll Charging
Single-axle toll charging offers cost efficiency by reducing toll fees for vehicles with fewer axles, benefiting drivers of motorcycles, small trucks, and passenger cars. This method simplifies toll calculation and decreases congestion at toll plazas by expediting the payment process for lighter vehicles. Implementing single-axle toll rates encourages road usage equity and supports environmental sustainability through incentivizing smaller, less impactful vehicles.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Multi-Axle Tolling
Multi-axle tolling offers precise revenue collection by charging vehicles based on the number of axles, ensuring heavier vehicles pay proportionally for road wear. This system promotes fairness and can reduce underpayment risks common in single-axle tolling, but it requires more sophisticated technology and infrastructure, increasing operational costs. Maintenance and calibration complexities may lead to occasional inaccuracies, impacting both efficiency and user trust.
Technology and Sensors in Axle-Based Toll Collection
Axle-based toll collection systems utilize advanced sensors such as inductive loops, piezoelectric cables, and laser scanners to accurately detect single-axle and multi-axle vehicles. Multi-axle toll technology incorporates sophisticated image recognition and infrared sensors to differentiate axle counts, ensuring precise toll classification and automated fee calculation. Integration with GPS and real-time data analytics enhances system efficiency by enabling dynamic toll pricing based on axle configuration and traffic conditions.
Regulatory Guidelines for Axle-Based Toll Fees
Regulatory guidelines for axle-based toll fees vary by jurisdiction, typically imposing higher charges on multi-axle vehicles due to their increased road wear and environmental impact. Single-axle toll rates are often standardized and lower, reflecting their lighter load and reduced infrastructure strain. Compliance with these regulations ensures equitable road maintenance funding and supports traffic decongestion strategies.
Cost Implications for Transportation Companies
Single-axle tolls are generally lower than multi-axle tolls, making them more cost-effective for transportation companies operating lighter vehicles or smaller loads. Multi-axle toll fees increase significantly with the number of axles, directly impacting the expenses of heavy-duty trucks and freight carriers. Efficient route planning and axle load management can reduce toll expenses, optimizing operational costs for logistics and transportation businesses.
Future Trends in Axle-Based Tolling Systems
Future trends in axle-based tolling systems emphasize advanced sensor technologies and AI-powered analytics to differentiate single-axle tolls from multi-axle tolls with greater accuracy. Integration with smart infrastructure and real-time data processing enables dynamic pricing models that incentivize efficient vehicle usage and reduce congestion. Enhanced interoperability across regions and automated enforcement mechanisms are set to streamline toll collection, improving revenue management and traffic flow.
Single-axle toll vs Multi-axle toll Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com