Pulling codes involves extracting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle's onboard computer to identify known issues quickly. Live data analysis monitors real-time sensor data and system performance, offering deeper insights into intermittent problems that codes alone may not reveal. Combining both methods enhances accuracy in diagnosing complex vehicle malfunctions.
Table of Comparison
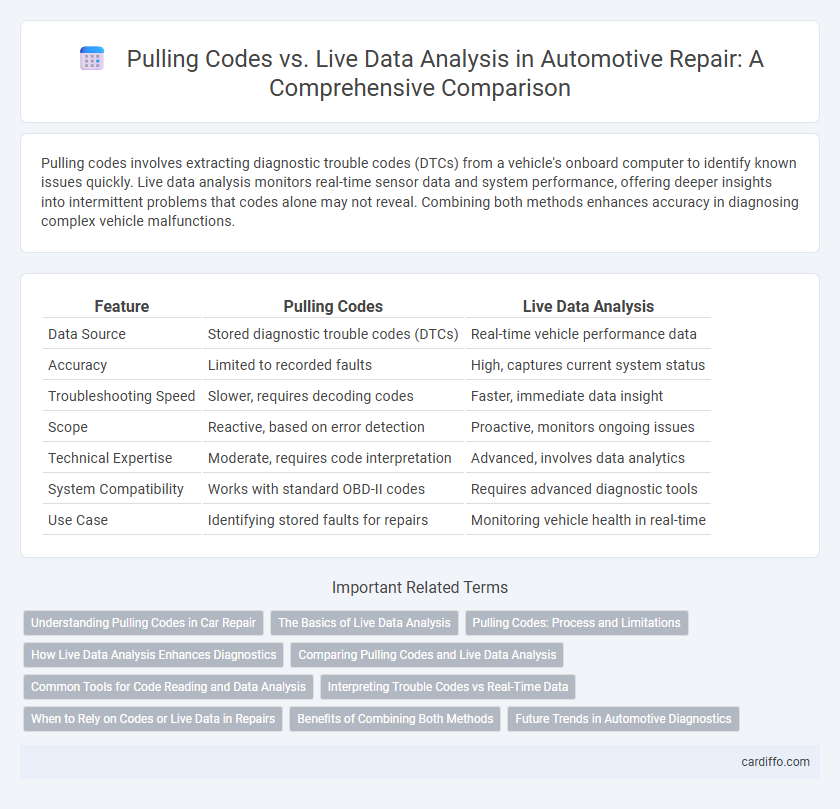
| Feature | Pulling Codes | Live Data Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) | Real-time vehicle performance data |
| Accuracy | Limited to recorded faults | High, captures current system status |
| Troubleshooting Speed | Slower, requires decoding codes | Faster, immediate data insight |
| Scope | Reactive, based on error detection | Proactive, monitors ongoing issues |
| Technical Expertise | Moderate, requires code interpretation | Advanced, involves data analytics |
| System Compatibility | Works with standard OBD-II codes | Requires advanced diagnostic tools |
| Use Case | Identifying stored faults for repairs | Monitoring vehicle health in real-time |
Understanding Pulling Codes in Car Repair
Pulling codes in car repair involves retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle's onboard computer system to identify specific malfunctions. This method provides a clear starting point for technicians by pinpointing areas needing attention, often using an OBD-II scanner. While pulling codes offers valuable insights, it captures only stored error information, making it crucial to complement this approach with live data analysis for comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
The Basics of Live Data Analysis
Live data analysis provides real-time insights by continuously monitoring sensor outputs and system parameters during vehicle operation. Unlike pulling codes, which only identifies stored fault codes after a malfunction occurs, live data allows technicians to observe dynamic changes and pinpoint issues more accurately. Accessing parameters such as RPM, temperature, and sensor voltages helps in diagnosing intermittent problems and verifying component functionality on the spot.
Pulling Codes: Process and Limitations
Pulling codes involves retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in a vehicle's onboard computer to identify issues with various systems. This process provides a snapshot of faults but may not capture intermittent problems or real-time fluctuations affecting performance. Limitations include delayed fault detection, lack of detailed sensor data, and potential oversight of emerging issues without continuous monitoring.
How Live Data Analysis Enhances Diagnostics
Live data analysis enhances diagnostics by providing real-time information on vehicle sensor readings and system performance, enabling technicians to identify intermittent faults that static code pulling may miss. Unlike pulling diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) alone, live data offers insight into engine parameters, fuel delivery, and emission controls as they operate, improving accuracy and repair efficiency. This dynamic approach reduces guesswork, accelerates problem-solving, and ensures precise troubleshooting in complex automotive systems.
Comparing Pulling Codes and Live Data Analysis
Pulling codes involves retrieving stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from a vehicle's onboard computer to identify specific issues, providing a snapshot of past and present faults. Live data analysis offers real-time monitoring of sensor outputs and system operations, enabling technicians to detect intermittent problems and assess vehicle performance dynamically. Combining code retrieval with live data streaming enhances diagnostic accuracy and repair efficiency in automotive maintenance.
Common Tools for Code Reading and Data Analysis
Common tools for pulling codes include OBD-II scanners such as Autel MaxiCOM and BlueDriver, which retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to identify vehicle malfunctions. For live data analysis, tools like Torque Pro and ScanGauge provide real-time sensor readings and performance metrics, enabling dynamic monitoring of engine parameters. Utilizing both code readers and live data analyzers enhances diagnostic accuracy and accelerates repair workflows.
Interpreting Trouble Codes vs Real-Time Data
Interpreting trouble codes provides a snapshot of stored fault data, highlighting specific error conditions detected by a vehicle's onboard diagnostics. Real-time data analysis offers continuous monitoring of sensor outputs and system parameters, enabling a dynamic assessment of vehicle performance and immediate identification of irregularities. Combining both methods enhances diagnostic accuracy by correlating historical fault codes with current operational behavior.
When to Rely on Codes or Live Data in Repairs
Rely on pulling diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for initial fault identification as they provide standardized error information from the vehicle's control modules. Use live data analysis to verify sensor readings, monitor real-time system performance, and pinpoint intermittent or complex issues not fully captured by stored codes. Combining both methods enhances repair accuracy and efficiency by ensuring faults are both detected and thoroughly understood.
Benefits of Combining Both Methods
Combining pulling codes with live data analysis enhances diagnostic accuracy by providing a comprehensive view of vehicle performance and fault conditions. Pulling codes offers precise identification of stored trouble codes, while live data analysis reveals real-time sensor readings and system behavior for dynamic issue detection. This integrated approach reduces repair time, prevents misdiagnosis, and improves overall vehicle reliability by addressing both historical faults and current operational anomalies.
Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics
Future trends in automotive diagnostics emphasize the integration of pulling codes with live data analysis to provide a more comprehensive understanding of vehicle performance. Advanced diagnostic tools leverage real-time sensor data alongside trouble codes to identify intermittent and complex issues that static code retrieval alone may miss. Machine learning algorithms will enhance predictive maintenance by analyzing live data streams, reducing repair times and improving overall vehicle reliability.
Pulling codes vs live data analysis Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com