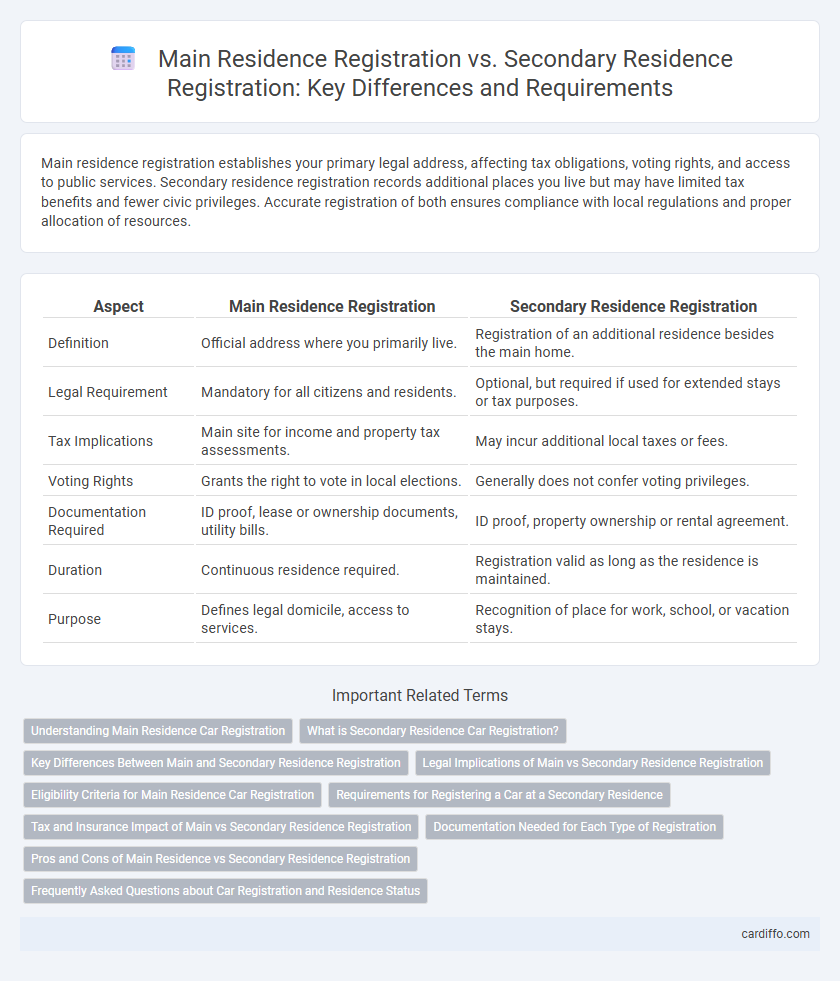
Main residence registration establishes your primary legal address, affecting tax obligations, voting rights, and access to public services. Secondary residence registration records additional places you live but may have limited tax benefits and fewer civic privileges. Accurate registration of both ensures compliance with local regulations and proper allocation of resources.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Main Residence Registration | Secondary Residence Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official address where you primarily live. | Registration of an additional residence besides the main home. |
| Legal Requirement | Mandatory for all citizens and residents. | Optional, but required if used for extended stays or tax purposes. |
| Tax Implications | Main site for income and property tax assessments. | May incur additional local taxes or fees. |
| Voting Rights | Grants the right to vote in local elections. | Generally does not confer voting privileges. |
| Documentation Required | ID proof, lease or ownership documents, utility bills. | ID proof, property ownership or rental agreement. |
| Duration | Continuous residence required. | Registration valid as long as the residence is maintained. |
| Purpose | Defines legal domicile, access to services. | Recognition of place for work, school, or vacation stays. |
Understanding Main Residence Car Registration
Main residence car registration requires the vehicle to be registered at the primary address where the owner lives most frequently, aligning with local DMV regulations to ensure accurate tax and insurance assessments. Unlike secondary residence registration, which applies when a vehicle is primarily used at a less frequent or temporary address, main residence registration affects eligibility for certain exemptions and regional compliance standards. Properly registering at the main residence helps maintain legal accountability and supports correct allocation of jurisdictional fees and services.
What is Secondary Residence Car Registration?
Secondary residence car registration refers to the official process of registering a vehicle at an address other than the owner's primary home, typically used for vehicles kept at vacation homes or temporary residences. It ensures legal compliance for using and parking vehicles at secondary locations, often involving different local regulations and tax implications compared to main residence registration. This type of registration helps authorities track vehicle whereabouts, enforce local traffic laws, and manage insurance coverage tied to the secondary address.
Key Differences Between Main and Secondary Residence Registration
Main residence registration typically reflects the primary dwelling where a person spends most of their time and is often tied to voting rights, tax obligations, and access to local services. Secondary residence registration applies to additional properties used occasionally, usually resulting in different tax rates and fewer civic benefits. Key differences include mandatory registration requirements, implications for municipal fees, and eligibility for local public services.
Legal Implications of Main vs Secondary Residence Registration
Main residence registration establishes the primary domicile for tax obligations, voting rights, and access to public services, impacting local taxation rates and eligibility for social benefits. Secondary residence registration typically involves additional property and municipal taxes, with limited voter registration rights and fewer local benefits due to its non-primary status. Legal consequences include penalties for failure to correctly register the main residence, affecting compliance with residency requirements and influencing inheritance and property regulations.
Eligibility Criteria for Main Residence Car Registration
Eligibility criteria for main residence car registration require the vehicle owner to have their primary and legal address within the registration jurisdiction, supported by official documents such as utility bills or lease agreements. The main residence registration mandates that the car is primarily used and garaged at this address, ensuring alignment with local tax and insurance regulations. Secondary residence addresses typically do not qualify for main residence car registration but may allow for supplementary vehicle documentation or secondary registration types.
Requirements for Registering a Car at a Secondary Residence
Registering a car at a secondary residence requires proof of valid residency documents such as a secondary residence lease agreement or utility bills linked to the secondary address. Vehicle owners must also present identification, a valid insurance policy, and the car's existing registration certificate. Compliance with local regulations, including potential additional fees or restrictions associated with secondary residences, is essential for successful registration.
Tax and Insurance Impact of Main vs Secondary Residence Registration
Registering a main residence typically results in lower property tax rates and eligibility for primary residence tax benefits, while secondary residence registration often incurs higher taxes and reduced insurance coverage options. Insurance premiums for a main residence are generally more favorable due to its primary occupancy status, whereas secondary homes may face increased rates and limited policy benefits. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize financial obligations and insurance protections based on residence classification.
Documentation Needed for Each Type of Registration
Main residence registration requires proof of identity, a signed lease or property deed, and a recent utility bill confirming occupancy, with some jurisdictions demanding additional documents such as a certificate of residence. Secondary residence registration often necessitates similar identification documents, proof of ownership or rental agreement, but may also require authorization from the primary residence municipality and justification for the secondary residence. Both types of registration typically involve submitting official forms to local government offices, where accuracy and completeness of documentation ensure smooth processing.
Pros and Cons of Main Residence vs Secondary Residence Registration
Main residence registration offers benefits like access to local healthcare, voting rights, and eligibility for social services, but it may involve higher tax liabilities compared to secondary residence registration. Secondary residence registration provides flexibility for individuals maintaining multiple homes and can reduce tax burdens, though it often limits access to public services and local political participation. Choosing between main and secondary residence registration depends on factors such as tax implications, service access, and personal residency priorities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Car Registration and Residence Status
Car registration requirements often differ based on whether the address listed is a main residence or a secondary residence, impacting legal eligibility and taxation. Registering a vehicle at a main residence typically requires proof of primary residency, such as utility bills or lease agreements, while secondary residence registration may involve additional documentation or restrictions. Questions frequently arise regarding insurance implications, registration fees, and residency verification for vehicles registered at multiple addresses.
Main Residence Registration vs Secondary Residence Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com