Registering an electric vehicle (EV) often involves different fees and incentives compared to gasoline vehicle registration due to environmental policies promoting cleaner energy. EV registration may include reduced fees or tax credits, while gasoline vehicles typically incur standard charges that reflect fuel consumption and emissions. Understanding these distinctions ensures compliance with local regulations and maximizes available benefits for electric vehicle owners.
Table of Comparison
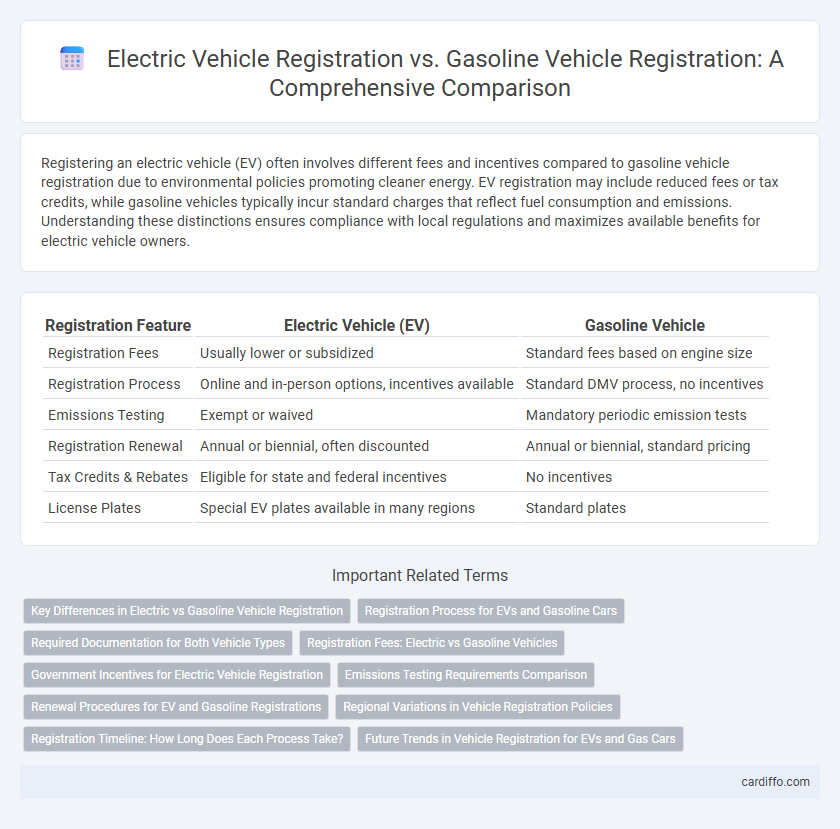
| Registration Feature | Electric Vehicle (EV) | Gasoline Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| Registration Fees | Usually lower or subsidized | Standard fees based on engine size |
| Registration Process | Online and in-person options, incentives available | Standard DMV process, no incentives |
| Emissions Testing | Exempt or waived | Mandatory periodic emission tests |
| Registration Renewal | Annual or biennial, often discounted | Annual or biennial, standard pricing |
| Tax Credits & Rebates | Eligible for state and federal incentives | No incentives |
| License Plates | Special EV plates available in many regions | Standard plates |
Key Differences in Electric vs Gasoline Vehicle Registration
Electric vehicle registration often requires documentation of battery capacity and may include eligibility for incentives or rebates, unlike gasoline vehicle registration which focuses primarily on engine displacement and emissions compliance. Registration fees for electric vehicles can be lower or subject to special surcharges to compensate for reduced fuel tax revenue. Additionally, electric vehicles might have specific registration procedures reflecting their environmental impact and state-level policy variations.
Registration Process for EVs and Gasoline Cars
Electric vehicle registration often requires submission of battery certification and proof of installation of a charging system, while gasoline vehicle registration primarily focuses on emissions testing and fuel system verification. EV registration may involve incentives or reduced fees depending on the region, contrasting with the standard procedures for internal combustion engine vehicles. Both processes mandate ownership verification, insurance documentation, and vehicle identification number (VIN) inspection to complete registration.
Required Documentation for Both Vehicle Types
Electric vehicle registration typically requires proof of vehicle purchase, a valid government-issued identification, and compliance with state-specific emissions or exemption certificates, whereas gasoline vehicle registration mandates documents such as proof of insurance, vehicle title, and emissions test results where applicable. Both vehicle types often require a completed application form and payment of registration fees, with electric vehicles sometimes needing additional documentation related to battery certification or tax credit eligibility. Ensuring accurate documentation submission streamlines the registration process for both electric and gasoline vehicles.
Registration Fees: Electric vs Gasoline Vehicles
Electric vehicle registration fees are often higher than those for gasoline vehicles due to state-imposed surcharges aimed at offsetting lost fuel tax revenue. Gasoline vehicle registration fees primarily depend on vehicle weight and age, while electric vehicles may incur flat fees or tiered charges based on battery capacity or range. These fee structures vary widely by state, with some states offering reduced or waived fees for electric vehicles to encourage adoption.
Government Incentives for Electric Vehicle Registration
Electric vehicle registration often benefits from government incentives such as tax credits, reduced registration fees, and access to HOV lanes, encouraging eco-friendly transportation. These incentives contrast with gasoline vehicle registration, which typically lacks such benefits due to higher emissions and environmental impact. State and federal programs prioritize electric vehicle adoption by providing financial and regulatory advantages during the registration process.
Emissions Testing Requirements Comparison
Electric vehicle registration typically excludes emissions testing due to their zero tailpipe emissions, contrasting with gasoline vehicle registration that mandates regular emissions tests to monitor pollutants like CO2, NOx, and particulate matter. Gasoline vehicles often require biennial or annual emissions inspections to comply with state or regional environmental regulations aimed at reducing air pollution. This fundamental difference reflects regulatory efforts to promote cleaner transportation and lower urban smog levels through stricter emissions compliance for combustion engines.
Renewal Procedures for EV and Gasoline Registrations
Electric vehicle registration renewals often require submission of battery health reports or proof of eligibility for state incentives, reflecting eco-friendly policies. Gasoline vehicle registration renewals typically involve emissions testing and payment of standard fees based on vehicle weight or engine size. Both types demand timely renewal to avoid penalties, but EV renewals may include specific documentation to maintain incentive eligibility.
Regional Variations in Vehicle Registration Policies
Electric vehicle registration policies differ significantly across regions, with some areas offering incentives such as reduced fees or expedited processing compared to gasoline vehicle registrations. States like California implement stricter regulations and additional documentation requirements for gasoline vehicles to encourage electric vehicle adoption. Regional variations also impact the duration of registration validity and emission testing mandates, reflecting localized environmental priorities.
Registration Timeline: How Long Does Each Process Take?
Electric vehicle registration typically takes 5 to 10 business days due to additional inspections and documentation related to battery and emissions compliance. Gasoline vehicle registration is usually faster, often completed within 3 to 7 business days, as it requires standard emissions testing and less specialized paperwork. Delays in electric vehicle registration can occur in states without established EV infrastructure, impacting the overall timeline.
Future Trends in Vehicle Registration for EVs and Gas Cars
Electric vehicle registration is expected to surge due to government incentives, expanding charging infrastructure, and stricter emissions regulations accelerating the shift away from gasoline vehicles. Advances in digital vehicle identification and blockchain technology promise to streamline EV registration processes, enhancing data security and transparency compared to traditional gas car registration systems. Market analysis forecasts EV registrations will outpace gasoline vehicles by 2030, driven by consumer demand for sustainable transportation and policy mandates targeting carbon neutrality.
Electric Vehicle Registration vs Gasoline Vehicle Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com