Fixed Interval Maintenance follows a predetermined schedule regardless of equipment condition, ensuring routine inspections and part replacements to prevent unexpected failures. Condition-Based Maintenance relies on real-time data and sensor monitoring to perform maintenance only when specific indicators show signs of wear or malfunction. This approach optimizes resource use, reduces downtime, and extends equipment lifespan by addressing issues precisely when needed.
Table of Comparison
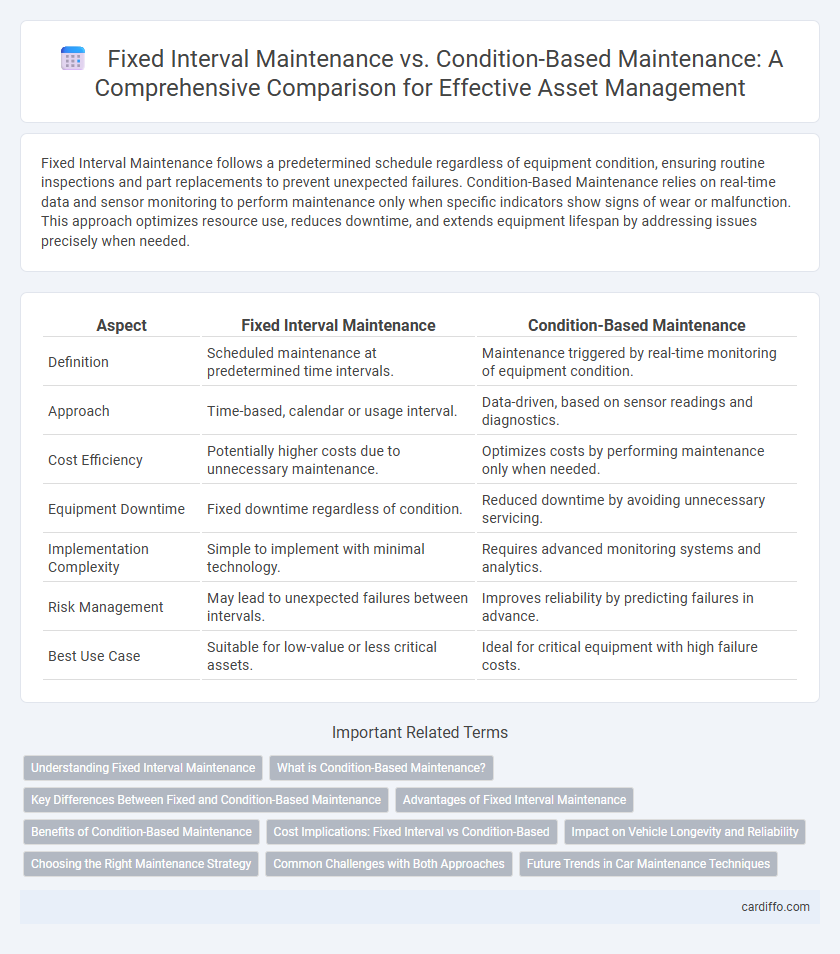
| Aspect | Fixed Interval Maintenance | Condition-Based Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance at predetermined time intervals. | Maintenance triggered by real-time monitoring of equipment condition. |
| Approach | Time-based, calendar or usage interval. | Data-driven, based on sensor readings and diagnostics. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher costs due to unnecessary maintenance. | Optimizes costs by performing maintenance only when needed. |
| Equipment Downtime | Fixed downtime regardless of condition. | Reduced downtime by avoiding unnecessary servicing. |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple to implement with minimal technology. | Requires advanced monitoring systems and analytics. |
| Risk Management | May lead to unexpected failures between intervals. | Improves reliability by predicting failures in advance. |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for low-value or less critical assets. | Ideal for critical equipment with high failure costs. |
Understanding Fixed Interval Maintenance
Fixed Interval Maintenance involves scheduling maintenance activities at predetermined time intervals regardless of equipment condition, helping organizations plan resources and minimize unexpected failures. This approach relies on historical data and manufacturer recommendations to define the maintenance frequency, ensuring consistent upkeep. While it simplifies maintenance management, it may lead to unnecessary tasks or overlooked wear if equipment conditions vary significantly.
What is Condition-Based Maintenance?
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) monitors equipment performance and health in real-time using sensors and data analytics to predict failures before they occur. This approach reduces unnecessary maintenance activities by only addressing issues when specific indicators reveal deterioration or imminent failure. CBM enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime by enabling targeted interventions based on actual equipment condition.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Condition-Based Maintenance
Fixed Interval Maintenance schedules routine tasks at predetermined time intervals regardless of equipment condition, ensuring consistent upkeep but potentially leading to unnecessary servicing. Condition-Based Maintenance relies on real-time data and sensor inputs to perform maintenance only when specific indicators signify wear or failure risk, optimizing resource use and reducing downtime. The key difference lies in Fixed Interval's time-driven approach versus Condition-Based's data-driven strategy, which enhances precision and cost-effectiveness in maintenance planning.
Advantages of Fixed Interval Maintenance
Fixed Interval Maintenance offers predictable scheduling that simplifies resource allocation and minimizes downtime by performing maintenance at regular, predefined intervals. This approach reduces the risk of unexpected failures by maintaining equipment before wear reaches critical levels, ensuring consistent operational reliability. Fixed Interval Maintenance also streamlines record-keeping and compliance adherence by providing structured maintenance logs aligned with manufacturer recommendations.
Benefits of Condition-Based Maintenance
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) enhances equipment reliability by continuously monitoring real-time data using sensors, reducing unexpected failures. It optimizes maintenance schedules based on actual asset conditions, leading to decreased downtime and lower labor costs compared to Fixed Interval Maintenance. CBM also extends equipment lifespan by addressing issues before they escalate, improving overall operational efficiency.
Cost Implications: Fixed Interval vs Condition-Based
Fixed Interval Maintenance often incurs higher costs due to scheduled overhauls regardless of equipment condition, leading to unnecessary part replacements and labor expenses. Condition-Based Maintenance optimizes costs by performing repairs only when sensor data or performance metrics indicate deterioration, reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan. Analyzing equipment criticality and failure patterns helps determine the most cost-effective strategy between these maintenance approaches.
Impact on Vehicle Longevity and Reliability
Fixed interval maintenance ensures scheduled checks and replacements, reducing unexpected breakdowns and maintaining baseline vehicle reliability. Condition-based maintenance leverages real-time data from sensors to address issues only when necessary, significantly extending vehicle longevity by preventing excessive wear and avoiding premature parts replacement. Employing condition-based strategies enhances both reliability and lifespan by targeting maintenance precisely, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy
Selecting the optimal maintenance strategy involves evaluating equipment criticality, operational environment, and cost implications between Fixed Interval Maintenance (FIM) and Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM). FIM schedules maintenance at predetermined intervals regardless of equipment condition, ensuring regular upkeep but potentially leading to unnecessary downtime or resource use. CBM leverages real-time data and predictive analytics to perform maintenance only when indicators show declining performance or imminent failure, optimizing maintenance efficiency and reducing unplanned outages.
Common Challenges with Both Approaches
Fixed Interval Maintenance often results in unnecessary part replacements, leading to increased costs and potential downtime. Condition-Based Maintenance faces difficulties in accurately monitoring equipment health due to sensor malfunctions or data inconsistencies. Both approaches struggle with balancing maintenance frequency and operational efficiency, causing challenges in optimizing resource allocation and minimizing unexpected failures.
Future Trends in Car Maintenance Techniques
Future trends in car maintenance techniques emphasize a shift from fixed interval maintenance to advanced condition-based maintenance systems using IoT sensors and real-time data analytics. Predictive algorithms leverage engine performance metrics and wear indicators to optimize service schedules, reducing downtime and extending vehicle lifespan. Integration of AI-driven diagnostics enhances precision in detecting component failures before they occur, transforming traditional maintenance paradigms.
Fixed Interval Maintenance vs Condition-Based Maintenance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com