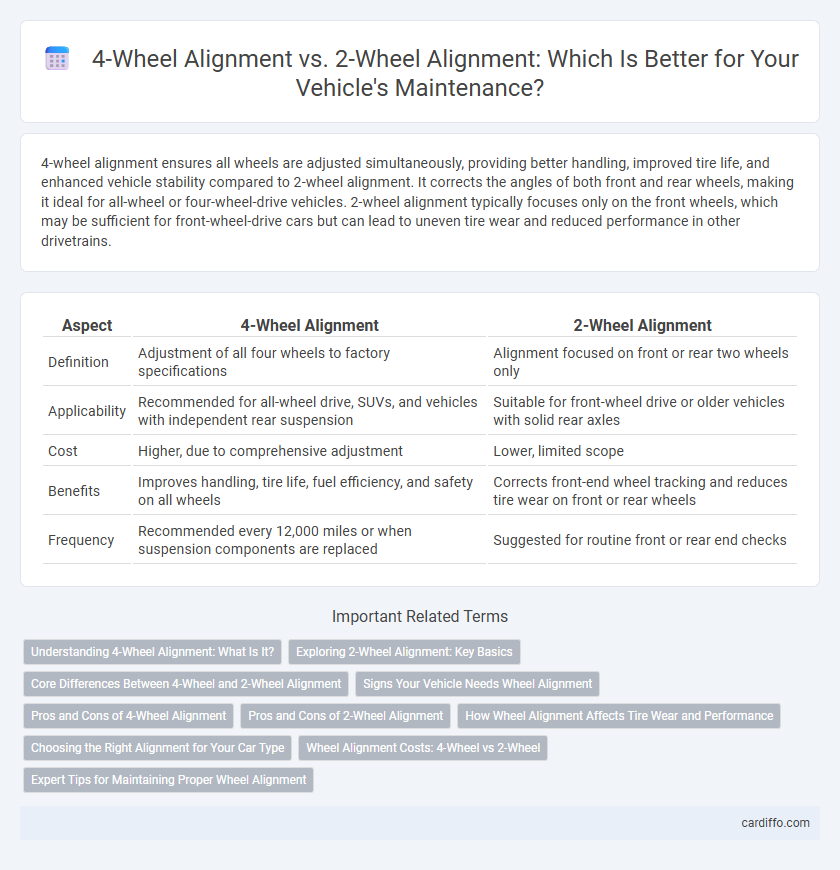
4-wheel alignment ensures all wheels are adjusted simultaneously, providing better handling, improved tire life, and enhanced vehicle stability compared to 2-wheel alignment. It corrects the angles of both front and rear wheels, making it ideal for all-wheel or four-wheel-drive vehicles. 2-wheel alignment typically focuses only on the front wheels, which may be sufficient for front-wheel-drive cars but can lead to uneven tire wear and reduced performance in other drivetrains.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | 4-Wheel Alignment | 2-Wheel Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjustment of all four wheels to factory specifications | Alignment focused on front or rear two wheels only |
| Applicability | Recommended for all-wheel drive, SUVs, and vehicles with independent rear suspension | Suitable for front-wheel drive or older vehicles with solid rear axles |
| Cost | Higher, due to comprehensive adjustment | Lower, limited scope |
| Benefits | Improves handling, tire life, fuel efficiency, and safety on all wheels | Corrects front-end wheel tracking and reduces tire wear on front or rear wheels |
| Frequency | Recommended every 12,000 miles or when suspension components are replaced | Suggested for routine front or rear end checks |
Understanding 4-Wheel Alignment: What Is It?
4-wheel alignment involves adjusting the angles of all four wheels to the manufacturer's specifications to ensure optimal handling, tire wear, and vehicle stability. It is essential for vehicles with independent rear suspension or all-wheel drive systems where both front and rear wheels need precise alignment. Compared to 2-wheel alignment, which only adjusts the front wheels, 4-wheel alignment addresses advanced suspension components and improves overall driving safety and performance.
Exploring 2-Wheel Alignment: Key Basics
2-wheel alignment primarily adjusts the front wheels to ensure proper steering and tire wear, making it suitable for vehicles with front-wheel drive or minimal alignment issues. This type of alignment focuses on camber and toe settings, enhancing handling and vehicle stability without the comprehensive adjustments required in 4-wheel alignment. Understanding these basics helps vehicle owners maintain optimal tire performance and extend tire lifespan efficiently.
Core Differences Between 4-Wheel and 2-Wheel Alignment
4-wheel alignment adjusts all four wheels simultaneously to ensure optimal handling, tire wear, and vehicle stability, targeting camber, caster, and toe angles on both front and rear axles. In contrast, 2-wheel alignment focuses only on the front wheels, primarily correcting steering wheel alignment and front tire angles without addressing rear wheel settings. The core difference lies in precision and vehicle dynamics: 4-wheel alignment is essential for all-wheel-drive vehicles and those with independent rear suspension, while 2-wheel alignment suits front-wheel-drive cars with solid rear axles.
Signs Your Vehicle Needs Wheel Alignment
Uneven tire wear, vehicle pulling to one side, and a crooked steering wheel are clear signs your vehicle needs wheel alignment, whether 4-wheel or 2-wheel. 4-wheel alignment adjusts all wheels and is ideal for modern cars with independent suspension, improving handling and tire life, while 2-wheel alignment focuses on the front wheels and suits older or front-wheel-drive vehicles. Regular checks can prevent premature tire damage and improve fuel efficiency by ensuring proper wheel angles.
Pros and Cons of 4-Wheel Alignment
4-wheel alignment provides precise calibration of all wheels, enhancing vehicle stability, tire lifespan, and fuel efficiency compared to 2-wheel alignment, which adjusts only the front wheels. This comprehensive approach corrects rear wheel angles, preventing uneven tire wear and improving handling performance, especially on all-wheel-drive and rear-wheel-drive vehicles. However, 4-wheel alignment tends to be more expensive and time-consuming than 2-wheel alignment, making it less cost-effective for front-wheel-drive vehicles with minimal rear wheel adjustment needs.
Pros and Cons of 2-Wheel Alignment
2-wheel alignment primarily adjusts the front wheels, offering a cost-effective option suitable for front-wheel drive vehicles and routine maintenance. Its limitations include neglecting the rear wheels, which can result in uneven tire wear and compromised vehicle handling if the rear alignment is off. For comprehensive suspension and steering performance, 4-wheel alignment is preferred, but 2-wheel alignment remains a practical choice for maintaining front-end precision.
How Wheel Alignment Affects Tire Wear and Performance
4-wheel alignment adjusts the angles of all four wheels for precise handling and even tire wear, enhancing overall vehicle stability and safety. 2-wheel alignment targets only the front wheels, which may result in uneven tire wear and reduced performance on vehicles with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive. Proper wheel alignment minimizes tire degradation, improves fuel efficiency, and ensures optimal steering response, prolonging tire lifespan and vehicle performance.
Choosing the Right Alignment for Your Car Type
Choosing the right wheel alignment depends on your vehicle's drivetrain and suspension system, as 4-wheel alignment is essential for all-wheel drive and independent suspension vehicles to ensure optimal handling and tire longevity. Front-wheel drive cars often require 2-wheel alignment focusing on the front wheels, which can be more cost-effective while maintaining accurate steering control. Selecting the correct alignment type prevents uneven tire wear, improves fuel efficiency, and enhances overall driving safety.
Wheel Alignment Costs: 4-Wheel vs 2-Wheel
4-wheel alignment generally costs more than 2-wheel alignment due to the comprehensive adjustment of all four wheels for optimum vehicle performance and tire longevity. While 2-wheel alignment mainly targets the front wheels, it is typically less expensive but may not address rear wheel misalignment issues that affect handling and tire wear. Investing in a 4-wheel alignment ensures balanced alignment across both axles, preventing uneven tire degradation and enhancing fuel efficiency.
Expert Tips for Maintaining Proper Wheel Alignment
Maintaining proper wheel alignment enhances tire longevity and vehicle handling, with expert tips emphasizing regular inspections every 6,000 miles or after impacts like potholes. Four-wheel alignment addresses both front and rear wheels, providing comprehensive correction for modern vehicles with independent suspension systems, while two-wheel alignment typically focuses on front wheels and suits older models or rear-wheel-drive cars. Precision measurements using advanced alignment machines ensure optimal camber, caster, and toe settings, reducing uneven tire wear and improving fuel efficiency.
4-Wheel Alignment vs 2-Wheel Alignment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com