Manual fueling requires hands-on operation, increasing the risk of human error and inconsistent fuel measurements. Automated fueling systems use advanced sensors and software to deliver precise fuel amounts, improving efficiency and reducing spills. Businesses adopting automated fueling enhance safety protocols and optimize fuel management processes.
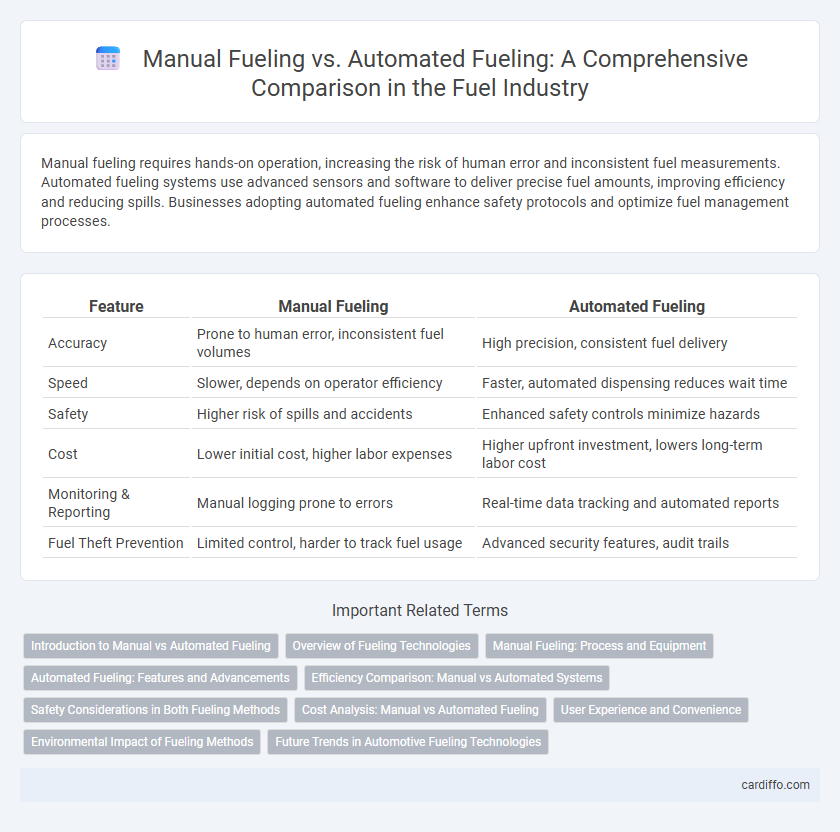
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Fueling | Automated Fueling |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Prone to human error, inconsistent fuel volumes | High precision, consistent fuel delivery |
| Speed | Slower, depends on operator efficiency | Faster, automated dispensing reduces wait time |
| Safety | Higher risk of spills and accidents | Enhanced safety controls minimize hazards |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher labor expenses | Higher upfront investment, lowers long-term labor cost |
| Monitoring & Reporting | Manual logging prone to errors | Real-time data tracking and automated reports |
| Fuel Theft Prevention | Limited control, harder to track fuel usage | Advanced security features, audit trails |
Introduction to Manual vs Automated Fueling
Manual fueling relies on human operators to control fuel dispensing, which can lead to inconsistencies and increased risk of spills or errors. Automated fueling uses advanced sensors, software, and payment systems to streamline the process, improving accuracy, safety, and efficiency. Integration of automated fueling systems also enables real-time monitoring and data analytics, optimizing fuel management in commercial and industrial settings.
Overview of Fueling Technologies
Manual fueling involves direct human operation to dispense fuel, relying on physical interaction with pumps and gauges, which can lead to inconsistencies and slower service times. Automated fueling technology uses sensor-based systems and software integration to precisely control fuel delivery, enhancing accuracy, safety, and operational efficiency. Innovations in automated fueling include RFID authentication and real-time monitoring, significantly reducing errors and improving fuel management processes.
Manual Fueling: Process and Equipment
Manual fueling involves the direct operation of fuel dispensers by personnel, requiring careful handling to ensure safety and accuracy. Equipment used includes hand pumps, fuel nozzles, safety gloves, and spill containment kits designed to minimize risks and environmental impact. This hands-on approach demands thorough training and adherence to protocols to prevent fuel contamination and maintain operational efficiency.
Automated Fueling: Features and Advancements
Automated fueling systems integrate IoT sensors and advanced software to monitor fuel levels, optimize dispensing accuracy, and reduce waste. Key features include real-time data analytics, remote management capabilities, and automated payment processing, enhancing fueling efficiency and security. Recent advancements focus on AI-driven predictive maintenance and improved user interfaces for seamless operation and reduced downtime.
Efficiency Comparison: Manual vs Automated Systems
Automated fueling systems significantly increase efficiency by reducing fueling time per vehicle by up to 40% compared to manual methods. Manual fueling often results in inconsistent flow rates and higher labor costs, whereas automated systems enable precise fuel dispensing and real-time monitoring, minimizing errors and wastage. Implementing automated technologies leads to improved throughput, operational cost savings, and enhanced fuel management accuracy.
Safety Considerations in Both Fueling Methods
Manual fueling poses higher risks due to human error, exposure to hazardous fumes, and potential fuel spills, requiring stringent safety protocols such as grounding and use of personal protective equipment. Automated fueling systems enhance safety by minimizing direct human contact, incorporating leak detection sensors, and utilizing fail-safe shutoff mechanisms to prevent overflows and accidents. Both methods demand regular maintenance and employee training to ensure compliance with industry safety standards and reduce the likelihood of fire hazards or environmental contamination.
Cost Analysis: Manual vs Automated Fueling
Manual fueling requires higher labor costs due to the need for on-site personnel, while automated fueling systems reduce operational expenses by minimizing human intervention and improving fuel dispensing efficiency. Automated fueling technology also decreases potential errors and fuel loss, leading to lower overall fuel expenses compared to manual processes. Initial investment in automated infrastructure is offset over time by significant savings in labor, fuel management, and system accuracy.
User Experience and Convenience
Manual fueling often involves extended wait times and increased interaction with fuel pumps, which can lead to user frustration and inefficiencies during busy periods. Automated fueling systems enhance user experience by offering seamless, contactless transactions that reduce refueling time and minimize errors. Integration with mobile apps and loyalty programs further elevates convenience, making automated fueling the preferred choice for modern consumers seeking efficiency and ease.
Environmental Impact of Fueling Methods
Manual fueling often leads to higher emissions due to fuel spillage and inefficient dispensing techniques, increasing environmental contamination risks. Automated fueling systems minimize fuel waste through precise measurement and controlled flow rates, significantly reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Implementing automated fueling technologies contributes to lower greenhouse gas output and enhances overall fuel efficiency, supporting sustainable environmental practices.
Future Trends in Automotive Fueling Technologies
Automotive fueling technologies are rapidly evolving from manual fueling toward automated systems, driven by advancements in smart sensors, IoT integration, and AI-powered fuel dispensers. Future trends highlight the rise of contactless, automated fuel delivery platforms that enhance efficiency, reduce human error, and support alternative fuel types such as hydrogen and electric charging. Integration with connected vehicle networks and predictive analytics is expected to further optimize fueling processes and streamline fleet management solutions.
manual fueling vs automated fueling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com