Flex-Fuel vehicles operate on a blend of gasoline and ethanol, offering versatility and environmental benefits by reducing emissions. Dedicated Fuel vehicles run exclusively on a single type of fuel, such as pure ethanol or gasoline, optimizing engine performance for that specific fuel. Choosing between Flex-Fuel and Dedicated Fuel depends on the priority of flexibility versus specialized efficiency and fuel availability.
Table of Comparison
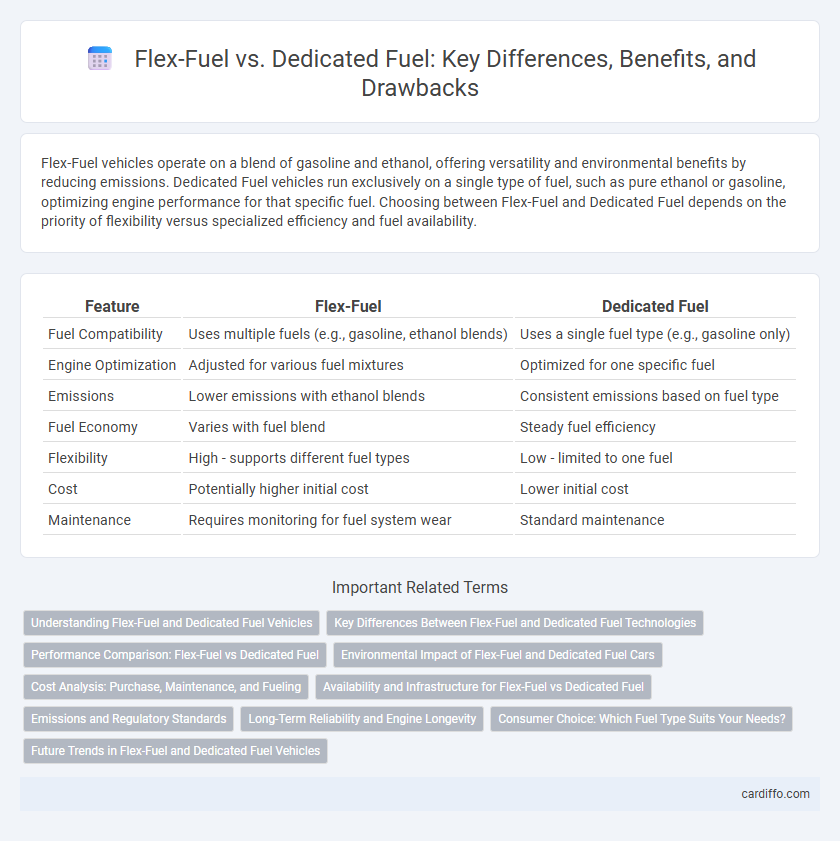
| Feature | Flex-Fuel | Dedicated Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Compatibility | Uses multiple fuels (e.g., gasoline, ethanol blends) | Uses a single fuel type (e.g., gasoline only) |
| Engine Optimization | Adjusted for various fuel mixtures | Optimized for one specific fuel |
| Emissions | Lower emissions with ethanol blends | Consistent emissions based on fuel type |
| Fuel Economy | Varies with fuel blend | Steady fuel efficiency |
| Flexibility | High - supports different fuel types | Low - limited to one fuel |
| Cost | Potentially higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Maintenance | Requires monitoring for fuel system wear | Standard maintenance |
Understanding Flex-Fuel and Dedicated Fuel Vehicles
Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) are engineered to run on varying proportions of ethanol-blended fuels, such as E85 (85% ethanol, 15% gasoline), providing users flexibility in fuel choice and potential cost savings. Dedicated fuel vehicles, in contrast, operate exclusively on a single fuel type, typically gasoline or diesel, optimizing engine performance and emissions for that specific fuel. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers choose vehicles aligned with fuel availability, environmental impact, and performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Flex-Fuel and Dedicated Fuel Technologies
Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) operate on gasoline or a blend of gasoline and ethanol, primarily E85, offering versatility in fuel choice and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Dedicated fuel vehicles are designed to run exclusively on a single fuel type, such as pure ethanol or gasoline, optimizing engine performance and emissions for that specific fuel. The key differences lie in fuel compatibility, engine tuning, and emissions standards, with flex-fuel vehicles providing broader fuel options but slightly lower efficiency compared to the optimized performance of dedicated fuel systems.
Performance Comparison: Flex-Fuel vs Dedicated Fuel
Flex-fuel vehicles demonstrate slightly lower fuel efficiency compared to dedicated fuel vehicles due to their ability to run on varying ethanol-gasoline blends, affecting combustion optimization. Dedicated fuel engines, optimized for a specific fuel type such as pure gasoline or pure ethanol, deliver higher power output and improved fuel economy under consistent fuel conditions. Performance differences also include emissions levels, where dedicated ethanol engines typically produce fewer greenhouse gases than flex-fuel systems running on mixed fuels.
Environmental Impact of Flex-Fuel and Dedicated Fuel Cars
Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) using ethanol-blended fuels reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50% compared to traditional gasoline, thanks to renewable ethanol components that lower carbon footprints. Dedicated fuel cars optimized for specific fuels, such as electric or hydrogen-powered vehicles, produce minimal tailpipe emissions, significantly decreasing air pollutants and dependency on fossil fuels. However, the environmental advantage of flex-fuel depends on ethanol production methods, while dedicated fuel cars offer consistent lower emissions through specialized design and fuel use.
Cost Analysis: Purchase, Maintenance, and Fueling
Flex-fuel vehicles typically have higher upfront costs, approximately $1,000 to $2,000 more than dedicated fuel vehicles, due to their advanced fuel system technology. Maintenance expenses for flex-fuel vehicles can increase by around 10-15% because of the need for specialized components and sensors that handle ethanol blends. While fueling costs for flex-fuel vehicles vary based on ethanol prices, dedicated fuel vehicles offer more predictable fuel expenses, often leading to overall cost savings in long-term ownership.
Availability and Infrastructure for Flex-Fuel vs Dedicated Fuel
Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) benefit from broader availability and infrastructure, as they can run on gasoline or ethanol blends like E85, supported by widespread fueling stations primarily in regions such as the U.S. Midwest and Brazil. Dedicated fuel vehicles rely on a single fuel type, such as pure ethanol or gasoline, limiting their use to areas where specific fuel infrastructure is established, often resulting in fewer refueling options. The extensive network for flex fuels enhances convenience and flexibility, while dedicated fuel systems may offer optimized performance but with restricted fueling accessibility.
Emissions and Regulatory Standards
Flex-fuel vehicles emit higher levels of greenhouse gases compared to dedicated fuel vehicles due to less efficient combustion of ethanol blends, impacting compliance with stringent emissions standards like Euro 6 and Tier 3. Dedicated fuel vehicles optimized for gasoline or ethanol demonstrate lower tailpipe emissions, meeting stricter regulatory requirements for pollutants including NOx, CO, and particulate matter. Regulatory frameworks increasingly favor dedicated fuel technology to achieve carbon reduction targets and improve air quality through enhanced fuel-specific emission controls.
Long-Term Reliability and Engine Longevity
Flex-fuel vehicles, designed to run on varying ethanol-gasoline blends, may experience faster engine wear due to ethanol's corrosive properties impacting fuel system components over time. Dedicated fuel engines, optimized specifically for a single fuel type, typically demonstrate enhanced long-term reliability and engine longevity through precise combustion control and reduced material stress. Studies indicate that dedicated ethanol or gasoline engines maintain superior performance and lower maintenance costs compared to flex-fuel systems when evaluated over extended usage periods.
Consumer Choice: Which Fuel Type Suits Your Needs?
Flex-fuel vehicles offer versatility by running on gasoline or ethanol blends like E85, providing consumers with cost-saving and environmentally friendly options depending on fuel availability. Dedicated fuel vehicles, optimized for a single fuel type such as pure gasoline or diesel, deliver better fuel efficiency and performance tailored to that specific fuel. Consumers should evaluate their driving habits, fuel access, and environmental priorities to determine whether the adaptability of flex-fuel or the efficiency of dedicated fuel vehicles best suits their needs.
Future Trends in Flex-Fuel and Dedicated Fuel Vehicles
Flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) are expected to gain traction due to increasing availability of biofuels like ethanol and advancements in engine technologies enhancing fuel efficiency and emissions performance. Dedicated fuel vehicles, optimized for single fuel types such as pure gasoline or diesel, may see continued use in niche markets but face challenges from stricter emission regulations and the rise of alternative fuels. Innovations in flexible fuel systems and government policies supporting renewable energy integration will likely drive the future growth of flex-fuel vehicles in the global automotive market.
Flex-Fuel vs Dedicated Fuel Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com