E85 fuel consists of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, offering a renewable alternative with lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to regular gasoline. Vehicles designed for E85 use typically experience higher octane performance but may see slightly reduced fuel economy due to ethanol's lower energy content. Choosing E85 supports reducing fossil fuel dependence while regular gasoline remains widely available and compatible with all internal combustion engines.
Table of Comparison
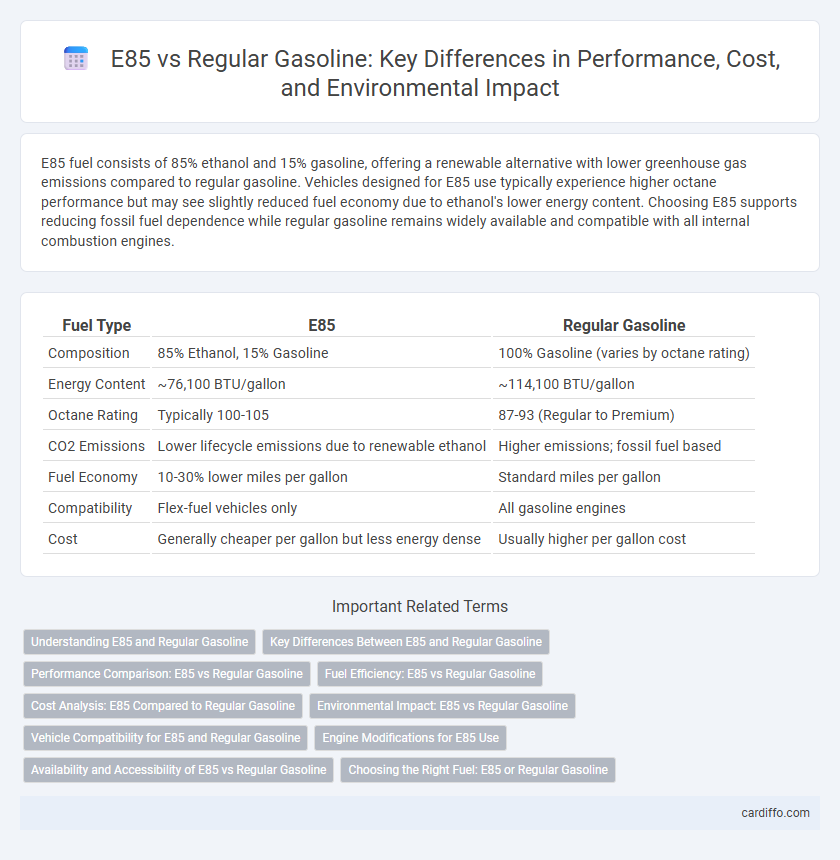
| Fuel Type | E85 | Regular Gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 85% Ethanol, 15% Gasoline | 100% Gasoline (varies by octane rating) |
| Energy Content | ~76,100 BTU/gallon | ~114,100 BTU/gallon |
| Octane Rating | Typically 100-105 | 87-93 (Regular to Premium) |
| CO2 Emissions | Lower lifecycle emissions due to renewable ethanol | Higher emissions; fossil fuel based |
| Fuel Economy | 10-30% lower miles per gallon | Standard miles per gallon |
| Compatibility | Flex-fuel vehicles only | All gasoline engines |
| Cost | Generally cheaper per gallon but less energy dense | Usually higher per gallon cost |
Understanding E85 and Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel consists of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, offering higher octane ratings and cleaner combustion compared to regular gasoline, which typically contains around 10% ethanol. E85 is primarily used in flex-fuel vehicles designed to accommodate higher ethanol content, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions but reduced fuel economy due to ethanol's lower energy density. Regular gasoline is more widely available and compatible with almost all conventional internal combustion engines, making it the standard fuel choice for most vehicles worldwide.
Key Differences Between E85 and Regular Gasoline
E85 consists of up to 85% ethanol blended with 15% gasoline, offering a higher octane rating compared to regular gasoline, which typically contains 87 octane. Vehicles using E85 benefit from reduced greenhouse gas emissions and renewable sourcing but may experience lower fuel economy due to ethanol's lower energy density. Regular gasoline provides greater energy content per gallon, ensuring better fuel efficiency and broader compatibility with traditional engines.
Performance Comparison: E85 vs Regular Gasoline
E85 ethanol fuel offers higher octane ratings, typically around 100-105, compared to regular gasoline's 87-92 octane, allowing for increased engine performance and higher compression ratios. Vehicles optimized for E85 can achieve improved horsepower and torque due to its cleaner combustion and cooling effects, though fuel economy tends to be lower because E85 contains less energy per gallon. Regular gasoline provides consistent mileage and wide availability, but E85's performance benefits make it a preferred choice for flex-fuel vehicles seeking enhanced power output.
Fuel Efficiency: E85 vs Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel, composed of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, typically delivers lower fuel efficiency than regular gasoline due to its lower energy content per gallon. Vehicles running on E85 may experience a 20-30% reduction in miles per gallon compared to those using regular gasoline. Despite this, E85 offers higher octane levels, which can enhance engine performance in flex-fuel vehicles optimized for ethanol blends.
Cost Analysis: E85 Compared to Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel, composed of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, often costs significantly less per gallon than regular gasoline due to lower production expenses and government subsidies promoting renewable energy. Despite its lower price, E85 delivers approximately 25-30% fewer miles per gallon, which affects overall cost efficiency when comparing fuel economy. Consumers need to evaluate local fuel prices, vehicle compatibility, and mileage impact to determine the true cost advantage of choosing E85 over regular gasoline.
Environmental Impact: E85 vs Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel, composed of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, produces significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to regular gasoline due to its renewable biofuel origin and higher oxygen content that promotes cleaner combustion. Ethanol in E85 reduces carbon monoxide and particulate matter emissions, leading to improved air quality and a smaller carbon footprint. However, the environmental benefits depend on the source of ethanol, with corn-based ethanol having greater land use impacts compared to cellulosic or advanced biofuels.
Vehicle Compatibility for E85 and Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel, composed of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, requires flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs) specifically designed or modified to handle higher alcohol content and corrosive properties, ensuring proper engine performance and fuel system durability. Regular gasoline is compatible with virtually all internal combustion engine vehicles without modification, offering more widespread availability and compatibility across conventional cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Choosing E85 mandates verifying vehicle compatibility to avoid potential engine damage or reduced efficiency, whereas regular gasoline remains the default fuel for non-flex-fuel vehicles.
Engine Modifications for E85 Use
E85 fuel requires specific engine modifications due to its higher ethanol content, which is more corrosive and has different combustion characteristics than regular gasoline. Flex-fuel vehicles typically include enhanced fuel injectors, specialized fuel pumps, and ethanol-resistant seals to handle the increased volume and prevent damage. Without these adjustments, engines may experience issues like poor fuel atomization, reduced lubrication, and potential component wear when running on E85.
Availability and Accessibility of E85 vs Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel is available at approximately 3,000 fuel stations across the United States, primarily concentrated in the Midwest and regions with high flex-fuel vehicle adoption. Regular gasoline, in contrast, is accessible at nearly every fuel station nationwide, offering widespread convenience for drivers. The limited availability of E85 restricts its accessibility for many consumers despite its potential environmental benefits.
Choosing the Right Fuel: E85 or Regular Gasoline
E85 fuel, composed of 85% ethanol and 15% gasoline, offers higher octane levels that improve engine performance and reduce carbon emissions compared to regular gasoline, which typically has about 10-15% ethanol. However, E85's lower energy content results in decreased fuel economy, making it more suitable for flex-fuel vehicles designed to optimize ethanol combustion. Choosing the right fuel depends on vehicle compatibility, environmental goals, and fuel availability in your region.
E85 vs Regular Gasoline Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com