City driving typically consumes more fuel due to frequent stops, idling, and lower speeds, causing the engine to work harder. Highway driving maintains a consistent speed, improving fuel efficiency by reducing acceleration and braking cycles. Optimizing speed and minimizing idling during city trips can help narrow the fuel economy gap between urban and highway driving.
Table of Comparison
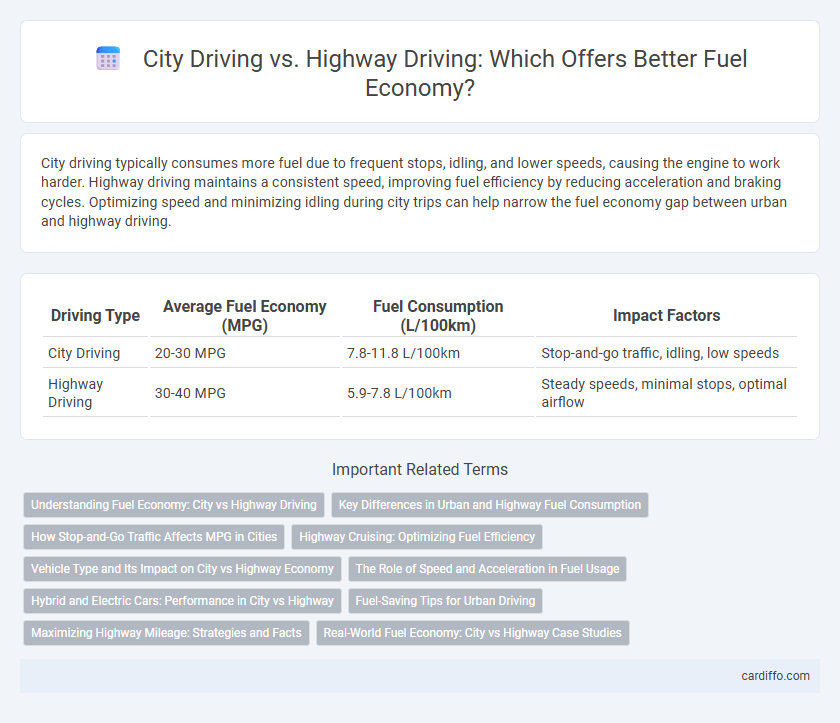
| Driving Type | Average Fuel Economy (MPG) | Fuel Consumption (L/100km) | Impact Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| City Driving | 20-30 MPG | 7.8-11.8 L/100km | Stop-and-go traffic, idling, low speeds |
| Highway Driving | 30-40 MPG | 5.9-7.8 L/100km | Steady speeds, minimal stops, optimal airflow |
Understanding Fuel Economy: City vs Highway Driving
City driving typically results in lower fuel economy due to frequent stops, idling, and lower average speeds that increase fuel consumption. Highway driving offers better fuel efficiency as vehicles maintain steady speeds and experience less braking, optimizing engine performance. Understanding the difference in miles per gallon (MPG) between city and highway conditions helps drivers estimate fuel costs and choose appropriate vehicles for their driving patterns.
Key Differences in Urban and Highway Fuel Consumption
City driving typically results in lower fuel economy due to frequent stops, idling, and acceleration, which increase fuel consumption. Highway driving maintains a more consistent speed, allowing engines to operate efficiently and achieve better miles per gallon (MPG). Urban fuel consumption can be 20-30% higher than highway driving due to these driving patterns and traffic congestion.
How Stop-and-Go Traffic Affects MPG in Cities
Stop-and-go traffic in city driving significantly reduces MPG because frequent acceleration and braking consume more fuel compared to steady speeds on highways. Vehicles operating in urban environments experience increased engine idling and turbocharger inefficiency, further decreasing fuel economy. Modern cars with start-stop systems help mitigate fuel waste, but overall city driving remains less fuel-efficient than highway driving due to traffic congestion patterns.
Highway Cruising: Optimizing Fuel Efficiency
Highway cruising offers optimal fuel efficiency due to steady speeds and minimal stops, reducing engine strain and fuel consumption. Maintaining a constant speed between 50-65 mph maximizes miles per gallon (MPG) by enhancing engine combustion and aerodynamic performance. Using cruise control further stabilizes throttle input, preventing unnecessary acceleration and improving overall fuel economy during long highway drives.
Vehicle Type and Its Impact on City vs Highway Economy
Fuel economy varies significantly between city and highway driving depending on the vehicle type, with hybrids and electric vehicles showing superior efficiency in stop-and-go city traffic due to regenerative braking and low-speed optimization. Conventional gasoline and diesel engines tend to achieve better fuel economy on highways where steady speeds minimize engine load and aerodynamic drag plays a larger role. SUVs and trucks generally experience greater fuel consumption in city driving because of their heavier weight and lower engine efficiency at low speeds, while sedans and compact cars maintain more consistent mileage across driving conditions.
The Role of Speed and Acceleration in Fuel Usage
Speed and acceleration significantly impact fuel consumption during city and highway driving, with higher speeds and rapid acceleration increasing fuel usage. City driving involves frequent stops and starts, causing engines to work harder and reduce fuel efficiency compared to the steady speeds maintained on highways. Optimal fuel economy is achieved by maintaining moderate speeds and smooth acceleration, minimizing unnecessary fuel waste.
Hybrid and Electric Cars: Performance in City vs Highway
Hybrid cars excel in city driving due to regenerative braking, which recovers energy during frequent stops and starts, significantly enhancing fuel economy. Electric vehicles (EVs) also perform efficiently in urban settings by maximizing battery usage with lower speeds and consistent acceleration, extending range in stop-and-go traffic. On highways, hybrids rely more on gasoline engines, reducing fuel efficiency, while EVs benefit from steady speeds but may experience range limitations due to higher energy consumption at sustained high velocities.
Fuel-Saving Tips for Urban Driving
Fuel economy in city driving typically suffers due to frequent stops, idling, and lower speeds compared to highway driving, resulting in higher fuel consumption per mile. Optimizing fuel efficiency in urban environments involves smooth acceleration, minimizing idling by turning off the engine during extended stops, and maintaining proper tire pressure to reduce rolling resistance. Utilizing technologies such as start-stop systems and avoiding excessive use of air conditioning further contribute to reducing fuel consumption during city driving.
Maximizing Highway Mileage: Strategies and Facts
Maximizing highway mileage involves maintaining a steady speed, typically between 50-65 mph, to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce engine strain. Using cruise control on highways helps sustain consistent acceleration, minimizing fuel consumption caused by frequent speed changes common in city driving. Proper tire inflation and regular vehicle maintenance further enhance fuel economy by reducing rolling resistance and engine inefficiency during long-distance travel.
Real-World Fuel Economy: City vs Highway Case Studies
Real-world fuel economy studies reveal that city driving typically results in lower miles per gallon due to frequent idling and stop-and-go traffic, averaging around 20-25 MPG for sedans. Highway driving increases fuel efficiency significantly, often reaching 30-40 MPG because of steady speeds and less braking. Data from multiple case studies confirm a 25-35% improvement in fuel economy on highways compared to urban routes, highlighting the impact of driving conditions on fuel consumption.
City Driving vs Highway Driving (fuel economy) Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com