Administrative fines are penalties imposed by government agencies for regulatory violations without court involvement, offering a faster resolution process. Judicial fines are imposed by courts as part of criminal or civil proceedings, often following a trial or legal hearing, ensuring due process. The key distinction lies in the enforcement mechanism and the legal context in which each fine is imposed.
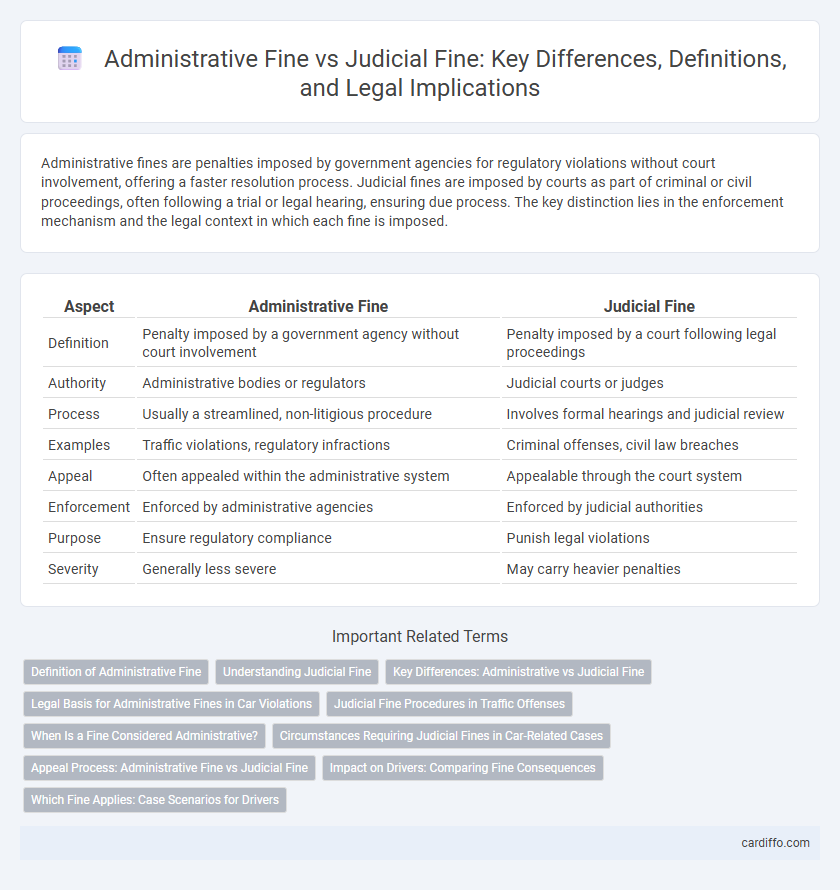
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Administrative Fine | Judicial Fine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Penalty imposed by a government agency without court involvement | Penalty imposed by a court following legal proceedings |
| Authority | Administrative bodies or regulators | Judicial courts or judges |
| Process | Usually a streamlined, non-litigious procedure | Involves formal hearings and judicial review |
| Examples | Traffic violations, regulatory infractions | Criminal offenses, civil law breaches |
| Appeal | Often appealed within the administrative system | Appealable through the court system |
| Enforcement | Enforced by administrative agencies | Enforced by judicial authorities |
| Purpose | Ensure regulatory compliance | Punish legal violations |
| Severity | Generally less severe | May carry heavier penalties |
Definition of Administrative Fine
An administrative fine is a monetary penalty imposed by a government agency or administrative authority as a consequence of violating regulations or administrative laws, without involving the judiciary. This type of fine serves as a tool for regulatory enforcement, aiming to ensure compliance with specific rules related to areas such as environmental protection, public health, or business licensing. Unlike judicial fines, administrative fines do not require a court proceeding and are typically resolved through administrative hearings or direct agency decisions.
Understanding Judicial Fine
A judicial fine is imposed by a court as a consequence of violating laws during a legal proceeding and forms part of the judicial sentencing process. Unlike administrative fines, which are typically levied by government agencies for regulatory infractions, judicial fines are connected to the adjudication of criminal or civil cases. This fine serves both as punishment and deterrence, reflecting the severity of the offense determined through judicial review.
Key Differences: Administrative vs Judicial Fine
Administrative fines are penalties imposed by government agencies for regulatory violations, often without court involvement, focusing on compliance enforcement and rapid resolution. Judicial fines are imposed by courts as part of a legal judgment following a trial or hearing, emphasizing legal adjudication and due process. Administrative fines typically handle minor infractions, while judicial fines address more serious offenses requiring formal legal proceedings.
Legal Basis for Administrative Fines in Car Violations
Legal basis for administrative fines in car violations stems primarily from traffic laws and regulations established by government agencies responsible for road safety and vehicle management. These fines are enforceable under statutes such as the Highway Traffic Act or Motor Vehicle Acts, which outline specific offenses and corresponding penalties without requiring court proceedings. Administrative fines serve as a regulatory tool to ensure compliance with traffic rules, providing a streamlined process for addressing infractions like speeding, illegal parking, and expired registrations.
Judicial Fine Procedures in Traffic Offenses
Judicial fine procedures in traffic offenses involve formal court hearings where evidence is presented, and the offender has the right to defend against charges, ensuring due process under the law. Courts typically assess the severity of the violation, prior offenses, and the offender's conduct before determining the penalty, which may include fines, license suspension, or community service. These procedures provide opportunities for appeals or negotiated settlements, distinguishing them from administrative fines that are often imposed without judicial intervention.
When Is a Fine Considered Administrative?
A fine is considered administrative when it is imposed by a government agency or regulatory body as a penalty for violating specific rules or regulations outside the criminal justice system. Administrative fines typically address minor infractions such as traffic violations, environmental breaches, or licensing issues, and do not require a court trial. These fines serve as a tool for regulatory enforcement to ensure compliance without involving judicial proceedings.
Circumstances Requiring Judicial Fines in Car-Related Cases
Judicial fines in car-related cases are required when violations involve criminal negligence, such as reckless driving causing injury or death, or repeat offenses that escalate beyond administrative penalties. Cases involving fraud, falsification of vehicle documents, or driving under the influence causing significant harm mandate judicial fines to ensure legal accountability. These circumstances demand court intervention to impose stricter penalties and uphold public safety standards.
Appeal Process: Administrative Fine vs Judicial Fine
The appeal process for administrative fines typically involves submitting a formal objection to the issuing authority or an administrative tribunal within a specified timeframe, often allowing for a quicker resolution. Judicial fines require filing a lawsuit or appeal in a court of law, where a judge reviews the case, which may involve more complex procedures and longer timelines. Understanding these distinct appeal mechanisms is crucial for effectively challenging fines and ensuring compliance with legal standards.
Impact on Drivers: Comparing Fine Consequences
Administrative fines typically result in immediate monetary penalties and may include points added to the driver's license, influencing insurance rates and driving privileges. Judicial fines, imposed by courts, often carry heavier financial burdens and potential criminal records, which can lead to longer-term legal consequences and stricter license suspensions. The difference in impact means administrative fines primarily affect short-term driving status, while judicial fines significantly impact a driver's legal record and future driving rights.
Which Fine Applies: Case Scenarios for Drivers
Administrative fines typically apply to traffic violations such as speeding, illegal parking, or failing to stop at a red light, where law enforcement issues the penalty directly. Judicial fines arise from court rulings in cases involving serious infractions like DUI, reckless driving, or repeated offenses that require a legal trial. Drivers must understand that administrative fines are processed swiftly through administrative channels, whereas judicial fines result from judicial proceedings and often include additional penalties like license suspension or community service.
Administrative Fine vs Judicial Fine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com