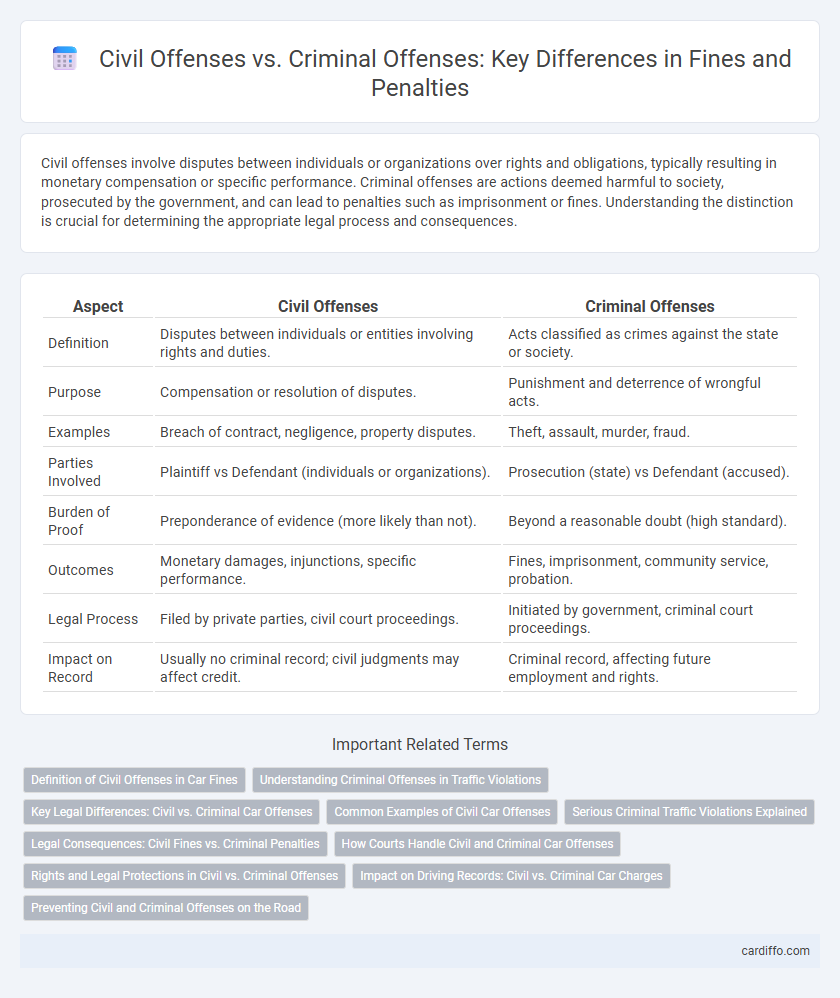
Civil offenses involve disputes between individuals or organizations over rights and obligations, typically resulting in monetary compensation or specific performance. Criminal offenses are actions deemed harmful to society, prosecuted by the government, and can lead to penalties such as imprisonment or fines. Understanding the distinction is crucial for determining the appropriate legal process and consequences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Civil Offenses | Criminal Offenses |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disputes between individuals or entities involving rights and duties. | Acts classified as crimes against the state or society. |
| Purpose | Compensation or resolution of disputes. | Punishment and deterrence of wrongful acts. |
| Examples | Breach of contract, negligence, property disputes. | Theft, assault, murder, fraud. |
| Parties Involved | Plaintiff vs Defendant (individuals or organizations). | Prosecution (state) vs Defendant (accused). |
| Burden of Proof | Preponderance of evidence (more likely than not). | Beyond a reasonable doubt (high standard). |
| Outcomes | Monetary damages, injunctions, specific performance. | Fines, imprisonment, community service, probation. |
| Legal Process | Filed by private parties, civil court proceedings. | Initiated by government, criminal court proceedings. |
| Impact on Record | Usually no criminal record; civil judgments may affect credit. | Criminal record, affecting future employment and rights. |
Definition of Civil Offenses in Car Fines
Civil offenses in car fines refer to violations of traffic laws that result in penalties such as fines or points on a driver's license, without involving criminal charges or imprisonment. These offenses typically include infractions like speeding, illegal parking, or failure to signal, which are handled through administrative procedures rather than court trials. The purpose of civil car fines is to enforce compliance with traffic regulations and promote road safety without criminal prosecution.
Understanding Criminal Offenses in Traffic Violations
Criminal offenses in traffic violations involve actions that pose significant risks to public safety, such as driving under the influence, reckless driving, and hit-and-run incidents. These offenses typically result in harsher penalties including fines, license suspension, and imprisonment, reflecting their serious impact on law and order. Understanding the legal distinctions and consequences of these criminal traffic offenses is essential for ensuring compliance and protecting public welfare.
Key Legal Differences: Civil vs. Criminal Car Offenses
Civil car offenses primarily involve disputes over damages or compensation due to accidents, where the injured party seeks restitution through lawsuits. Criminal car offenses, such as DUI or reckless driving, lead to prosecution by the state and can result in penalties like fines, license suspension, or imprisonment. The burden of proof in civil cases is the preponderance of evidence, whereas criminal cases require proof beyond a reasonable doubt.
Common Examples of Civil Car Offenses
Common examples of civil car offenses include traffic violations such as speeding, running a red light, and illegal parking, which typically result in fines or penalties rather than jail time. Accidents causing property damage or minor personal injury often lead to civil lawsuits for compensation rather than criminal charges. These offenses focus on resolving disputes and compensating victims rather than punishing offenders with criminal sanctions.
Serious Criminal Traffic Violations Explained
Serious criminal traffic violations include offenses such as DUI, vehicular manslaughter, and reckless driving causing injury, which carry severe penalties including imprisonment and heavy fines. Unlike civil offenses, these violations involve criminal liability and can result in a permanent criminal record, impacting future legal rights and insurance rates. Law enforcement and courts treat serious criminal traffic violations with greater scrutiny due to the potential harm to public safety and the intent or negligence involved.
Legal Consequences: Civil Fines vs. Criminal Penalties
Civil offenses result in monetary fines or compensation payments to the injured party, emphasizing restitution rather than punishment. Criminal offenses carry penalties such as imprisonment, probation, or larger fines imposed by the state to deter wrongdoing and ensure public safety. The legal consequences differ fundamentally, with civil fines addressing private disputes and criminal penalties serving as deterrents to unlawful behavior.
How Courts Handle Civil and Criminal Car Offenses
Courts handle civil car offenses by focusing on compensating victims for damages and losses through monetary awards, often requiring a preponderance of evidence to establish liability. In contrast, criminal car offenses involve prosecution by the state, prioritizing public safety and deterrence, with penalties including fines, license suspension, or imprisonment upon proof beyond a reasonable doubt. Civil cases aim to resolve disputes between parties, while criminal cases address violations of laws that protect society.
Rights and Legal Protections in Civil vs. Criminal Offenses
Civil offenses primarily involve disputes between individuals or entities where the plaintiff seeks compensation or specific performance, and legal protections focus on private rights and remedies such as monetary damages or injunctions. Criminal offenses address violations against state laws with the government prosecuting the accused, ensuring protections through constitutional rights like the right to a fair trial, protection against self-incrimination, and legal representation. Rights in criminal cases are typically more robust to prevent wrongful conviction, whereas civil cases emphasize restitution and resolution of private disputes.
Impact on Driving Records: Civil vs. Criminal Car Charges
Civil car charges typically result in points on a driving record, which can lead to increased insurance premiums and potential license suspensions. Criminal driving offenses, such as DUI or vehicular manslaughter, carry more severe penalties including felony records, longer license suspensions, and higher fines. These criminal convictions often have lasting impacts beyond insurance, potentially affecting employment and legal rights.
Preventing Civil and Criminal Offenses on the Road
Preventing civil and criminal offenses on the road requires strict enforcement of traffic laws and public awareness campaigns focused on safe driving practices. Implementing technologies such as speed cameras and breathalyzers effectively deters reckless behavior and DUI offenses, reducing accidents and legal violations. Coordinated efforts between law enforcement, policymakers, and communities enhance road safety and minimize both civil disputes and criminal charges related to traffic incidents.
Civil offenses vs Criminal offenses Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com