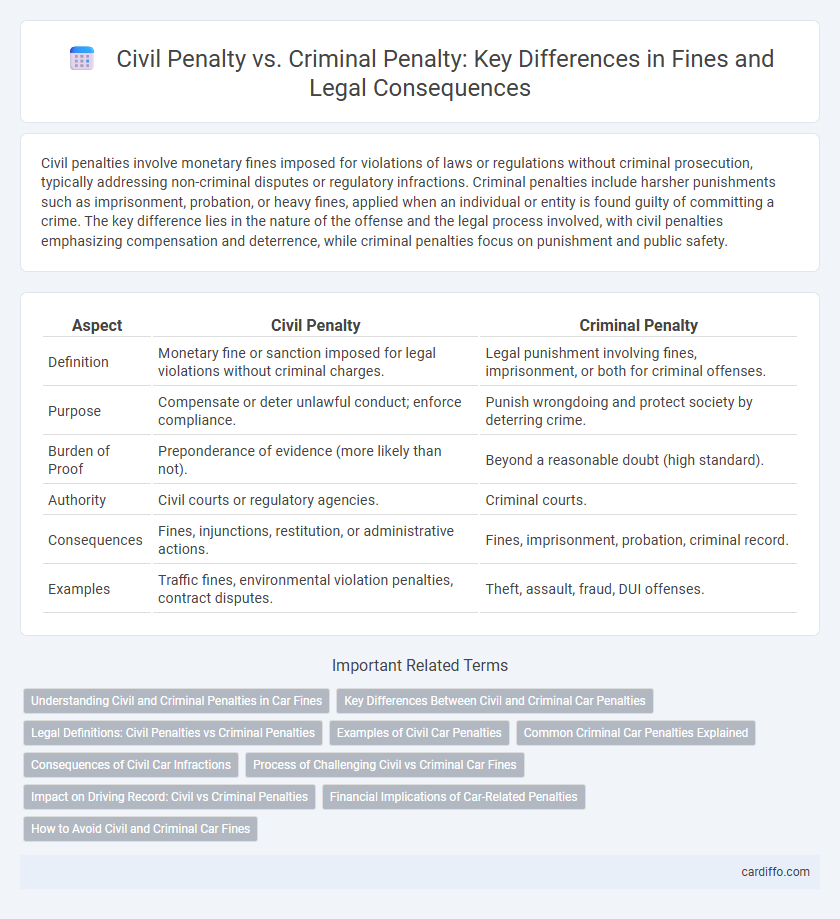
Civil penalties involve monetary fines imposed for violations of laws or regulations without criminal prosecution, typically addressing non-criminal disputes or regulatory infractions. Criminal penalties include harsher punishments such as imprisonment, probation, or heavy fines, applied when an individual or entity is found guilty of committing a crime. The key difference lies in the nature of the offense and the legal process involved, with civil penalties emphasizing compensation and deterrence, while criminal penalties focus on punishment and public safety.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Civil Penalty | Criminal Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary fine or sanction imposed for legal violations without criminal charges. | Legal punishment involving fines, imprisonment, or both for criminal offenses. |
| Purpose | Compensate or deter unlawful conduct; enforce compliance. | Punish wrongdoing and protect society by deterring crime. |
| Burden of Proof | Preponderance of evidence (more likely than not). | Beyond a reasonable doubt (high standard). |
| Authority | Civil courts or regulatory agencies. | Criminal courts. |
| Consequences | Fines, injunctions, restitution, or administrative actions. | Fines, imprisonment, probation, criminal record. |
| Examples | Traffic fines, environmental violation penalties, contract disputes. | Theft, assault, fraud, DUI offenses. |
Understanding Civil and Criminal Penalties in Car Fines
Civil penalties in car fines typically involve monetary fines imposed for violations such as speeding or parking infractions, designed to compensate the state without resulting in a criminal record. Criminal penalties for traffic offenses often include harsher consequences like license suspension, imprisonment, or probation, reflecting more serious violations such as DUI or reckless driving. Understanding the distinction helps drivers recognize that civil penalties address administrative or financial responsibility, while criminal penalties carry legal ramifications affecting personal liberty.
Key Differences Between Civil and Criminal Car Penalties
Civil car penalties primarily involve monetary fines and compensation claims aimed at remedying damages or violations of traffic regulations. Criminal car penalties can include imprisonment, probation, or community service, reflecting the severity of offenses such as reckless driving or DUI. Civil cases require a preponderance of evidence, while criminal cases demand proof beyond a reasonable doubt.
Legal Definitions: Civil Penalties vs Criminal Penalties
Civil penalties are monetary fines imposed by regulatory agencies to enforce compliance with laws without initiating criminal prosecution, typically addressing violations such as environmental infractions or administrative breaches. Criminal penalties involve prosecution by the state leading to punishments like imprisonment, probation, or larger fines, reflecting offenses such as fraud or assault with clear elements of intent or harm. The legal distinction centers on the burden of proof, with civil penalties requiring a preponderance of evidence and criminal penalties demanding proof beyond a reasonable doubt.
Examples of Civil Car Penalties
Civil car penalties typically include fines for speeding, parking violations, and running a red light, with amounts varying by jurisdiction but often ranging from $50 to $500. Other examples involve penalties for failing to maintain insurance or vehicle registration, which can lead to additional fines or license suspension. These penalties are monetary and non-criminal, designed to enforce traffic laws and encourage safer driving without resulting in jail time.
Common Criminal Car Penalties Explained
Common criminal car penalties include imprisonment, fines, and license suspension, reflecting the severity of offenses such as DUI, reckless driving, and vehicular manslaughter. Civil penalties typically involve monetary fines and points on the driver's license without criminal prosecution. Understanding the distinction helps drivers anticipate legal consequences and maintain compliance with traffic laws.
Consequences of Civil Car Infractions
Civil car infractions primarily result in monetary fines, points added to the driver's license, and potential increases in insurance premiums. These penalties do not lead to criminal records but can accumulate to cause license suspension or revocation. The financial burden and impact on driving privileges emphasize the importance of addressing civil violations promptly to avoid escalated consequences.
Process of Challenging Civil vs Criminal Car Fines
Challenging civil car fines typically involves submitting a formal appeal or request for a hearing within a specified time frame, often managed by a traffic tribunal or administrative court, where evidence and mitigating circumstances can be presented. In contrast, contesting criminal car fines requires navigating a more complex judicial process, including arraignment, potential pre-trial motions, and trial before a judge or jury, with greater procedural safeguards and possible legal representation. Both processes demand strict adherence to deadlines and procedural rules, but criminal cases carry higher stakes, including possible imprisonment and criminal records.
Impact on Driving Record: Civil vs Criminal Penalties
Civil penalties typically result in points added to a driving record, which can lead to increased insurance premiums and potential license suspension. Criminal penalties often carry more severe consequences, including longer license suspension periods, mandatory court appearances, and possible jail time, greatly affecting one's driving privileges. The severity of criminal penalties usually causes more substantial and lasting damage to the driving record compared to civil penalties.
Financial Implications of Car-Related Penalties
Civil penalties for car-related violations typically involve fines that vary based on the severity of the infraction and jurisdiction, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Criminal penalties may include higher fines combined with potential jail time, probation, or license suspension, significantly increasing the overall financial burden. Understanding the distinction between these penalties is crucial for evaluating risk and managing the economic impact of traffic violations.
How to Avoid Civil and Criminal Car Fines
To avoid civil and criminal car fines, always adhere to traffic laws, including speed limits, seat belt use, and driving under the influence regulations. Regular vehicle maintenance and timely payment of registrations reduce risk factors that trigger penalties. Consult legal guidelines to understand specific violations and enforce compliance proactively.
Civil Penalty vs Criminal Penalty Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com