Upstream sensors measure oxygen levels before the catalytic converter to monitor air-fuel mixture and optimize combustion efficiency, directly impacting emission control. Downstream sensors detect oxygen levels after the catalytic converter to assess its performance and ensure harmful pollutants are effectively reduced. Accurate data from both upstream and downstream sensors enable the vehicle's engine control unit to maintain optimal emission standards and reduce environmental impact.
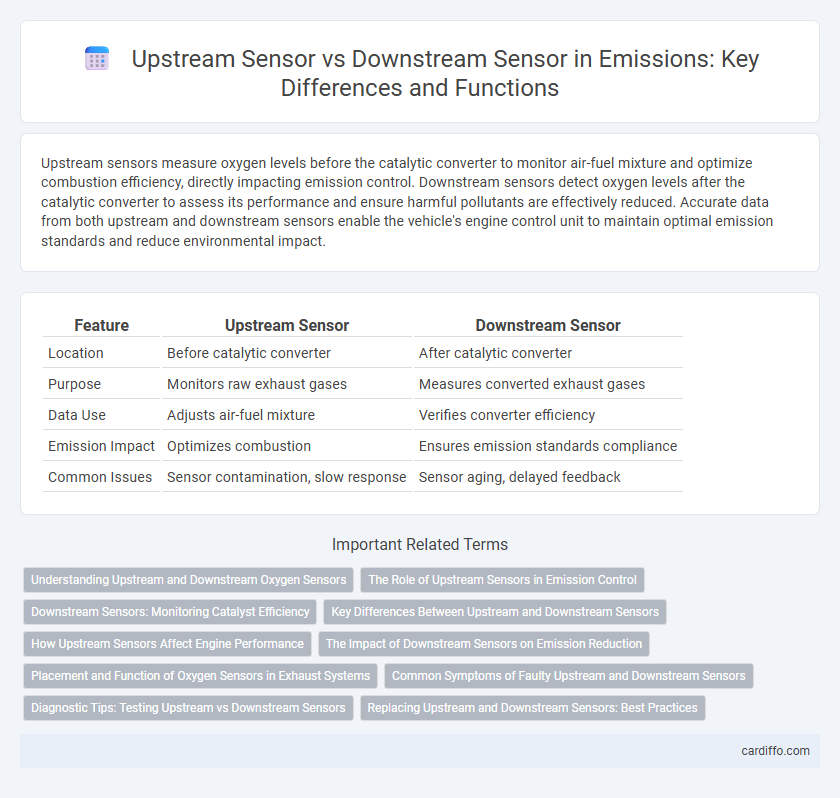
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Upstream Sensor | Downstream Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Before catalytic converter | After catalytic converter |
| Purpose | Monitors raw exhaust gases | Measures converted exhaust gases |
| Data Use | Adjusts air-fuel mixture | Verifies converter efficiency |
| Emission Impact | Optimizes combustion | Ensures emission standards compliance |
| Common Issues | Sensor contamination, slow response | Sensor aging, delayed feedback |
Understanding Upstream and Downstream Oxygen Sensors
Upstream oxygen sensors, located before the catalytic converter, monitor the air-fuel mixture by measuring oxygen levels in the exhaust gases to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency. Downstream oxygen sensors, positioned after the catalytic converter, assess the effectiveness of the converter by detecting residual oxygen to ensure emissions compliance. Understanding the differences between upstream and downstream sensors is critical for accurate diagnostics and maintaining low vehicle emissions.
The Role of Upstream Sensors in Emission Control
Upstream sensors monitor exhaust gas composition before the catalytic converter, providing critical real-time data to the engine control unit (ECU) for precise air-fuel mixture adjustments. These sensors enhance emission control by detecting oxygen levels early, enabling efficient combustion and reducing harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons. Upstream sensor accuracy directly impacts the catalyst's performance, ensuring optimal conversion of emissions downstream.
Downstream Sensors: Monitoring Catalyst Efficiency
Downstream sensors play a critical role in monitoring catalyst efficiency by measuring the levels of pollutants such as NOx and CO in the exhaust gases after they pass through the catalytic converter. These sensors provide precise feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to ensure optimal catalyst performance and effective emission reduction. Accurate data from downstream sensors helps in maintaining compliance with stringent emission standards and prolonging catalytic converter lifespan.
Key Differences Between Upstream and Downstream Sensors
Upstream sensors are installed before the catalytic converter to monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases, providing real-time feedback for fuel mixture adjustments to optimize engine performance and reduce emissions. Downstream sensors are positioned after the catalytic converter to evaluate its efficiency by measuring residual oxygen, ensuring compliance with emission standards. The main difference lies in their function: upstream sensors manage engine combustion, while downstream sensors assess the converter's effectiveness.
How Upstream Sensors Affect Engine Performance
Upstream sensors, such as oxygen sensors located before the catalytic converter, play a critical role in optimizing engine performance by providing real-time data on the air-fuel mixture. Accurate readings from upstream sensors enable precise fuel injection adjustments, resulting in improved combustion efficiency, reduced emissions, and better fuel economy. Malfunctioning upstream sensors can lead to engine misfires, increased fuel consumption, and elevated pollutant levels, highlighting their impact on overall engine operation.
The Impact of Downstream Sensors on Emission Reduction
Downstream sensors play a critical role in emission reduction by accurately monitoring exhaust gases after combustion, enabling real-time adjustments in the engine control system to minimize harmful emissions. These sensors provide vital data on pollutants such as NOx, CO, and hydrocarbons, facilitating compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Their precise detection capabilities enhance catalytic converter performance, resulting in significantly lower emission levels and improved air quality.
Placement and Function of Oxygen Sensors in Exhaust Systems
Upstream oxygen sensors are positioned before the catalytic converter to monitor the oxygen levels in exhaust gases, enabling precise air-fuel mixture adjustments for optimal combustion efficiency. Downstream oxygen sensors are installed after the catalytic converter to measure the converter's effectiveness in reducing emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Proper placement of these sensors is crucial for accurate emission control and engine performance monitoring.
Common Symptoms of Faulty Upstream and Downstream Sensors
Faulty upstream oxygen sensors often cause rough engine idling, increased fuel consumption, and elevated emissions due to incorrect air-fuel mixture readings. Downstream sensor issues commonly lead to failed emissions tests, delayed catalytic converter response, and persistent check engine light activation. Both sensor malfunctions can result in inefficient exhaust gas monitoring and compromised vehicle performance.
Diagnostic Tips: Testing Upstream vs Downstream Sensors
Testing upstream sensors involves monitoring oxygen levels before the catalytic converter to ensure accurate air-fuel mixture readings, which are critical for optimal engine performance and emissions control. Downstream sensor diagnostics focus on detecting the efficiency of the catalytic converter by measuring oxygen levels after the converter, identifying potential failures in emissions reduction. Using a scan tool to compare voltage fluctuations between upstream and downstream sensors allows technicians to pinpoint sensor malfunctions or catalytic converter issues effectively.
Replacing Upstream and Downstream Sensors: Best Practices
Replacing upstream and downstream emission sensors requires precise identification of sensor type and position within the exhaust system to ensure accurate readings. Best practices include using OEM-approved sensors, following manufacturer torque specifications, and performing post-installation diagnostic checks to verify sensor functionality and emission compliance. Proper calibration and avoiding contamination during replacement help maintain optimal sensor performance and vehicle emission standards.
Upstream Sensor vs Downstream Sensor Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com