A cracked head gasket causes coolant and oil to mix, leading to engine overheating and potential severe damage, while a warped cylinder head results from uneven heat distribution, causing poor sealing and compression loss. Diagnosing the issue requires careful inspection, as symptoms such as white smoke, engine misfires, and coolant leaks can indicate either problem. Repairing a cracked head gasket typically involves gasket replacement, whereas a warped cylinder head may need resurfacing or replacement to restore proper engine function.
Table of Comparison
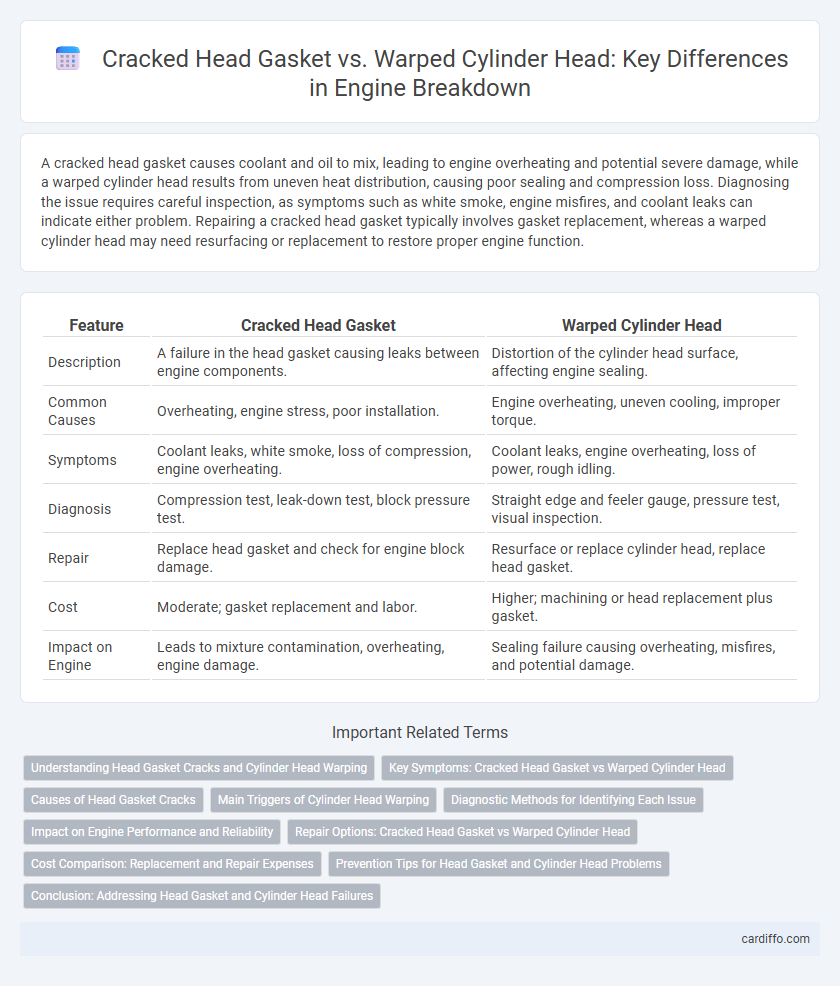
| Feature | Cracked Head Gasket | Warped Cylinder Head |
|---|---|---|
| Description | A failure in the head gasket causing leaks between engine components. | Distortion of the cylinder head surface, affecting engine sealing. |
| Common Causes | Overheating, engine stress, poor installation. | Engine overheating, uneven cooling, improper torque. |
| Symptoms | Coolant leaks, white smoke, loss of compression, engine overheating. | Coolant leaks, engine overheating, loss of power, rough idling. |
| Diagnosis | Compression test, leak-down test, block pressure test. | Straight edge and feeler gauge, pressure test, visual inspection. |
| Repair | Replace head gasket and check for engine block damage. | Resurface or replace cylinder head, replace head gasket. |
| Cost | Moderate; gasket replacement and labor. | Higher; machining or head replacement plus gasket. |
| Impact on Engine | Leads to mixture contamination, overheating, engine damage. | Sealing failure causing overheating, misfires, and potential damage. |
Understanding Head Gasket Cracks and Cylinder Head Warping
A cracked head gasket often results in coolant leakage, combustion gas escape, and engine overheating, signaling a compromised seal between the engine block and cylinder head. Warped cylinder heads, typically caused by excessive heat, lead to uneven surface contact, which can create gaps allowing coolant and oil to mix or further gasket damage. Diagnosing between a cracked head gasket and a warped cylinder head requires pressure testing and surface inspections to identify the primary issue affecting engine performance and reliability.
Key Symptoms: Cracked Head Gasket vs Warped Cylinder Head
Key symptoms of a cracked head gasket include white smoke from the exhaust, coolant loss without visible leaks, and engine overheating due to coolant leakage into combustion chambers. In contrast, a warped cylinder head typically causes engine misfires, rough idling, and persistent overheating due to improper sealing between the head and engine block. Both issues can lead to poor engine performance, but the presence of milky oil indicates a head gasket crack, while surface irregularities detected through a straight edge test point to a warped cylinder head.
Causes of Head Gasket Cracks
Head gasket cracks primarily occur due to engine overheating, which causes repeated thermal expansion and contraction, stressing the gasket material. Poor installation, manufacturing defects, and high engine combustion pressures also contribute to gasket failure by creating weak spots prone to cracking. Unlike warped cylinder heads that result from sustained heat distortion, cracked head gaskets signal localized damage compromising the sealing between the engine block and cylinder head.
Main Triggers of Cylinder Head Warping
Excessive engine overheating and prolonged exposure to high temperatures are the main triggers of cylinder head warping, causing metal expansion and distortion. Coolant leaks, especially from a failing head gasket, reduce cooling system efficiency and contribute to uneven heat distribution. Improper torque settings during head installation also increase the risk of warping by creating uneven pressure on the cylinder head surface.
Diagnostic Methods for Identifying Each Issue
Diagnosing a cracked head gasket involves a combustion leak test using a chemical test kit to detect exhaust gases in the coolant, while a compression test can reveal inconsistent cylinder pressure indicative of gasket failure. Warped cylinder heads are typically identified through a valve clearance inspection and by measuring the flatness of the cylinder head surface with a straight edge and feeler gauge. Infrared thermometers and pressure tests can further distinguish heat-related deformation from sealing issues specific to gasket cracks.
Impact on Engine Performance and Reliability
A cracked head gasket causes coolant and oil to mix, leading to overheating, loss of compression, and engine misfires that severely reduce performance and reliability. A warped cylinder head results in improper sealing between the head and engine block, causing similar symptoms such as coolant leaks and diminished compression, but often allows temporary operation before catastrophic failure. Both conditions demand immediate repair to prevent further engine damage and ensure consistent power output and longevity.
Repair Options: Cracked Head Gasket vs Warped Cylinder Head
Repair options for a cracked head gasket typically involve a full gasket replacement and thorough inspection for underlying engine damage. Warped cylinder heads require precision machining to restore flatness or complete replacement if warping exceeds repair limits. Choosing between repair or replacement depends on the extent of damage, with costs and engine performance impact guiding the decision.
Cost Comparison: Replacement and Repair Expenses
Repairing a cracked head gasket typically costs between $1,000 and $2,000, mainly due to labor-intensive gasket replacement and potential engine disassembly. Replacing or machining a warped cylinder head can range from $500 to $1,200, depending on the severity of warping and whether resurfacing or full replacement is required. Comparing expenses, a warped cylinder head repair is generally more affordable than addressing a cracked head gasket, but both repairs hinge on the vehicle make, model, and extent of damage.
Prevention Tips for Head Gasket and Cylinder Head Problems
Regularly monitor engine temperature and perform timely coolant flushes to prevent overheating, which reduces the risk of a cracked head gasket and warped cylinder head. Ensure proper torque specifications are followed when installing the head gasket to maintain a secure seal and avoid warping. Use high-quality engine oil and replace it on schedule to minimize wear and thermal stress on the cylinder head components.
Conclusion: Addressing Head Gasket and Cylinder Head Failures
Addressing head gasket failures requires prompt replacement to prevent coolant leaks and engine overheating that lead to severe engine damage. Warped cylinder head issues often demand precision machining or complete replacement to restore proper sealing and prevent loss of compression. Timely diagnosis and repair of both cracked head gaskets and warped cylinder heads are essential to maintain engine performance and avoid costly breakdowns.
cracked head gasket vs warped cylinder head Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com