Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by providing a high burst of power, essential for reliable ignition. Reserve Minutes indicate the duration a battery can supply a consistent power load if the vehicle's alternator fails, reflecting the battery's endurance. Understanding the balance between CCA for starting strength and Reserve Minutes for sustained power helps optimize battery performance based on specific vehicle needs.
Table of Comparison
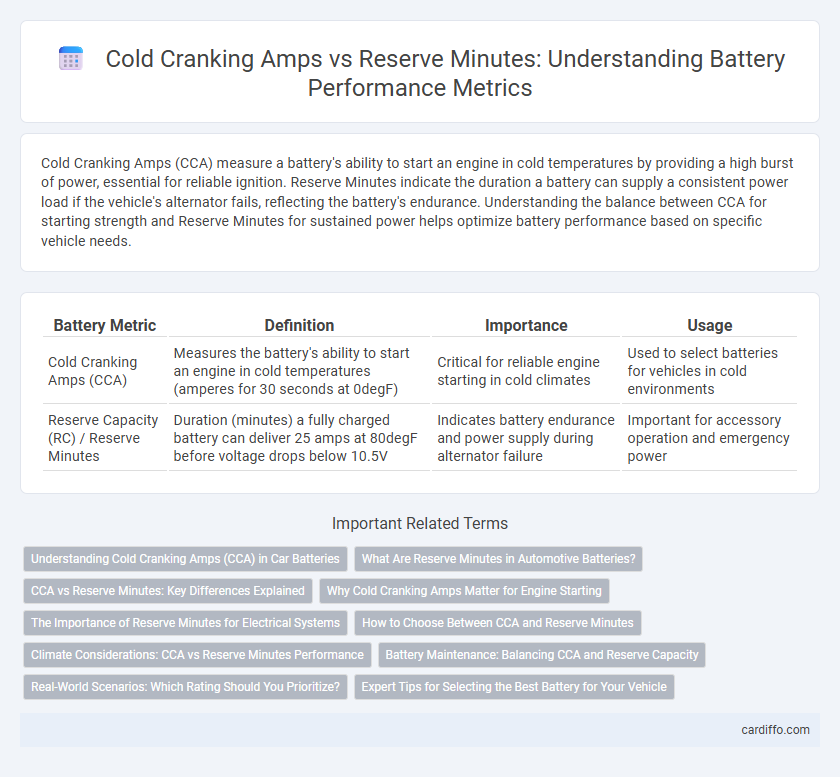
| Battery Metric | Definition | Importance | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) | Measures the battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures (amperes for 30 seconds at 0degF) | Critical for reliable engine starting in cold climates | Used to select batteries for vehicles in cold environments |
| Reserve Capacity (RC) / Reserve Minutes | Duration (minutes) a fully charged battery can deliver 25 amps at 80degF before voltage drops below 10.5V | Indicates battery endurance and power supply during alternator failure | Important for accessory operation and emergency power |
Understanding Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) in Car Batteries
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a car battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of current at 0degF (-18degC) for 30 seconds without dropping below 7.2 volts. This specification is crucial for ensuring reliable engine starts in winter conditions, as higher CCA ratings correlate with better low-temperature performance. Unlike Reserve Capacity, which indicates how long a battery can supply power if the alternator fails, CCA specifically focuses on cold-start power demands.
What Are Reserve Minutes in Automotive Batteries?
Reserve minutes in automotive batteries indicate the duration a fully charged battery can maintain a minimum voltage necessary to operate a vehicle's electrical system without the engine running, typically measured in minutes. This rating reflects the battery's ability to provide sustained power during emergencies, such as when the alternator fails or during extended use of accessories. Unlike Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), which measure the battery's starting power in cold temperatures, reserve minutes assess the battery's endurance under continuous load conditions.
CCA vs Reserve Minutes: Key Differences Explained
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures by delivering a high burst of current, whereas Reserve Minutes represent the duration a battery can power essential systems if the alternator fails. CCA focuses on immediate power output crucial for ignition, while Reserve Minutes indicate the battery's endurance under continuous load. Understanding these key differences helps in selecting a battery that meets both starting performance and backup power needs.
Why Cold Cranking Amps Matter for Engine Starting
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to deliver a high burst of current at low temperatures, directly impacting engine starting performance in cold weather. Higher CCA ratings ensure reliable ignition by providing sufficient power to turn the engine over despite battery capacity reduction in freezing conditions. Reserve Minutes indicate how long a battery can run essential vehicle systems without the engine but do not influence the initial power needed for cold starts.
The Importance of Reserve Minutes for Electrical Systems
Reserve Minutes indicate how long a battery can power a vehicle's electrical system without the engine running, crucial for maintaining functions like lights, radio, and onboard computers during engine off periods. This metric ensures reliability during power interruptions, preventing system failures and preserving essential electronics. Unlike Cold Cranking Amps, which measure starting power, Reserve Minutes reflect continuous energy supply critical for modern vehicles' electrical demands.
How to Choose Between CCA and Reserve Minutes
Choosing between Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Reserve Minutes depends on the vehicle's climate and usage needs; CCA is crucial for cold weather performance, ensuring the battery can start the engine in low temperatures. Reserve Minutes indicate how long the battery can power essential systems if the alternator fails, benefiting drivers who require reliable backup during extended electrical demands. Assessing local climate and driving habits helps determine whether starting power or sustained energy reserve is more critical for optimal battery selection.
Climate Considerations: CCA vs Reserve Minutes Performance
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measure a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making them crucial for harsh winter climates where freezing conditions require high starting power. Reserve Minutes indicate how long a battery can sustain a minimum voltage without engine power, which is essential in warmer climates where prolonged accessory use or occasional engine failures are more common. Understanding the balance between CCA and Reserve Minutes helps optimize battery performance based on regional climate demands, ensuring reliability and longevity.
Battery Maintenance: Balancing CCA and Reserve Capacity
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) indicate a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, while Reserve Minutes measure how long a battery can power a vehicle's electrical system if the alternator fails. Proper battery maintenance requires balancing high CCA for reliable cold-start performance with sufficient Reserve Capacity to ensure prolonged operation during power interruptions. Regular testing and monitoring of both CCA and Reserve Capacity help optimize battery lifespan and vehicle reliability.
Real-World Scenarios: Which Rating Should You Prioritize?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, making it crucial for vehicles in winter climates, while Reserve Capacity (RC) indicates how long the battery can power accessories if the alternator fails, important for extended power needs. For drivers in cold regions, CCA should be prioritized to ensure reliable engine starts in freezing conditions, whereas in warmer areas or for vehicles with high electrical demands, RC becomes more critical. Understanding your local climate and electrical usage helps determine whether Cold Cranking Amps or Reserve Capacity better suits your battery performance requirements.
Expert Tips for Selecting the Best Battery for Your Vehicle
When selecting the best battery for your vehicle, focus on Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) to ensure reliable engine starts in low temperatures, with a higher CCA rating indicating stronger starting power. Reserve Minutes measure how long the battery can power essential functions if the alternator fails, making it crucial for maintaining electrical systems during extended outages. Expert tips recommend matching or exceeding your vehicle manufacturer's CCA specifications while balancing Reserve Minutes based on your driving environment and climate conditions.
Cold Cranking Amps vs Reserve Minutes Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com