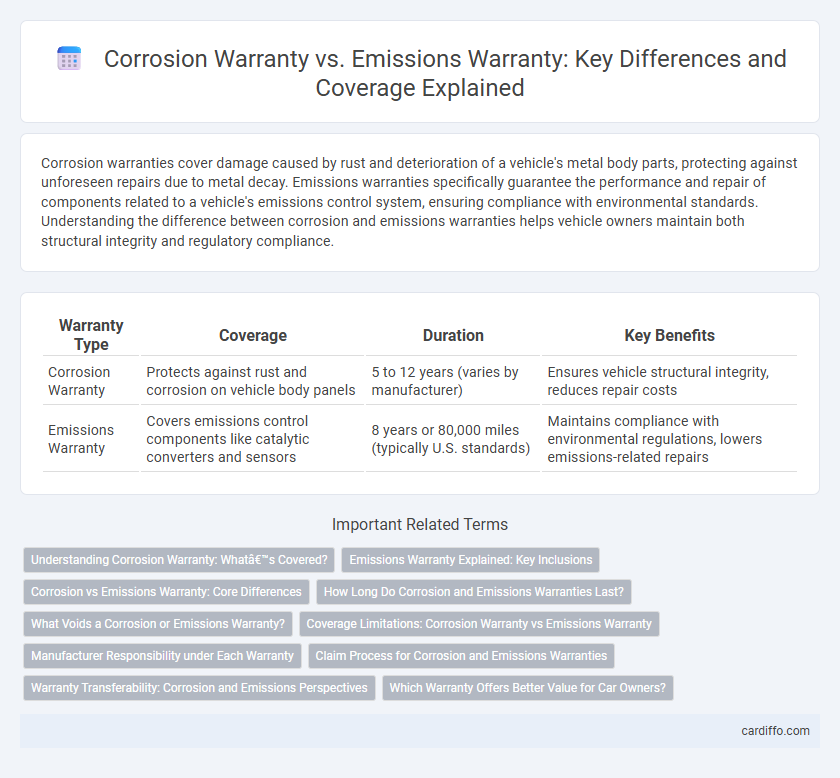
Corrosion warranties cover damage caused by rust and deterioration of a vehicle's metal body parts, protecting against unforeseen repairs due to metal decay. Emissions warranties specifically guarantee the performance and repair of components related to a vehicle's emissions control system, ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Understanding the difference between corrosion and emissions warranties helps vehicle owners maintain both structural integrity and regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
| Warranty Type | Coverage | Duration | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Warranty | Protects against rust and corrosion on vehicle body panels | 5 to 12 years (varies by manufacturer) | Ensures vehicle structural integrity, reduces repair costs |
| Emissions Warranty | Covers emissions control components like catalytic converters and sensors | 8 years or 80,000 miles (typically U.S. standards) | Maintains compliance with environmental regulations, lowers emissions-related repairs |
Understanding Corrosion Warranty: What’s Covered?
Corrosion warranty specifically covers rust and corrosion damage to a vehicle's metal components, typically including perforation or rust-through on body panels, frame, and structural parts. Unlike emissions warranty that protects against failures in emission control systems like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors, corrosion warranty addresses long-term exposure effects such as weather, salt, and moisture causing metal deterioration. Understanding the precise terms and duration of corrosion warranty helps vehicle owners safeguard against costly repairs related to body corrosion beyond normal wear and tear.
Emissions Warranty Explained: Key Inclusions
Emissions warranty covers critical components that control a vehicle's pollution output, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and engine control modules, ensuring compliance with environmental standards. This warranty typically lasts 8 years or 80,000 miles, protecting against defects that cause increased emissions or engine performance issues. Unlike corrosion warranty which focuses on rust and body integrity, emissions warranty guarantees the vehicle meets regulatory air quality requirements throughout the coverage period.
Corrosion vs Emissions Warranty: Core Differences
Corrosion warranty primarily covers protection against rust and metal deterioration in vehicle body panels, typically lasting longer than emissions warranty periods, which focus on ensuring compliance with environmental standards by covering components related to the vehicle's exhaust and emission control systems. Emissions warranties mandate repair or replacement of parts like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors to maintain regulatory pollution limits, whereas corrosion warranties address structural integrity by preventing perforation and damage caused by rust. Understanding these core differences helps vehicle owners prioritize maintenance and claims based on the nature of potential defects and regulatory requirements.
How Long Do Corrosion and Emissions Warranties Last?
Corrosion warranties typically last between 5 to 12 years, covering rust-through repairs on vehicle panels, while emissions warranties vary from 2 to 8 years, protecting components like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors. Federal regulations in the U.S. mandate emissions warranty coverage for at least 2 years or 24,000 miles, with specific components covered up to 8 years or 80,000 miles. Understanding the duration differences helps consumers assess long-term protection against rust damage and pollution-control system repairs.
What Voids a Corrosion or Emissions Warranty?
Corrosion warranties are voided by neglecting proper vehicle maintenance or using incompatible repairs and coatings that accelerate rust formation. Emissions warranties become void if unauthorized modifications are made to the engine or exhaust system, or if the vehicle operates with defective emission control components. Both warranties require adherence to manufacturer-recommended service schedules and use of approved parts to remain valid.
Coverage Limitations: Corrosion Warranty vs Emissions Warranty
Corrosion warranty typically covers rust and perforation issues in vehicle body panels for a specified duration or mileage, excluding surface rust and damage caused by accidents or modifications. Emissions warranty guarantees that emission control components will function properly to comply with environmental regulations, often covering parts like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors but not issues arising from misuse or external damage. Coverage limitations for corrosion warranty often center on physical deterioration due to environmental exposure, whereas emissions warranty limits focus on functional performance affecting regulatory compliance.
Manufacturer Responsibility under Each Warranty
Manufacturer responsibility under a corrosion warranty typically includes repairing or replacing vehicle components affected by rust or perforation caused by defects in materials or workmanship within a specified time frame or mileage limit. In contrast, emissions warranty obligations require manufacturers to ensure vehicle compliance with environmental standards by covering repairs of emission control components like catalytic converters or oxygen sensors for a defined period, often regulated by government agencies. Both warranties mandate manufacturers to uphold vehicle reliability and regulatory compliance, but corrosion warranties focus on durability against physical degradation, while emissions warranties emphasize environmental performance.
Claim Process for Corrosion and Emissions Warranties
The claim process for Corrosion Warranty requires documentation of visible rust or perforation on the vehicle's body panels, often necessitating a vehicle inspection by an authorized dealer to verify the issue. Emissions Warranty claims involve diagnostic tests performed on the vehicle's emission control system to confirm component failure or malfunction within the coverage period, usually handled through specialized service centers. Both warranties require timely submission of service records and completion of repairs by certified technicians to qualify for coverage under the manufacturer's terms.
Warranty Transferability: Corrosion and Emissions Perspectives
Corrosion warranty transferability typically varies by manufacturer but often extends to subsequent vehicle owners within a specified time or mileage limit, ensuring continued protection against rust damage. Emissions warranties are federally mandated to be transferable to all vehicle owners during the coverage period, supporting environmental compliance across ownership changes. Understanding these distinct transfer policies helps consumers maximize warranty benefits and maintain both vehicle integrity and regulatory adherence.
Which Warranty Offers Better Value for Car Owners?
Corrosion warranties typically cover the vehicle's body panels against rust and perforation for a period ranging from 5 to 12 years, offering peace of mind for long-term vehicle durability. Emissions warranties ensure compliance with environmental regulations by covering critical components like the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and engine control devices, usually for 8 years or 80,000 miles. For car owners prioritizing cost savings and vehicle longevity, corrosion warranties often provide better value, whereas emissions warranties are essential for regulatory compliance and avoiding costly repairs related to pollution control systems.
Corrosion Warranty vs Emissions Warranty Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com