Peak hour tolling imposes higher charges during periods of maximum traffic congestion to manage demand and reduce road overcrowding. Off-peak tolling offers reduced rates during less busy times, encouraging drivers to travel outside peak hours and improving traffic flow. Strategic implementation of these tolling methods optimizes road usage and minimizes congestion-related delays.
Table of Comparison
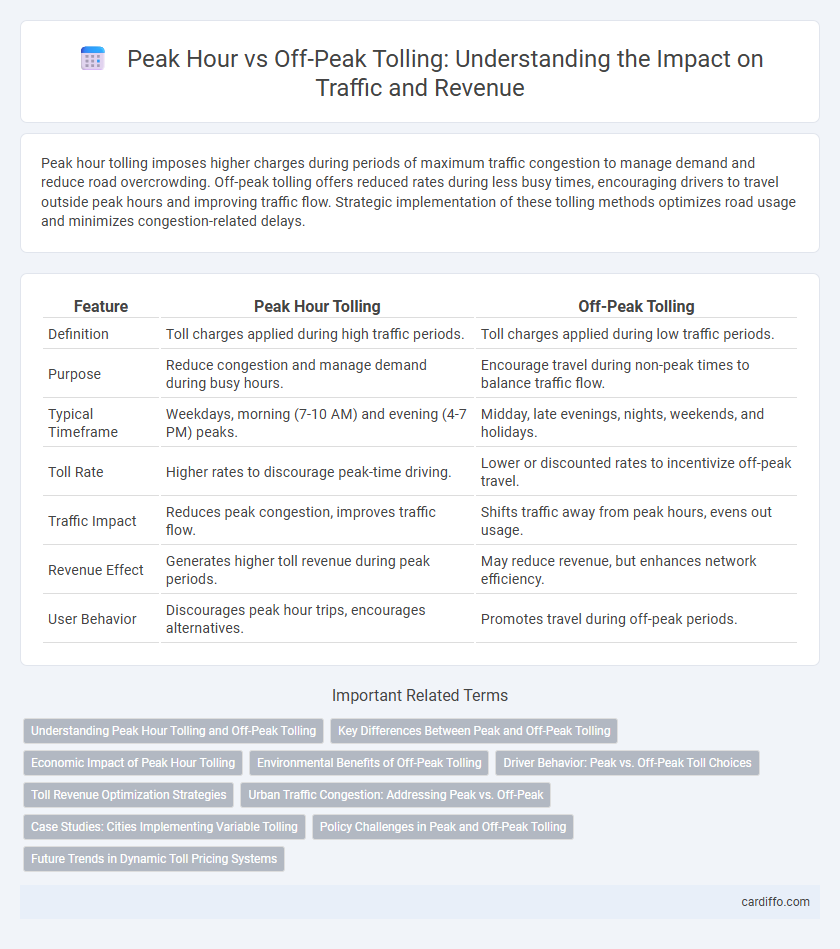
| Feature | Peak Hour Tolling | Off-Peak Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toll charges applied during high traffic periods. | Toll charges applied during low traffic periods. |
| Purpose | Reduce congestion and manage demand during busy hours. | Encourage travel during non-peak times to balance traffic flow. |
| Typical Timeframe | Weekdays, morning (7-10 AM) and evening (4-7 PM) peaks. | Midday, late evenings, nights, weekends, and holidays. |
| Toll Rate | Higher rates to discourage peak-time driving. | Lower or discounted rates to incentivize off-peak travel. |
| Traffic Impact | Reduces peak congestion, improves traffic flow. | Shifts traffic away from peak hours, evens out usage. |
| Revenue Effect | Generates higher toll revenue during peak periods. | May reduce revenue, but enhances network efficiency. |
| User Behavior | Discourages peak hour trips, encourages alternatives. | Promotes travel during off-peak periods. |
Understanding Peak Hour Tolling and Off-Peak Tolling
Peak hour tolling charges higher fees during periods of maximum traffic congestion, typically morning and evening rush hours, to manage demand and reduce road congestion. Off-peak tolling applies lower rates during times of lighter traffic, encouraging travelers to shift trips outside busy periods and optimizing traffic flow. Understanding these tolling strategies helps cities balance transportation efficiency and revenue generation while minimizing congestion-related delays.
Key Differences Between Peak and Off-Peak Tolling
Peak hour tolling imposes higher charges during designated rush hours to manage traffic congestion and encourage off-peak travel. Off-peak tolling offers reduced rates during non-peak times, promoting smoother traffic flow and cost savings for drivers traveling during less busy periods. The key difference lies in pricing strategy and traffic regulation focus, with peak tolling targeting congestion control and off-peak tolling incentivizing flexible travel times.
Economic Impact of Peak Hour Tolling
Peak hour tolling generates significant economic benefits by reducing congestion, which lowers travel time costs and enhances productivity for commuters and businesses alike. By shifting traffic away from peak periods, toll revenues can be reinvested into infrastructure improvements, supporting long-term economic growth. However, increased toll costs during peak hours may disproportionately affect lower-income drivers, potentially necessitating targeted subsidies or alternative transport options to mitigate economic inequality.
Environmental Benefits of Off-Peak Tolling
Off-peak tolling reduces traffic congestion and vehicle emissions by encouraging drivers to travel during less crowded times, leading to lower overall air pollution. It helps decrease greenhouse gas emissions and improves urban air quality by minimizing idling and stop-and-go traffic typical of peak hours. This shift supports sustainable transportation goals and contributes to healthier, more livable cities.
Driver Behavior: Peak vs. Off-Peak Toll Choices
Drivers tend to alter their route and departure time decisions based on toll pricing during peak hours, often opting for alternative routes or delaying trips to avoid higher peak hour tolls. Off-peak tolling encourages more consistent traffic distribution as lower fees incentivize travel during less congested times, reducing overall congestion. Behavioral patterns show increased elasticity in trip timing, with many drivers shifting travel to off-peak periods to minimize toll expenses and commute stress.
Toll Revenue Optimization Strategies
Peak hour tolling maximizes revenue by charging higher rates during periods of greatest traffic congestion, effectively managing demand and increasing toll income. Off-peak tolling encourages travel during less congested times with reduced rates, optimizing roadway usage and supporting steady cash flow throughout the day. Combining dynamic pricing models with real-time traffic data enhances toll revenue optimization by balancing traffic distribution and maximizing overall collection efficiency.
Urban Traffic Congestion: Addressing Peak vs. Off-Peak
Peak hour tolling strategically targets urban traffic congestion by imposing higher fees during the busiest travel periods, effectively discouraging non-essential trips and alleviating roadway overcrowding. Off-peak tolling offers reduced rates that encourage travel during less congested times, optimizing traffic distribution throughout the day and enhancing overall urban mobility. Implementing dynamic toll pricing based on real-time traffic data can further balance demand, reducing congestion-related delays and improving air quality in densely populated city centers.
Case Studies: Cities Implementing Variable Tolling
Cities like Los Angeles and Singapore have successfully implemented peak hour tolling to reduce congestion during rush hours, demonstrating significant improvements in traffic flow and commuter behavior. Off-peak tolling in Stockholm has shown increased road usage efficiency while maintaining environmental benefits by encouraging travel during less congested times. These case studies highlight how variable tolling systems can optimize urban mobility and revenue generation based on real-time traffic data and demand patterns.
Policy Challenges in Peak and Off-Peak Tolling
Peak hour tolling policies face challenges related to congestion management and public acceptance, as higher fees may disproportionately affect lower-income commuters and lead to political resistance. Off-peak tolling encounters difficulties in maintaining revenue stability and incentivizing traffic distribution without causing underutilization during non-peak times. Both approaches require careful calibration of toll rates and investment in alternative transit options to balance traffic flow and equity concerns effectively.
Future Trends in Dynamic Toll Pricing Systems
Future trends in dynamic toll pricing systems emphasize real-time data integration and AI-driven algorithms to optimize peak hour and off-peak toll rates, enhancing traffic flow and reducing congestion. Advanced sensor networks and machine learning models enable adaptive toll adjustments based on vehicle density, time of day, and environmental factors. These innovations aim to balance road usage, promote sustainability, and improve revenue efficiency in urban transportation networks.
Peak Hour Tolling vs Off-Peak Tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com