Congestion pricing targets high-traffic areas during peak times to reduce traffic volume and improve flow, charging drivers based on demand. Distance-based tolling charges drivers according to the miles traveled, encouraging efficient use of road networks regardless of time. Both methods aim to manage road usage but differ in pricing strategy and impact on driver behavior.
Table of Comparison
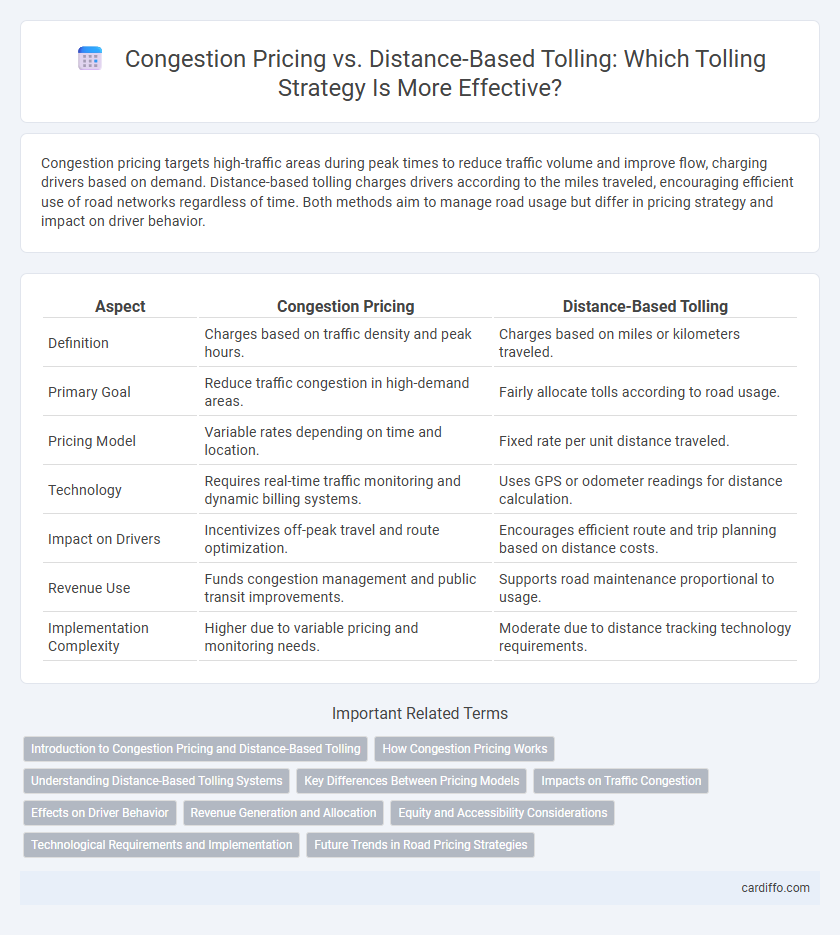
| Aspect | Congestion Pricing | Distance-Based Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Charges based on traffic density and peak hours. | Charges based on miles or kilometers traveled. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce traffic congestion in high-demand areas. | Fairly allocate tolls according to road usage. |
| Pricing Model | Variable rates depending on time and location. | Fixed rate per unit distance traveled. |
| Technology | Requires real-time traffic monitoring and dynamic billing systems. | Uses GPS or odometer readings for distance calculation. |
| Impact on Drivers | Incentivizes off-peak travel and route optimization. | Encourages efficient route and trip planning based on distance costs. |
| Revenue Use | Funds congestion management and public transit improvements. | Supports road maintenance proportional to usage. |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher due to variable pricing and monitoring needs. | Moderate due to distance tracking technology requirements. |
Introduction to Congestion Pricing and Distance-Based Tolling
Congestion pricing charges drivers based on the time and location to reduce traffic during peak hours, improving road efficiency by managing demand. Distance-based tolling calculates fees according to the miles traveled, promoting fairness by directly linking costs to road usage. Both methods aim to optimize traffic flow, reduce emissions, and fund infrastructure maintenance.
How Congestion Pricing Works
Congestion pricing works by charging drivers variable fees based on traffic levels during peak hours to reduce road congestion and encourage off-peak travel. Sensors and cameras monitor real-time traffic flow, allowing toll rates to adjust dynamically according to demand, with higher prices deterring excess vehicles on crowded roads. This approach improves travel speed, decreases emissions, and optimizes road capacity compared to distance-based tolling, which charges users solely based on mileage traveled.
Understanding Distance-Based Tolling Systems
Distance-based tolling systems charge drivers based on the exact miles traveled on a tolled road, using GPS or electronic transponders to calculate fees accurately. This method promotes fairer pricing by reflecting actual road usage and helps reduce traffic congestion by incentivizing shorter trips or off-peak travel. Compared to congestion pricing, distance-based tolling offers precise revenue generation for infrastructure maintenance and improved traffic management aligned with travel behavior.
Key Differences Between Pricing Models
Congestion pricing charges drivers higher fees during peak traffic times to reduce road overcrowding, whereas distance-based tolling calculates fees based on the miles traveled regardless of time. Congestion pricing targets demand management by incentivizing off-peak travel, while distance-based tolling emphasizes fairness by charging users proportionally to their road usage. These models differ fundamentally in balancing traffic reduction goals versus equitable cost distribution for infrastructure maintenance.
Impacts on Traffic Congestion
Congestion pricing directly targets peak traffic demand by charging higher fees during busy periods, effectively reducing traffic volumes and smoothing flow in urban areas. Distance-based tolling charges drivers based on the miles traveled, which can encourage shorter trips and distribute traffic more evenly across a network but may have less immediate impact on rush-hour congestion. Studies show congestion pricing often leads to significant decreases in traffic delays and emissions in downtown zones, while distance-based tolling supports equitable road usage and long-term congestion management.
Effects on Driver Behavior
Congestion pricing directly influences driver behavior by charging higher tolls during peak traffic periods, encouraging commuters to travel during off-peak hours or use alternative routes to avoid fees. Distance-based tolling motivates drivers to reduce total travel distance, promoting shorter trips and potential shifts to public transportation or carpooling. Both pricing strategies effectively manage traffic demand but target different behavioral adjustments to optimize road usage and reduce congestion.
Revenue Generation and Allocation
Congestion pricing maximizes revenue generation by charging dynamic fees based on real-time traffic demand, effectively reducing peak-hour congestion while allocating funds toward public transit and infrastructure improvements. Distance-based tolling generates consistent revenue by charging drivers according to miles traveled, incentivizing efficient route usage and enabling equitable distribution of toll revenues for highway maintenance and expansion projects. Both systems optimize revenue streams differently; congestion pricing targets demand management, whereas distance-based tolling emphasizes fairness and infrastructure funding stability.
Equity and Accessibility Considerations
Congestion pricing targets urban traffic hotspots by charging vehicles during peak times to reduce central area congestion, but it can disproportionately impact low-income drivers who may lack flexible travel options. Distance-based tolling charges drivers based on miles traveled, promoting fairness by linking fees directly to road usage while enabling variable rates that consider socioeconomic factors and vehicle types. Implementing equity-focused exemptions or subsidies in both models enhances accessibility for vulnerable populations, ensuring transportation affordability without compromising congestion reduction goals.
Technological Requirements and Implementation
Congestion pricing systems rely heavily on real-time traffic monitoring technologies such as sensors and cameras to dynamically adjust toll rates based on traffic flow, requiring advanced data analytics platforms and robust communication networks. Distance-based tolling uses GPS or automated vehicle identification systems to track vehicle mileage, demanding precise location tracking technologies and strong data security measures. Implementation of either system involves substantial investments in infrastructure, integration with existing road management systems, and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Future Trends in Road Pricing Strategies
Congestion pricing and distance-based tolling are evolving as key components in future road pricing strategies, offering dynamic solutions to urban traffic management. Advanced technologies like GPS and real-time data analytics enable more precise and adaptive tolling systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing congestion. Cities worldwide are increasingly adopting these models to promote sustainable mobility and optimize infrastructure usage.
Congestion pricing vs distance-based tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com