HOV lane tolling offers a dynamic pricing model that prioritizes traffic flow by charging single-occupancy vehicles while allowing high-occupancy vehicles free or reduced-rate access, promoting carpooling and reducing congestion. General lane tolling applies a uniform fee to all vehicles regardless of occupancy, potentially leading to slower traffic movement and less incentive for ridesharing. By targeting tolls based on vehicle occupancy, HOV lane tolling enhances traffic efficiency and environmental benefits compared to traditional general lane tolling systems.
Table of Comparison
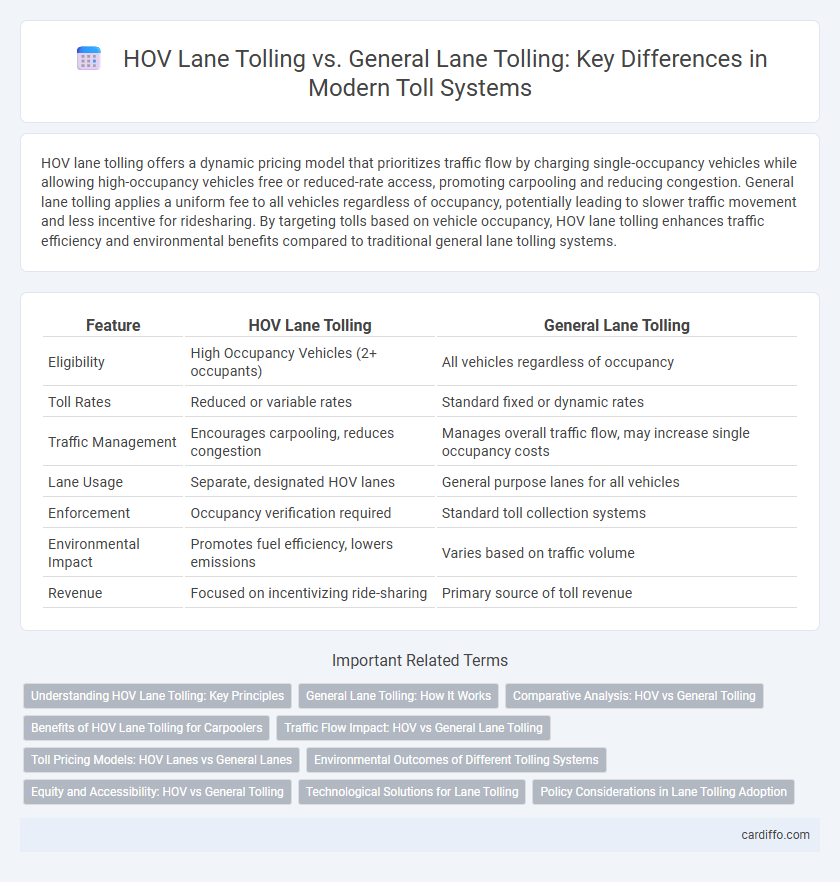
| Feature | HOV Lane Tolling | General Lane Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | High Occupancy Vehicles (2+ occupants) | All vehicles regardless of occupancy |
| Toll Rates | Reduced or variable rates | Standard fixed or dynamic rates |
| Traffic Management | Encourages carpooling, reduces congestion | Manages overall traffic flow, may increase single occupancy costs |
| Lane Usage | Separate, designated HOV lanes | General purpose lanes for all vehicles |
| Enforcement | Occupancy verification required | Standard toll collection systems |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes fuel efficiency, lowers emissions | Varies based on traffic volume |
| Revenue | Focused on incentivizing ride-sharing | Primary source of toll revenue |
Understanding HOV Lane Tolling: Key Principles
HOV lane tolling charges vehicles based on occupancy to maintain traffic flow and encourage carpooling, optimizing highway efficiency. Unlike general lane tolling where all vehicles pay, HOV tolls often apply variable rates depending on occupancy, time, and congestion levels. This strategic pricing reduces single-occupancy vehicle use, lowers emissions, and improves overall transportation sustainability.
General Lane Tolling: How It Works
General lane tolling uses electronic toll collection systems such as RFID transponders and automatic license plate recognition to charge all vehicles passing through toll points without requiring lane changes or stops. Cameras and sensors record vehicle information, enabling seamless toll deduction from prepaid accounts or billing by mail for non-registered users. This method minimizes traffic disruption and supports dynamic pricing based on congestion levels and time of day.
Comparative Analysis: HOV vs General Tolling
HOV lane tolling typically targets single-occupancy vehicles entering high-occupancy vehicle lanes, using dynamic pricing to manage congestion and incentivize carpooling, whereas general lane tolling applies uniform charges across all lanes regardless of occupancy. Studies show HOV lane tolling can reduce traffic volumes by up to 30% during peak hours compared to general tolling, enhancing traffic flow efficiency and decreasing commute times. Revenue from HOV lane tolling tends to be more variable due to occupancy-based exemptions, while general lane tolling provides a steadier income stream, facilitating infrastructure funding.
Benefits of HOV Lane Tolling for Carpoolers
HOV lane tolling offers significant benefits for carpoolers by providing reduced or waived toll fees, encouraging shared rides and decreasing overall traffic congestion. This targeted tolling system enhances travel time reliability for high-occupancy vehicles while promoting environmental sustainability through lower emissions. By prioritizing carpoolers, HOV lane tolling improves commute efficiency and supports transportation equity.
Traffic Flow Impact: HOV vs General Lane Tolling
HOV lane tolling maintains smoother traffic flow by incentivizing carpooling and reducing vehicle density in high-occupancy lanes, which helps decrease congestion during peak hours. General lane tolling evenly distributes traffic across all lanes but can lead to increased overall bottlenecks as vehicles slow down or change lanes to avoid toll charges. Traffic management studies show that HOV tolling improves travel times by up to 20% compared to general tolling methods, enhancing commuter efficiency and reducing emissions.
Toll Pricing Models: HOV Lanes vs General Lanes
Toll pricing models for HOV lanes typically incorporate dynamic pricing strategies to encourage carpooling and reduce congestion, often charging solo drivers higher rates during peak hours. General lanes usually employ fixed or variable toll rates based on traffic volume, without differentiating vehicle occupancy. These pricing distinctions optimize traffic flow and maximize revenue while promoting efficient use of HOV lanes.
Environmental Outcomes of Different Tolling Systems
HOV lane tolling reduces vehicle emissions more effectively by encouraging carpooling and lowering single-occupancy vehicle traffic, resulting in decreased air pollution and greenhouse gas output. General lane tolling tends to maintain higher overall traffic volumes, leading to increased congestion and elevated emissions from idling vehicles. Implementing HOV tolling systems can enhance environmental benefits by improving traffic flow and promoting sustainable transportation choices.
Equity and Accessibility: HOV vs General Tolling
HOV lane tolling promotes equity by providing discounted or free access to carpoolers, encouraging ridesharing and reducing overall congestion, which benefits lower-income commuters who rely on shared transportation. General lane tolling imposes uniform charges that can disproportionately impact low-income drivers who may have no viable alternatives to single-occupancy vehicle travel. Ensuring affordable access to HOV lanes through variable or reduced toll rates enhances transportation accessibility and supports social equity objectives.
Technological Solutions for Lane Tolling
HOV lane tolling leverages advanced technologies such as transponders, electronic toll collection (ETC) systems, and real-time vehicle classification sensors to enforce occupancy requirements while maintaining traffic flow. General lane tolling primarily utilizes RFID and automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) systems integrated with dynamic pricing algorithms for efficient toll collection based on vehicle type and congestion levels. Both solutions increasingly deploy machine learning and AI for fraud detection, occupancy verification, and adaptive toll pricing to optimize road usage and reduce congestion.
Policy Considerations in Lane Tolling Adoption
HOV lane tolling policy must balance efficiency improvements with equity concerns, ensuring that toll rates do not disproportionately impact low-income commuters. General lane tolling often generates higher revenue but may exacerbate congestion disparities and environmental impacts compared to managed HOV lanes. Policymakers must consider regional traffic patterns, enforcement costs, and public acceptance when adopting tolling strategies to optimize both transportation funding and mobility outcomes.
HOV lane tolling vs general lane tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com