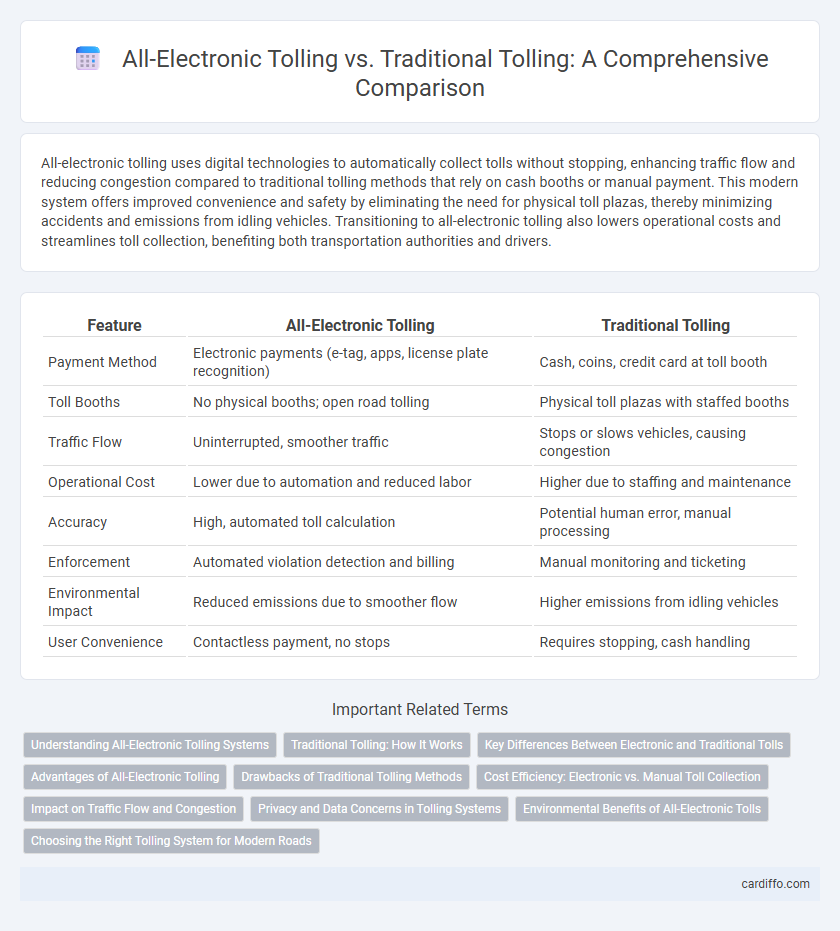
All-electronic tolling uses digital technologies to automatically collect tolls without stopping, enhancing traffic flow and reducing congestion compared to traditional tolling methods that rely on cash booths or manual payment. This modern system offers improved convenience and safety by eliminating the need for physical toll plazas, thereby minimizing accidents and emissions from idling vehicles. Transitioning to all-electronic tolling also lowers operational costs and streamlines toll collection, benefiting both transportation authorities and drivers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | All-Electronic Tolling | Traditional Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Method | Electronic payments (e-tag, apps, license plate recognition) | Cash, coins, credit card at toll booth |
| Toll Booths | No physical booths; open road tolling | Physical toll plazas with staffed booths |
| Traffic Flow | Uninterrupted, smoother traffic | Stops or slows vehicles, causing congestion |
| Operational Cost | Lower due to automation and reduced labor | Higher due to staffing and maintenance |
| Accuracy | High, automated toll calculation | Potential human error, manual processing |
| Enforcement | Automated violation detection and billing | Manual monitoring and ticketing |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced emissions due to smoother flow | Higher emissions from idling vehicles |
| User Convenience | Contactless payment, no stops | Requires stopping, cash handling |
Understanding All-Electronic Tolling Systems
All-electronic tolling systems utilize advanced technologies such as RFID transponders, automatic license plate recognition cameras, and real-time payment processing to eliminate the need for physical toll booths. These systems enable seamless traffic flow by allowing vehicles to pass through toll points without stopping, reducing congestion and emissions. Compared to traditional tolling, all-electronic tolling enhances efficiency, improves user convenience, and supports dynamic pricing models for better traffic management.
Traditional Tolling: How It Works
Traditional tolling operates through physical toll booths where drivers stop or slow down to pay tolls using cash, coins, or electronic cards. Toll collectors manually process payments, and automatic systems like RFID or barcode readers may assist, though physical interaction remains necessary. This method can cause traffic congestion and delays due to the need for vehicles to stop or reduce speed at toll plazas.
Key Differences Between Electronic and Traditional Tolls
Electronic tolling utilizes RFID tags, camera recognition, and automated billing to enable seamless, cashless toll payments, significantly reducing traffic congestion and operational costs. Traditional tolling relies on physical toll booths with cash or card payments, often causing delays and requiring higher labor expenses. The accuracy and convenience of electronic toll systems enhance traffic flow efficiency and enable data-driven traffic management compared to manual, labor-intensive traditional toll collection methods.
Advantages of All-Electronic Tolling
All-electronic tolling (AET) eliminates the need for physical toll booths, reducing traffic congestion and improving travel time reliability on highways. It enhances safety by minimizing collision risks associated with stopping or slowing down at toll plazas and promotes environmental benefits through decreased vehicle emissions. AET systems leverage modern technologies like RFID and automatic license plate recognition to provide seamless, cashless transactions that increase operational efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Drawbacks of Traditional Tolling Methods
Traditional tolling methods cause significant traffic congestion due to manual payment processing, leading to increased fuel consumption and emissions. The reliance on physical toll booths results in higher operational costs, including staffing and maintenance expenses. These systems also face challenges with toll evasion and inaccuracies in fee collection, reducing overall revenue efficiency.
Cost Efficiency: Electronic vs. Manual Toll Collection
All-electronic tolling significantly reduces operational expenses by eliminating the need for physical toll booths and cash handling, leading to lower labor and maintenance costs compared to traditional manual toll collection. Electronic toll collection systems utilize RFID and license plate recognition technology, improving transaction speed and accuracy while minimizing revenue leakage. Studies show that all-electronic tolling can cut costs by up to 60%, making it a more cost-efficient solution for highway authorities and transportation agencies.
Impact on Traffic Flow and Congestion
All-electronic tolling significantly improves traffic flow by eliminating the need for vehicles to stop or slow down at toll plazas, reducing bottlenecks and congestion during peak hours. Traditional tolling systems often cause delays due to manual payment processing, leading to increased fuel consumption and emissions. By streamlining toll collection, all-electronic systems enhance overall roadway efficiency and lessen traffic-related environmental impact.
Privacy and Data Concerns in Tolling Systems
All-electronic tolling systems collect extensive vehicle and driver data through transponders and license plate recognition, raising significant privacy concerns compared to traditional tolling methods that require physical transactions. The continuous data capture in all-electronic tolling can lead to unauthorized tracking, data breaches, and potential misuse of personal information by third parties. Enhanced encryption protocols and strict data governance are essential to mitigate privacy risks inherent in automated toll collection systems.
Environmental Benefits of All-Electronic Tolls
All-electronic tolling (AET) significantly reduces vehicle idling time at toll plazas, leading to lower carbon emissions and improved air quality compared to traditional tolling methods. The seamless, non-stop transaction process decreases fuel consumption by minimizing stop-and-go traffic congestion. Studies indicate that highways with AET experience up to a 30% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to sustainable transportation goals.
Choosing the Right Tolling System for Modern Roads
All-electronic tolling (AET) leverages advanced sensor and camera technology to process payments without stopping, reducing congestion and emissions on busy highways. Traditional tolling systems require physical toll booths and manual or automated payment collection, leading to slower traffic flow and higher operational costs. Selecting the right tolling system depends on factors like traffic volume, infrastructure costs, and user convenience, with AET increasingly favored for modern roads due to its efficiency and scalability.
All-Electronic Tolling vs Traditional Tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com