Tire siping significantly enhances traction by creating additional biting edges that improve grip on wet, icy, or snowy surfaces, reducing the risk of hydroplaning and slips. Tires without siping tend to have smoother tread blocks, which may offer better performance on dry roads but lack the extra traction needed for challenging conditions. Choosing between siped and non-siped tires depends on the typical driving environment, prioritizing safety in variable weather versus optimized wear and handling on dry pavement.
Table of Comparison
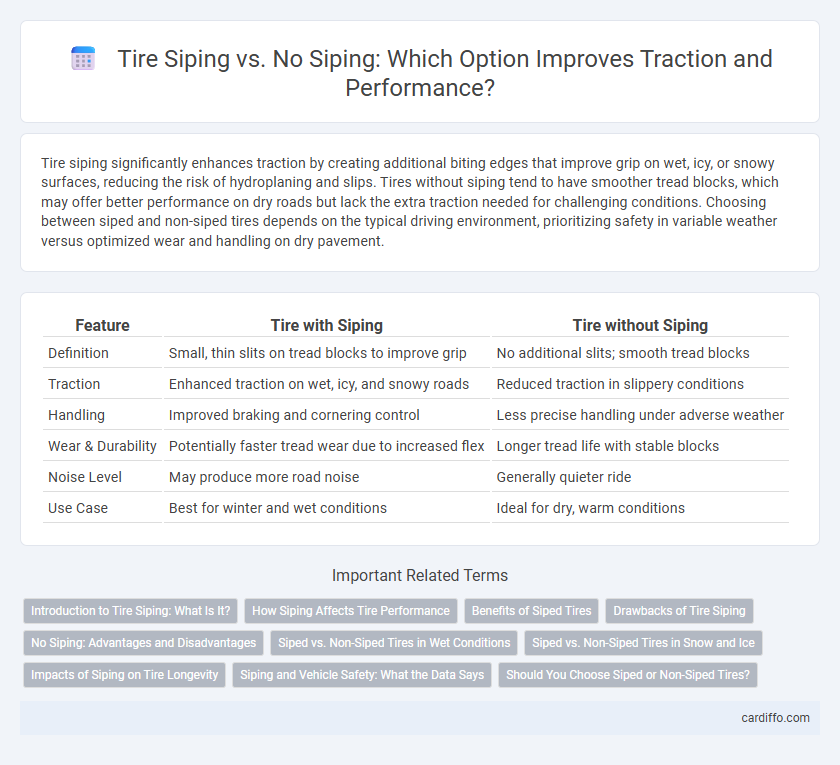
| Feature | Tire with Siping | Tire without Siping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, thin slits on tread blocks to improve grip | No additional slits; smooth tread blocks |
| Traction | Enhanced traction on wet, icy, and snowy roads | Reduced traction in slippery conditions |
| Handling | Improved braking and cornering control | Less precise handling under adverse weather |
| Wear & Durability | Potentially faster tread wear due to increased flex | Longer tread life with stable blocks |
| Noise Level | May produce more road noise | Generally quieter ride |
| Use Case | Best for winter and wet conditions | Ideal for dry, warm conditions |
Introduction to Tire Siping: What Is It?
Tire siping involves creating thin slits on the tire tread to enhance traction and improve grip on wet, icy, or slippery surfaces. These small cuts increase the tire's flexibility, allowing it to conform better to road irregularities and expel water more efficiently. Tires without siping typically offer less traction in adverse weather conditions, making siped tires a preferred choice for improved safety and performance.
How Siping Affects Tire Performance
Tire siping improves traction by creating additional biting edges that enhance grip on wet, icy, or snowy surfaces, reducing the risk of hydroplaning. Sipes increase tire flexibility, allowing better conforming to road irregularities and improving braking performance without significantly compromising tread life. Tires without siping offer enhanced stability and longer wear in dry conditions but typically exhibit reduced traction in adverse weather.
Benefits of Siped Tires
Siped tires offer enhanced traction by increasing the number of biting edges, which improves grip on wet, icy, and snowy surfaces. This design helps reduce hydroplaning and boosts braking performance, providing better overall safety in adverse weather conditions. Tires without siping may perform adequately on dry roads but lack the improved wet and winter traction that siped tires deliver.
Drawbacks of Tire Siping
Tire siping improves traction by creating small slits that enhance grip on wet and icy surfaces but can reduce tread life due to increased tread flexibility and wear. Excessive siping may compromise tire stability and handling precision, particularly at high speeds or under heavy loads. Tires without siping tend to offer better durability and structural integrity, making them preferable for dry conditions and extended tire lifespan.
No Siping: Advantages and Disadvantages
No siping in tires offers advantages such as increased tread block stiffness, which enhances dry road grip and improves steering response. However, tires without siping may experience reduced traction on wet or icy surfaces due to less effective water evacuation and decreased flexibility. This trade-off makes no-siping tires better suited for dry conditions but less optimal for challenging weather environments.
Siped vs. Non-Siped Tires in Wet Conditions
Siped tires feature thin slits in the tread that enhance water evacuation and increase grip on wet surfaces, reducing the risk of hydroplaning. Non-siped tires have a smoother tread pattern which may perform well on dry roads but offer less traction and stability in wet conditions. Choosing siped tires significantly improves wet-weather handling, braking, and overall safety compared to non-siped alternatives.
Siped vs. Non-Siped Tires in Snow and Ice
Siped tires feature small slits that enhance traction by increasing the tire's grip on snow and ice, significantly improving safety and control during winter conditions. Non-siped tires lack these slits, resulting in reduced flexibility and limited adhesion on slippery surfaces, which can lead to longer stopping distances and decreased handling performance. Choosing siped tires for snowy and icy environments ensures better braking efficiency, stability, and overall traction compared to non-siped alternatives.
Impacts of Siping on Tire Longevity
Tire siping significantly enhances traction by creating additional biting edges, improving grip on slippery surfaces like ice and wet roads, which reduces uneven wear and prolongs tire life. However, excessive siping can compromise tire tread stability, potentially accelerating wear in high-stress driving conditions. Optimizing siping patterns balances improved traction with durable tread integrity, maximizing overall tire longevity.
Siping and Vehicle Safety: What the Data Says
Tire siping significantly improves vehicle safety by enhancing traction on wet, icy, and slippery road surfaces, reducing the risk of hydroplaning and skidding. Studies reveal that tires with siping show better grip performance in adverse weather conditions, leading to shorter stopping distances and improved vehicle control. Data from automotive safety tests confirm that well-siped tires contribute to increased driver confidence and reduced accident rates in challenging driving environments.
Should You Choose Siped or Non-Siped Tires?
Siped tires feature thin slits in the tread that enhance traction on wet, icy, or snowy roads by improving water evacuation and increasing the biting edges. Non-siped tires generally offer better dry road stability and longer tread life due to their solid tread blocks but may compromise grip in slippery conditions. Choosing between siped and non-siped tires depends on typical driving conditions; siped tires are ideal for regions with frequent rain or snow, while non-siped tires suit primarily dry, stable climates.
Tire siping vs No siping Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com