Local registration offers streamlined processing and compliance with state-specific requirements, ensuring vehicles meet regional safety and emissions standards. Out-of-state registration often involves additional documentation and fees to transfer vehicle ownership or residency, which can extend processing times. Understanding the differences helps avoid penalties and ensures proper legal status for driving within the jurisdiction.
Table of Comparison
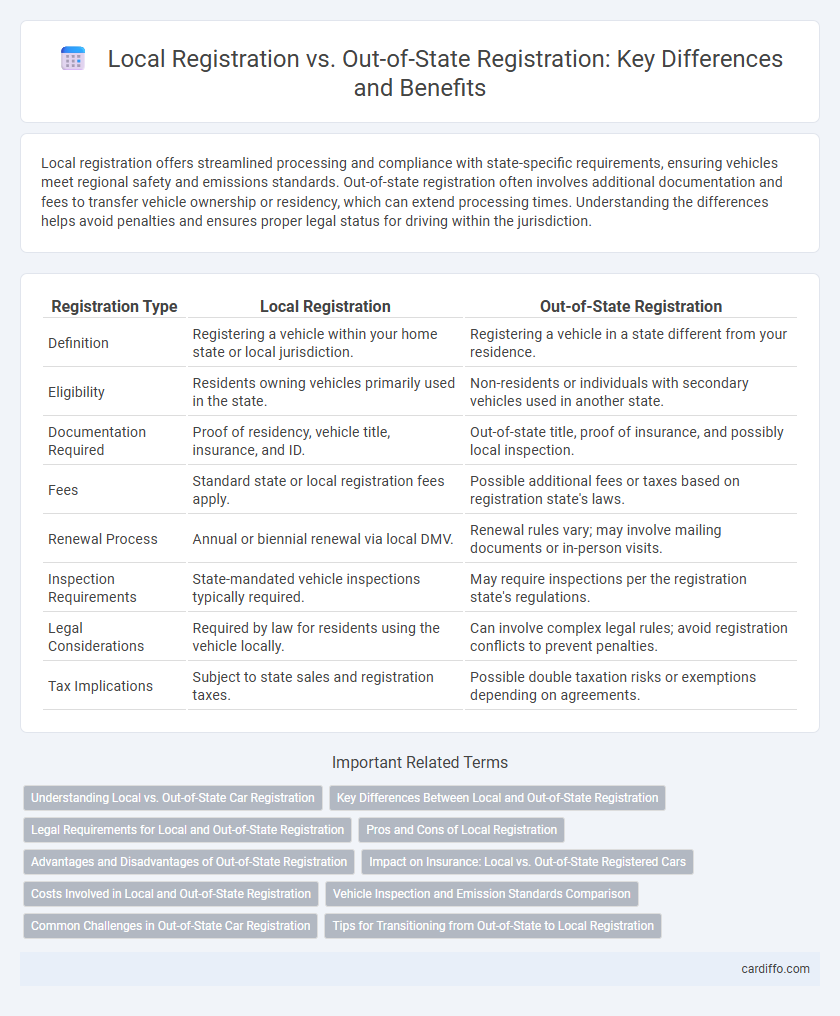
| Registration Type | Local Registration | Out-of-State Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Registering a vehicle within your home state or local jurisdiction. | Registering a vehicle in a state different from your residence. |
| Eligibility | Residents owning vehicles primarily used in the state. | Non-residents or individuals with secondary vehicles used in another state. |
| Documentation Required | Proof of residency, vehicle title, insurance, and ID. | Out-of-state title, proof of insurance, and possibly local inspection. |
| Fees | Standard state or local registration fees apply. | Possible additional fees or taxes based on registration state's laws. |
| Renewal Process | Annual or biennial renewal via local DMV. | Renewal rules vary; may involve mailing documents or in-person visits. |
| Inspection Requirements | State-mandated vehicle inspections typically required. | May require inspections per the registration state's regulations. |
| Legal Considerations | Required by law for residents using the vehicle locally. | Can involve complex legal rules; avoid registration conflicts to prevent penalties. |
| Tax Implications | Subject to state sales and registration taxes. | Possible double taxation risks or exemptions depending on agreements. |
Understanding Local vs. Out-of-State Car Registration
Local car registration requires vehicle owners to register their cars in the state where the vehicle is primarily garaged, ensuring compliance with local tax, insurance, and safety regulations. Out-of-state registration applies when a vehicle is registered in a different state than where it is primarily driven, which may lead to legal issues, fines, or difficulties with law enforcement. Understanding the differences in fees, documentation, and renewal processes between local and out-of-state registrations helps vehicle owners avoid penalties and maintain lawful operation.
Key Differences Between Local and Out-of-State Registration
Local registration requires vehicle owners to register their vehicles within the state where the vehicle is primarily used, ensuring compliance with state-specific regulations and taxes. Out-of-state registration involves registering a vehicle in a state different from where it is primarily operated, often leading to differences in registration fees, insurance requirements, and renewal processes. Key distinctions include variations in documentation needed, the impact on insurance policies, and potential legal implications related to residency and vehicle usage.
Legal Requirements for Local and Out-of-State Registration
Local registration requires compliance with specific state-issued documents such as proof of residency and payment of local taxes, while out-of-state registration mandates submission of home state registration along with verification of vehicle compliance with the new state's emissions and safety standards. Legal requirements for local registration often include obtaining a state driver's license and registering within a prescribed timeframe after establishing residency. For out-of-state registration, the law typically necessitates surrendering previous registration, undergoing vehicle inspection, and paying both registration and potential transfer fees according to the new state's motor vehicle department guidelines.
Pros and Cons of Local Registration
Local registration offers the advantage of streamlined processing and easier access to in-person support at nearby government offices, reducing wait times for document verification and approvals. However, it may involve stricter residency requirements and limited flexibility for individuals who frequently move or conduct business across state lines. Choosing local registration often results in better compliance with local regulations but can restrict mobility compared to out-of-state registration options.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Out-of-State Registration
Out-of-state registration offers advantages such as potential lower fees, tax benefits, and greater privacy by avoiding local DMV records. However, it presents disadvantages including possible legal complications, non-compliance with state residency requirements, and increased risk of fines or vehicle impoundment if discovered. Vehicle owners must weigh cost savings against the likelihood of enforcement and long-term registration issues.
Impact on Insurance: Local vs. Out-of-State Registered Cars
Local registration often leads to lower insurance premiums due to familiarity with regional risk factors and quicker claims processing. Out-of-state registration can result in higher insurance costs as insurers perceive increased risk from unfamiliar vehicle usage zones and potential delays in claim settlements. Understanding these insurance implications helps vehicle owners make informed decisions about registration status.
Costs Involved in Local and Out-of-State Registration
Local vehicle registration typically involves lower fees and taxes compared to out-of-state registration, as local authorities base costs on regional factors such as vehicle type and emission standards. Out-of-state registration often incurs higher fees, including additional penalties, processing fees, and varying state-specific taxes, which can increase overall costs significantly. Understanding these cost differences is crucial for vehicle owners considering relocation or purchasing vehicles from other states.
Vehicle Inspection and Emission Standards Comparison
Local vehicle registration often requires compliance with stringent vehicle inspection and emission standards tailored to the specific region's environmental policies, ensuring optimal road safety and air quality. Out-of-state registration may face different inspection criteria, potentially necessitating a secondary inspection to meet the local jurisdiction's emission standards. Differences in emission testing protocols, such as OBD-II diagnostics and tailpipe testing, highlight the importance of understanding regional requirements during the vehicle registration process.
Common Challenges in Out-of-State Car Registration
Out-of-state car registration often involves complex documentation requirements, such as proof of residency and vehicle inspection reports, which vary significantly by state. Many vehicle owners face delays due to discrepancies in emission standards or title status between the home and new registration states. Navigating differing fee structures and understanding the specific legal obligations for insurance coverage in the new state further complicate the registration process.
Tips for Transitioning from Out-of-State to Local Registration
When transitioning from out-of-state to local vehicle registration, gather essential documents such as the title, proof of insurance, and a valid ID to ensure a smooth process. Schedule a vehicle inspection if required by local DMV regulations to meet safety and emissions standards. Promptly submit your application within the state's designated timeframe to avoid penalties and comply with local registration laws.
Local Registration vs Out-of-State Registration Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com