Mechanical parking systems maximize space efficiency by automatically moving vehicles into designated spots using lifts or conveyors, reducing the need for wide aisles and simplifying parking in tight urban areas. Manual parking, relying on drivers to maneuver and park vehicles themselves, requires more space and longer time, often leading to increased congestion and potential for human error. Choosing mechanical parking solutions enhances throughput and safety while minimizing land use and operational costs.
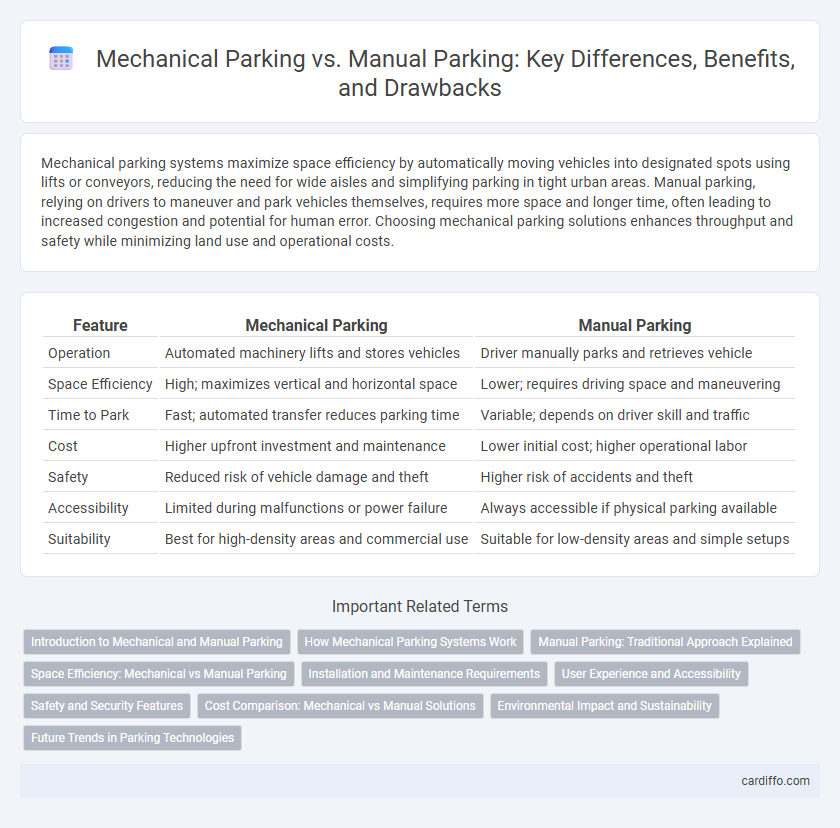
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Parking | Manual Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Automated machinery lifts and stores vehicles | Driver manually parks and retrieves vehicle |
| Space Efficiency | High; maximizes vertical and horizontal space | Lower; requires driving space and maneuvering |
| Time to Park | Fast; automated transfer reduces parking time | Variable; depends on driver skill and traffic |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment and maintenance | Lower initial cost; higher operational labor |
| Safety | Reduced risk of vehicle damage and theft | Higher risk of accidents and theft |
| Accessibility | Limited during malfunctions or power failure | Always accessible if physical parking available |
| Suitability | Best for high-density areas and commercial use | Suitable for low-density areas and simple setups |
Introduction to Mechanical and Manual Parking
Mechanical parking systems utilize automated machinery to efficiently stack or retrieve vehicles, maximizing space utilization in urban environments. Manual parking relies on drivers to independently park their vehicles within designated spots, requiring more physical space and time. Advanced mechanical solutions like automated car lifts and rotating platforms reduce congestion and provide scalable parking options compared to traditional manual methods.
How Mechanical Parking Systems Work
Mechanical parking systems operate by using automated lifts, conveyors, and rotating platforms to move vehicles into designated parking spaces, maximizing space efficiency and minimizing human effort. These systems rely on sensors and computerized controls to accurately position cars without the need for drivers to maneuver in tight spaces. Compared to manual parking, mechanical systems reduce the risk of vehicle damage and improve overall parking capacity in urban environments.
Manual Parking: Traditional Approach Explained
Manual parking relies on the driver's skill to maneuver the vehicle into a designated space, without automated assistance systems. This traditional method requires spatial awareness, precise control, and experience to avoid obstacles and optimally position the car. Unlike mechanical parking systems, manual parking demands active driver involvement and is widely used in urban areas with limited technological infrastructure.
Space Efficiency: Mechanical vs Manual Parking
Mechanical parking systems maximize space efficiency by stacking vehicles vertically or using automated lifts, enabling up to 60% more cars to fit within the same footprint compared to manual parking. Manual parking requires conventional maneuvering space for each vehicle, leading to inefficient use of horizontal space and limited capacity. Choosing mechanical parking solutions optimizes urban land use, reducing the need for expansive parking lots and enhancing overall spatial planning.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Mechanical parking systems require complex installation involving hydraulic or automated machinery, often demanding professional expertise and significant upfront costs. Maintenance for mechanical systems includes regular inspections of moving parts, lubrication, and electronic component checks to ensure operational safety and efficiency. Manual parking demands minimal installation, typically only a marked parking space, and maintenance is limited to surface upkeep without the need for specialized technical servicing.
User Experience and Accessibility
Mechanical parking systems enhance user experience by offering automated vehicle placement, reducing physical effort and minimizing parking errors. Accessibility improves significantly as these systems accommodate users with disabilities, providing seamless entry and exit without requiring manual intervention. Manual parking, while familiar, often demands more time, physical maneuvering skills, and may not be as accessible for individuals with mobility challenges.
Safety and Security Features
Mechanical parking systems enhance safety by minimizing human error through automated vehicle placement, reducing collision risks and unauthorized access with secure locking mechanisms. Manual parking relies on driver vigilance, increasing the potential for accidents and theft due to inconsistent security practices. Advanced mechanical parking integrates surveillance cameras and emergency alarms, offering superior protection compared to traditional manual methods.
Cost Comparison: Mechanical vs Manual Solutions
Mechanical parking systems typically involve higher upfront costs due to automation technology and installation requirements, but they offer long-term savings through increased space efficiency and reduced labor expenses. Manual parking solutions have lower initial investment but incur ongoing labor costs and use more space, which can limit overall capacity and revenue potential. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals mechanical systems deliver better value in high-demand or space-constrained environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mechanical parking systems reduce carbon emissions by minimizing vehicle idling and search times, thereby lowering fuel consumption and air pollution. Manual parking typically results in longer vehicle circulation within parking areas, increasing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to urban heat. Sustainable mechanical solutions also optimize spatial efficiency, allowing for greener, more compact urban development with reduced land use.
Future Trends in Parking Technologies
Mechanical parking systems leverage automated lifts and robotic platforms to optimize space and reduce human error, driving efficiency in urban environments. Emerging trends emphasize integration with smart city infrastructure, utilizing IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics to enhance real-time space allocation and energy management. Future developments point towards fully autonomous parking solutions, combining electric vehicle compatibility and dynamic user interfaces to streamline the parking experience.
Mechanical parking vs Manual parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com