Accessible parking spaces are specifically designed to accommodate individuals with disabilities, providing extra width, proximity to entrances, and clear signage to ensure ease of access. Standard parking spots lack these modifications, making them less convenient or even unusable for people with mobility challenges. Choosing accessible parking helps promote inclusivity and complies with legal requirements while ensuring safety and convenience for all users.
Table of Comparison
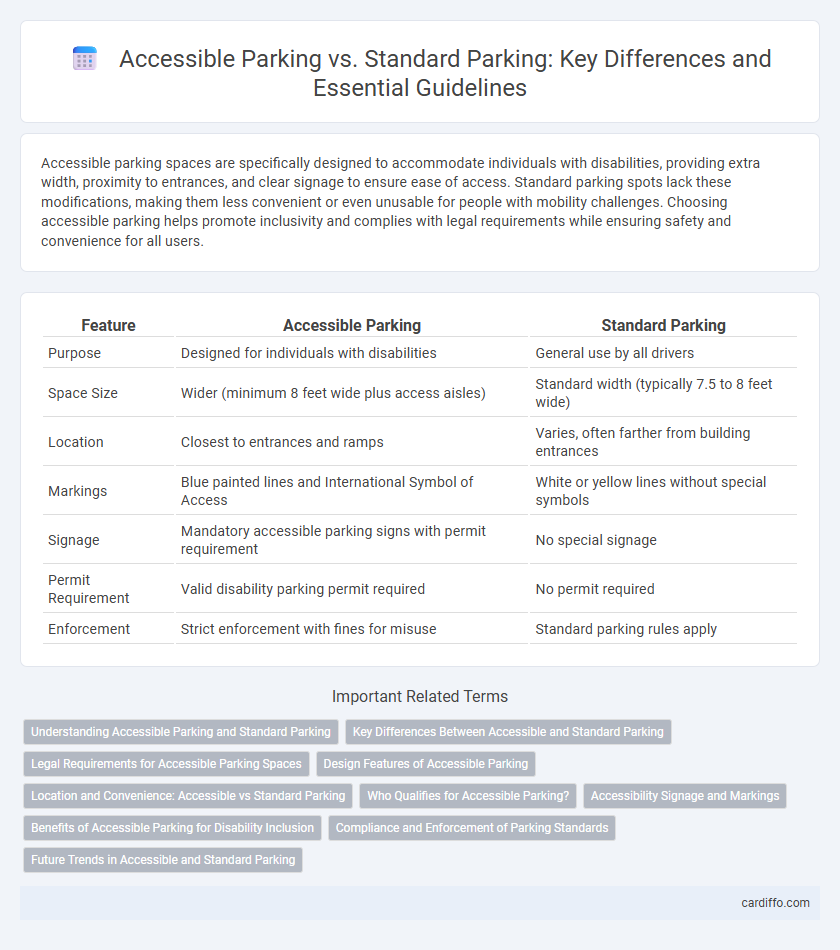
| Feature | Accessible Parking | Standard Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for individuals with disabilities | General use by all drivers |
| Space Size | Wider (minimum 8 feet wide plus access aisles) | Standard width (typically 7.5 to 8 feet wide) |
| Location | Closest to entrances and ramps | Varies, often farther from building entrances |
| Markings | Blue painted lines and International Symbol of Access | White or yellow lines without special symbols |
| Signage | Mandatory accessible parking signs with permit requirement | No special signage |
| Permit Requirement | Valid disability parking permit required | No permit required |
| Enforcement | Strict enforcement with fines for misuse | Standard parking rules apply |
Understanding Accessible Parking and Standard Parking
Accessible parking spaces are specifically designed to accommodate individuals with disabilities, featuring wider dimensions, curb ramps, and clear signage to ensure safe and convenient access to buildings and facilities. Standard parking spaces follow regular size specifications and do not include special accommodations, making them less suitable for people with mobility challenges. Compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) regulates the number and design of accessible parking spots, promoting equal access and inclusivity in parking availability.
Key Differences Between Accessible and Standard Parking
Accessible parking spaces are specifically designed for individuals with disabilities, featuring wider dimensions, adjacent access aisles, and proximity to building entrances to facilitate mobility aid use. These spaces comply with ADA regulations, including clear signage, surface markings, and curb cuts, ensuring ease of access and safety. Standard parking spaces lack these accommodations, have narrower widths, and are typically located farther from entrances, making them less suitable for users needing mobility assistance.
Legal Requirements for Accessible Parking Spaces
Accessible parking spaces must comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards, which mandate specific dimensions, signage, and proximity to building entrances to ensure usability for individuals with disabilities. Federal and state laws require a minimum ratio of accessible spots relative to the total number of parking spaces, varying based on the size of the parking lot or facility. Noncompliance with these legal requirements can result in significant fines and legal actions, emphasizing the importance of proper design and maintenance.
Design Features of Accessible Parking
Accessible parking spaces feature wider dimensions, typically 8 feet wide with an adjoining 5-foot access aisle, to accommodate wheelchair users and vehicles equipped with ramps or lifts. These spaces are strategically located near building entrances to minimize travel distance for individuals with mobility impairments. Design elements also include clear signage displaying the International Symbol of Accessibility and surface markings that enhance visibility and compliance with ADA standards.
Location and Convenience: Accessible vs Standard Parking
Accessible parking spaces are strategically located closest to building entrances, ramps, and elevators to provide maximum convenience for individuals with mobility challenges, ensuring easier access to facilities. Standard parking spots are typically situated further away, requiring longer walking distances that can be inconvenient for those with limited mobility or carrying heavy loads. The proximity of accessible parking reduces physical strain and enhances independence, making it essential in urban planning and facility design.
Who Qualifies for Accessible Parking?
Accessible parking spaces are reserved for individuals with disabilities who possess a valid accessible parking permit or license plate issued by local authorities. Qualifying individuals typically include those with mobility impairments, such as wheelchair users, people with limited walking ability, or certain medical conditions that require proximity to building entrances. Eligibility criteria and application processes vary by jurisdiction but generally require medical certification from a licensed healthcare provider.
Accessibility Signage and Markings
Accessible parking spaces feature highly visible accessibility signage with the International Symbol of Access, ensuring easy identification for individuals with disabilities. These spaces are clearly marked with bold blue paint and include additional floor markings and pavement symbols to enhance visibility. Standard parking lacks these specialized signs and markings, making it less identifiable for accessibility needs.
Benefits of Accessible Parking for Disability Inclusion
Accessible parking spaces provide essential benefits for disability inclusion by ensuring equal access to buildings and public spaces, reducing physical barriers for individuals with mobility challenges. These designated spots feature wider dimensions, curb cuts, and proximity to entrances, enhancing convenience and safety. Implementing accessible parking fosters greater independence and participation, promoting an inclusive environment for people with disabilities.
Compliance and Enforcement of Parking Standards
Accessible parking spaces are strictly regulated by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and require specific dimensions, signage, and surface markings to ensure compliance. Enforcement agencies routinely inspect facilities to verify adherence to these standards, imposing fines or mandates for non-compliant properties. Standard parking spaces, while subject to local zoning and safety regulations, generally face less stringent oversight and fewer specialized compliance requirements.
Future Trends in Accessible and Standard Parking
Future trends in accessible and standard parking emphasize the integration of smart technologies such as IoT sensors and real-time space availability apps to enhance user convenience and efficiency. Autonomous vehicles will likely increase demand for adaptive parking solutions that accommodate various mobility needs, including wider spaces and improved signage for accessible parking. Urban planning is shifting towards sustainable designs that promote accessible parking near public transport hubs and prioritize electric vehicle charging stations in both accessible and standard parking zones.
Accessible parking vs Standard parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com