Free parking offers convenience and cost savings but often comes with limited availability and less security. Paid parking ensures guaranteed spots, enhanced safety, and better location options, making it ideal for busy areas. Choosing between free and paid parking depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for convenience and security.
Table of Comparison
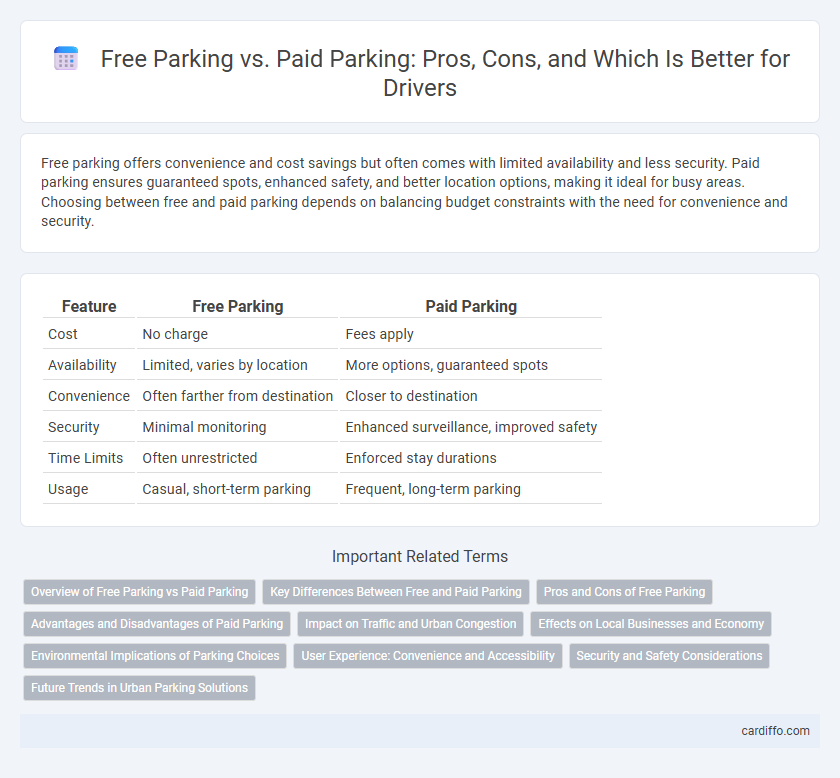
| Feature | Free Parking | Paid Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | No charge | Fees apply |
| Availability | Limited, varies by location | More options, guaranteed spots |
| Convenience | Often farther from destination | Closer to destination |
| Security | Minimal monitoring | Enhanced surveillance, improved safety |
| Time Limits | Often unrestricted | Enforced stay durations |
| Usage | Casual, short-term parking | Frequent, long-term parking |
Overview of Free Parking vs Paid Parking
Free parking offers cost savings and convenience for short-term stays but often lacks availability and security features. Paid parking provides guaranteed spaces, enhanced security, and better location options, though it incurs charges that can accumulate over time. Urban areas typically rely on paid parking to manage demand, while suburban or rural locations favor free parking due to lower congestion levels.
Key Differences Between Free and Paid Parking
Free parking offers cost savings and convenience but often lacks security, limited availability, and may encourage longer stays, leading to congestion. Paid parking provides regulated spaces with enhanced safety, maintenance, and turnover management, ensuring availability but incurring user fees. Businesses often prefer paid parking to control demand and improve revenue, while free parking boosts customer attraction but risks overcrowding and inefficient utilization.
Pros and Cons of Free Parking
Free parking offers convenience and cost savings, attracting more visitors and reducing stress related to finding a spot. It may lead to higher congestion, misuse of spaces, and increased traffic as drivers circle looking for free spots. Limited availability in free parking zones often results in inefficient land use and can hinder revenue opportunities for municipalities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Paid Parking
Paid parking offers benefits such as regulated space availability, reduced congestion, and increased municipal revenue for urban development projects. However, disadvantages include potential financial burden on commuters, increased risk of parking violations due to payment confusion, and sometimes limited accessibility for low-income individuals. Optimal paid parking systems balance cost with convenience, ensuring equitable access while managing demand effectively.
Impact on Traffic and Urban Congestion
Free parking encourages higher vehicle use, leading to increased traffic volume and worsening urban congestion, as drivers are more likely to drive and occupy valuable road space. Paid parking discourages unnecessary car trips by imposing a cost, effectively reducing traffic demand and easing congestion in crowded city centers. Implementing dynamic pricing for paid parking further optimizes traffic flow and promotes alternative transportation modes, improving overall urban mobility.
Effects on Local Businesses and Economy
Free parking increases foot traffic and encourages longer visits, boosting sales for local businesses by making shopping more accessible. Paid parking generates municipal revenue that can be reinvested in public infrastructure, enhancing the local economy and urban environment. However, excessive parking fees may deter potential customers, negatively affecting small retailers and overall economic activity.
Environmental Implications of Parking Choices
Free parking often encourages increased vehicle use, leading to higher emissions and greater urban heat island effects due to expansive paved surfaces. Paid parking can incentivize reduced car dependency by promoting alternative transportation methods, lowering carbon footprints and decreasing air pollution. Efficient parking policies that balance availability with environmental goals contribute significantly to sustainable urban mobility and improved air quality.
User Experience: Convenience and Accessibility
Free parking enhances user experience by eliminating cost barriers and offering greater accessibility, especially in urban areas with limited public transit. Paid parking often provides more reliable availability through managed spaces, real-time occupancy data, and improved security features, contributing to convenience for users seeking guaranteed spots. Balancing cost and accessibility is crucial for optimizing user satisfaction in parking facilities.
Security and Safety Considerations
Free parking areas often lack comprehensive security measures such as surveillance cameras and regular patrols, increasing the risk of vehicle theft or vandalism. Paid parking facilities typically invest in enhanced safety features including controlled access, well-lit environments, and monitoring systems to protect vehicles and ensure customer confidence. Choosing paid parking can provide greater peace of mind due to its structured approach to security and safety management.
Future Trends in Urban Parking Solutions
Emerging urban parking solutions emphasize smart technology integration, favoring automated payment systems and dynamic pricing models over traditional free parking to optimize space utilization and reduce congestion. Cities increasingly adopt sensor-based and AI-driven platforms that adjust parking fees based on demand, promoting turnover and minimizing traffic from drivers searching for free spots. Future trends suggest a shift toward prioritizing sustainable mobility, where paid parking structures support electric vehicle charging and integrate with multimodal transit networks, aligning with environmental goals and urban growth.
Free parking vs paid parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com