Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, boosting engine power with improved fuel efficiency and lag at higher RPMs, while superchargers rely on a belt-driven compressor for immediate boost and consistent power delivery but often consume more fuel. Choosing between a turbocharger and supercharger depends on desired performance characteristics, throttle response, and vehicle use. Turbochargers are preferred for maximizing horsepower and efficiency, whereas superchargers offer quicker acceleration and simplicity in installation.
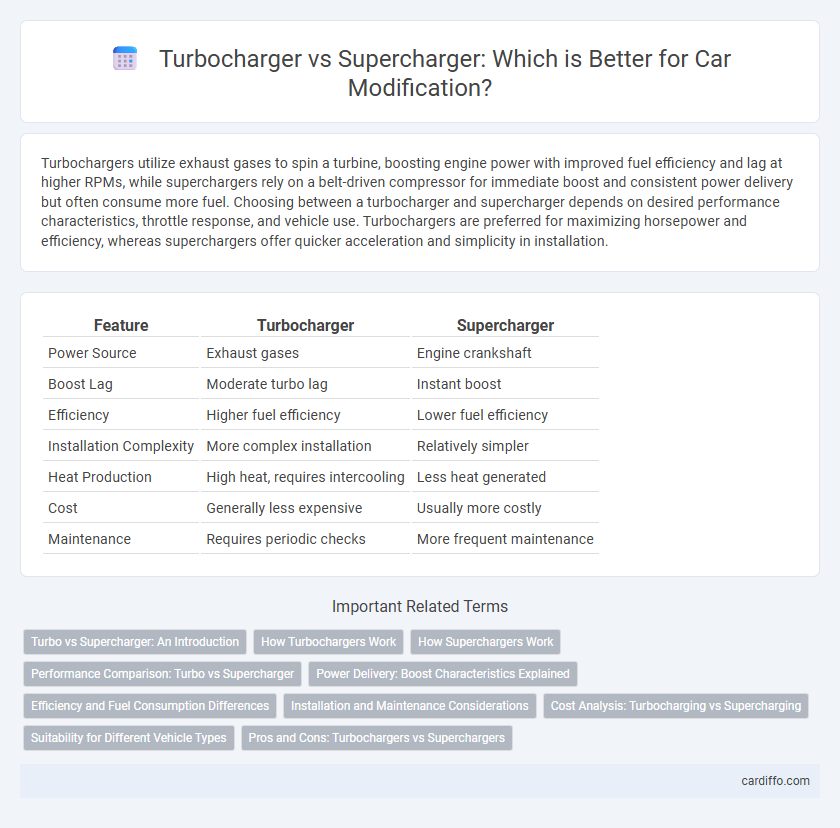
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Turbocharger | Supercharger |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Exhaust gases | Engine crankshaft |
| Boost Lag | Moderate turbo lag | Instant boost |
| Efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency | Lower fuel efficiency |
| Installation Complexity | More complex installation | Relatively simpler |
| Heat Production | High heat, requires intercooling | Less heat generated |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Usually more costly |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic checks | More frequent maintenance |
Turbo vs Supercharger: An Introduction
Turbochargers and superchargers are both forced induction systems designed to boost engine power by increasing air intake. Turbos use exhaust gases to spin a turbine, improving efficiency and reducing lag, while superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, providing instant boost but consuming more power. Choosing between a turbocharger and supercharger depends on performance goals, response preference, and installation complexity.
How Turbochargers Work
Turbochargers increase engine power by utilizing exhaust gases to spin a turbine connected to a compressor, which forces more air into the combustion chamber. This process improves air intake efficiency and boosts engine performance without significantly increasing engine size. Turbochargers are typically more efficient at higher RPMs compared to superchargers, which are mechanically driven directly by the engine.
How Superchargers Work
Superchargers increase engine power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber using a belt-driven compressor connected directly to the engine crankshaft. This mechanical linkage provides immediate boost without lag, enhancing throttle response and low-end torque. Unlike turbos, superchargers do not rely on exhaust gases, allowing consistent power delivery across the entire RPM range.
Performance Comparison: Turbo vs Supercharger
Turbochargers deliver higher peak power by using exhaust gases to spin the turbine, improving engine efficiency and fuel economy. Superchargers provide instant boost through a belt-driven compressor, offering superior low-end torque and throttle response. Choosing between the two depends on desired performance characteristics: turbos excel in high-RPM power, while superchargers enhance immediate acceleration.
Power Delivery: Boost Characteristics Explained
Turbochargers provide power delivery through exhaust-driven boost, resulting in a delayed but stronger surge of torque at higher RPMs, enhancing peak engine performance. Superchargers deliver immediate boost via a belt-driven compressor, offering consistent and linear power increase across the RPM range for improved throttle response. Understanding these distinct boost characteristics is crucial for tuning modifications aimed at optimizing engine power and drivability.
Efficiency and Fuel Consumption Differences
Turbochargers enhance engine efficiency by utilizing exhaust gases to increase air intake pressure, resulting in better fuel combustion compared to superchargers. Superchargers, driven mechanically by the engine, often consume more fuel due to increased parasitic drag despite providing immediate boost. Consequently, turbochargers generally offer superior fuel economy and performance efficiency in modified vehicles.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Turbochargers require exhaust system modifications and precise tuning for optimal installation, often demanding professional expertise due to their integration with the engine's exhaust flow. Superchargers are typically easier to install since they connect directly to the engine's intake system, but they can increase belt load and may require upgrades to the drive system. Maintenance of turbochargers involves monitoring for oil contamination and managing heat cycles, while superchargers generally need regular belt inspection and tension adjustments to ensure reliable performance.
Cost Analysis: Turbocharging vs Supercharging
Turbocharging typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to supercharging, with lower initial installation expenses and enhanced fuel efficiency leading to long-term savings. Superchargers generally have higher upfront costs due to their complex mechanical design and increased maintenance requirements. Evaluating total cost of ownership, turbochargers provide better value for performance enthusiasts prioritizing budget-conscious modifications.
Suitability for Different Vehicle Types
Turbochargers deliver optimal performance for lightweight vehicles and small engines by utilizing exhaust gases to boost power efficiently, making them ideal for compact cars and sports vehicles. Superchargers provide immediate power and better throttle response, benefiting heavier vehicles and muscle cars that require consistent low-end torque for towing or off-road use. Selecting between turbo and supercharger depends on vehicle weight, engine size, and desired driving characteristics to maximize modification effectiveness.
Pros and Cons: Turbochargers vs Superchargers
Turbochargers provide increased engine efficiency by utilizing exhaust gases to generate boost, leading to better fuel economy and higher power output, but they often suffer from turbo lag which delays throttle response. Superchargers offer immediate boost and improved throttle response due to their mechanical drive from the engine, enhancing low-end torque, yet they tend to reduce overall efficiency by consuming engine power. Choosing between turbos and superchargers depends on balancing the need for instantaneous power against fuel efficiency and driving style preferences.
turbo vs supercharger Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com