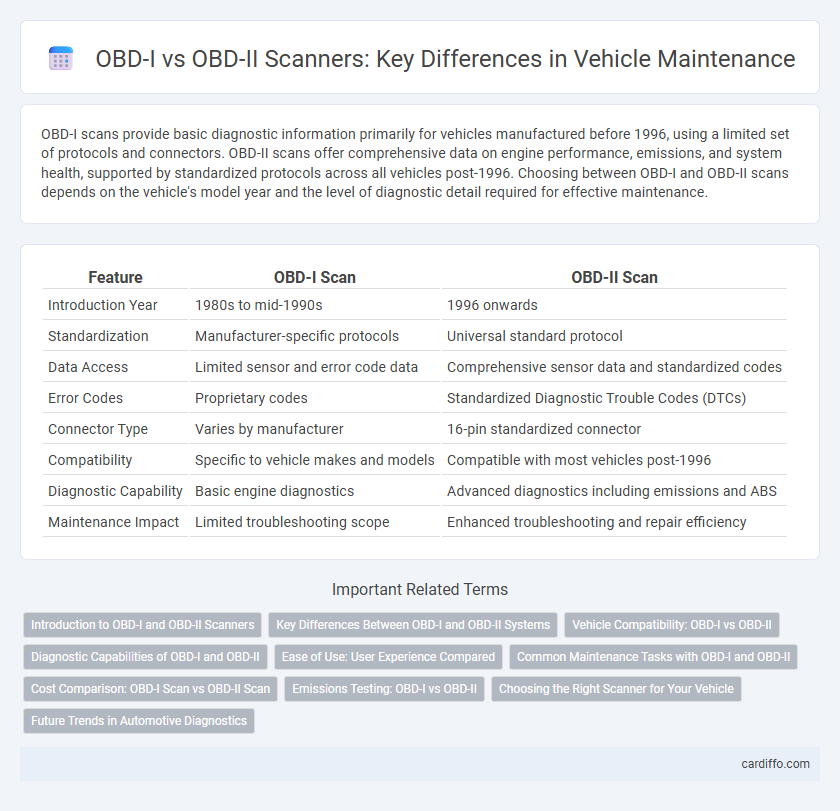
OBD-I scans provide basic diagnostic information primarily for vehicles manufactured before 1996, using a limited set of protocols and connectors. OBD-II scans offer comprehensive data on engine performance, emissions, and system health, supported by standardized protocols across all vehicles post-1996. Choosing between OBD-I and OBD-II scans depends on the vehicle's model year and the level of diagnostic detail required for effective maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | OBD-I Scan | OBD-II Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction Year | 1980s to mid-1990s | 1996 onwards |
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific protocols | Universal standard protocol |
| Data Access | Limited sensor and error code data | Comprehensive sensor data and standardized codes |
| Error Codes | Proprietary codes | Standardized Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) |
| Connector Type | Varies by manufacturer | 16-pin standardized connector |
| Compatibility | Specific to vehicle makes and models | Compatible with most vehicles post-1996 |
| Diagnostic Capability | Basic engine diagnostics | Advanced diagnostics including emissions and ABS |
| Maintenance Impact | Limited troubleshooting scope | Enhanced troubleshooting and repair efficiency |
Introduction to OBD-I and OBD-II Scanners
OBD-I scanners diagnose engine issues by accessing manufacturer-specific codes from vehicles produced before 1996, offering limited compatibility and basic fault detection. In contrast, OBD-II scanners provide standardized, comprehensive diagnostics across all vehicles manufactured after 1996, utilizing uniform trouble codes to enhance fault identification and repair accuracy. Understanding the differences between OBD-I and OBD-II scanners is essential for effective vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Differences Between OBD-I and OBD-II Systems
OBD-I systems, introduced in the early 1980s, provide limited diagnostic information primarily through simple trouble codes without standardized protocols, making scan tools manufacturer-specific. OBD-II systems, mandated in 1996, offer comprehensive diagnostics with standardized codes (SAE J1979), enhanced data access, and real-time monitoring across all vehicles, vastly improving fault detection and emissions control. The key differences include OBD-I's lack of uniformity, restricted sensor data, and minimal emission testing capability versus OBD-II's universal connector, extensive sensor coverage, and advanced readiness monitors.
Vehicle Compatibility: OBD-I vs OBD-II
OBD-I scan tools are compatible with vehicles manufactured primarily between 1981 and 1995, supporting early onboard diagnostics with limited data parameters. OBD-II scanners serve a broader range, compatible with vehicles made from 1996 onward, offering advanced diagnostics and standardized codes across multiple manufacturers. The transition from OBD-I to OBD-II systems ensures enhanced vehicle compatibility, enabling comprehensive engine and emissions monitoring for newer models.
Diagnostic Capabilities of OBD-I and OBD-II
OBD-II scans offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities compared to OBD-I, featuring standardized trouble codes and real-time data monitoring across all manufacturers. OBD-I systems provide limited diagnostic information with manufacturer-specific codes, making fault detection less comprehensive. The advanced sensor integration in OBD-II enables more accurate identification and troubleshooting of engine and emission-related issues.
Ease of Use: User Experience Compared
OBD-II scans offer greater ease of use compared to OBD-I due to standardized connectors and improved diagnostic protocols, making them compatible with modern scan tools and software. The user experience is enhanced by OBD-II's comprehensive access to vehicle systems, enabling faster and more accurate troubleshooting. OBD-I scans often require specialized adapters and lack unified communication standards, complicating the diagnostic process.
Common Maintenance Tasks with OBD-I and OBD-II
OBD-I scans monitor basic engine functions such as ignition timing and fuel mixture, useful for tasks like diagnosing ignition problems and fueling issues in vehicles produced before 1996. OBD-II scans provide comprehensive diagnostic codes covering emissions, fuel system, and sensors, facilitating advanced maintenance tasks including oxygen sensor testing and catalytic converter efficiency checks in cars from 1996 onward. Both systems enable real-time data reading but OBD-II's standardized protocol and broader diagnostics support more precise troubleshooting and preventative maintenance.
Cost Comparison: OBD-I Scan vs OBD-II Scan
OBD-I scans typically cost less due to simpler diagnostic protocols and limited data access, averaging around $20 to $50 for basic trouble code reading. OBD-II scans offer more comprehensive diagnostics with enhanced data access, which generally raises the price range to $50 to $150 or more, reflecting advanced features and compatibility with newer vehicles. Choosing between OBD-I and OBD-II scans depends on the vehicle's model year and the depth of diagnostic information required, impacting maintenance cost efficiency.
Emissions Testing: OBD-I vs OBD-II
OBD-I systems provide limited emissions data primarily focused on basic engine diagnostics, making emissions testing less comprehensive and often inaccurate compared to OBD-II. OBD-II scanners offer detailed real-time monitoring of various emission control components, enabling precise identification of faults and ensuring compliance with stricter emission standards. The enhanced capabilities of OBD-II systems improve vehicle emissions testing accuracy, facilitating better environmental protection and regulatory adherence.
Choosing the Right Scanner for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right OBD scanner depends on your vehicle's model year and diagnostic needs, with OBD-I scanners designed for pre-1996 vehicles and OBD-II scanners compatible with cars manufactured from 1996 onward. OBD-II scanners offer extensive diagnostic capabilities, including real-time data and standardized error codes, making them ideal for modern vehicles. Selecting an OBD scanner that matches your vehicle's onboard diagnostics system ensures accurate fault detection and efficient maintenance.
Future Trends in Automotive Diagnostics
OBD-II scan tools have become the industry standard due to their enhanced data accessibility and compatibility with modern vehicles, whereas OBD-I systems remain limited to older models with less diagnostic information. Future trends in automotive diagnostics emphasize seamless integration with telematics, real-time remote monitoring, and increased use of AI-driven predictive maintenance technologies to identify potential issues before failure. Wireless OBD-II scanners with smartphone apps are expected to dominate the market, providing vehicle owners and technicians with more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly diagnostic solutions.
Obd-I Scan vs Obd-II Scan Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com