Timing belts and serpentine belts play crucial roles in vehicle maintenance, each serving different functions with distinct lifespans. Timing belts synchronize engine camshaft and crankshaft rotation requiring regular replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles to prevent severe engine damage. Serpentine belts drive multiple peripheral devices like the alternator and power steering pump, typically lasting longer but still requiring periodic inspection and replacement to ensure optimal engine performance.
Table of Comparison
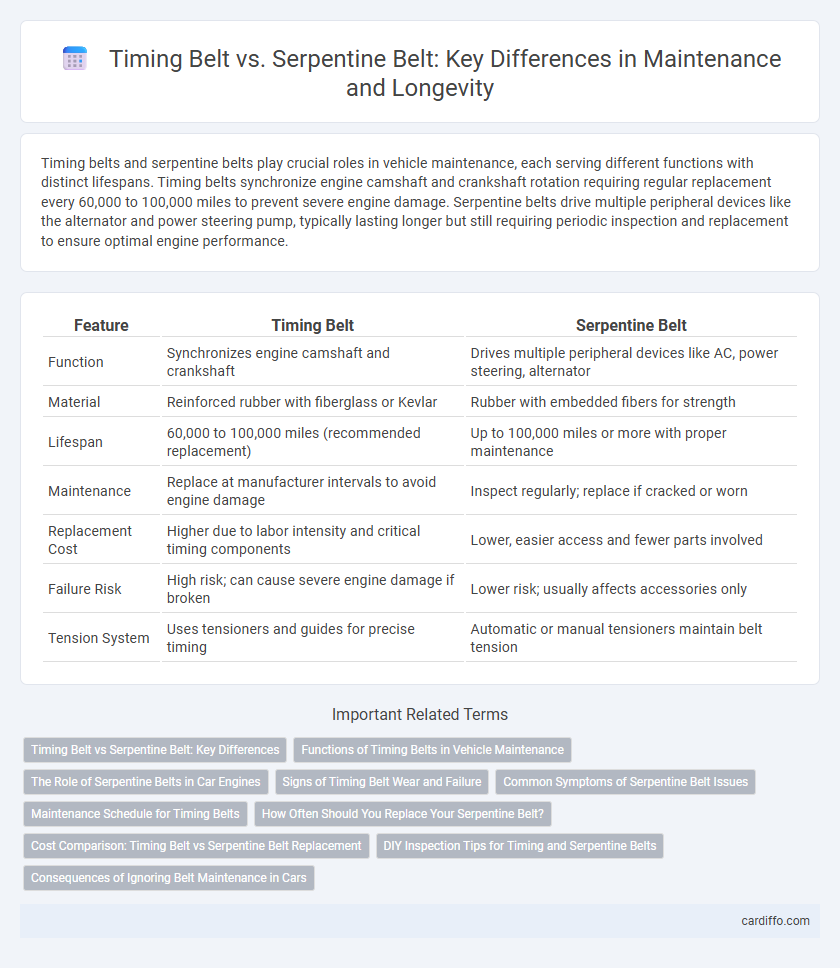
| Feature | Timing Belt | Serpentine Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Synchronizes engine camshaft and crankshaft | Drives multiple peripheral devices like AC, power steering, alternator |
| Material | Reinforced rubber with fiberglass or Kevlar | Rubber with embedded fibers for strength |
| Lifespan | 60,000 to 100,000 miles (recommended replacement) | Up to 100,000 miles or more with proper maintenance |
| Maintenance | Replace at manufacturer intervals to avoid engine damage | Inspect regularly; replace if cracked or worn |
| Replacement Cost | Higher due to labor intensity and critical timing components | Lower, easier access and fewer parts involved |
| Failure Risk | High risk; can cause severe engine damage if broken | Lower risk; usually affects accessories only |
| Tension System | Uses tensioners and guides for precise timing | Automatic or manual tensioners maintain belt tension |
Timing Belt vs Serpentine Belt: Key Differences
Timing belts are crucial for synchronizing the engine's camshaft and crankshaft, ensuring precise valve timing, while serpentine belts drive multiple peripheral devices like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Timing belts typically require replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles to prevent engine damage, whereas serpentine belts usually last between 50,000 and 70,000 miles but are easier to inspect and replace. Understanding these differences helps maintain engine performance and avoid costly repairs related to belt failure.
Functions of Timing Belts in Vehicle Maintenance
Timing belts synchronize the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring precise valve timing critical for engine performance and preventing engine damage. They enable the engine's intake and exhaust valves to open and close at optimal intervals, maintaining efficient combustion and preventing piston interference. Regular inspection and timely replacement of timing belts are essential to avoid costly engine repairs and maintain vehicle reliability.
The Role of Serpentine Belts in Car Engines
Serpentine belts play a crucial role in car engines by driving multiple peripheral devices such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor through a single, continuous belt. Unlike timing belts, which synchronize the engine's camshaft and crankshaft, serpentine belts are responsible for powering essential engine accessories, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and efficiency. Regular inspection and timely replacement of serpentine belts are vital to prevent engine accessory failure and maintain overall engine functionality.
Signs of Timing Belt Wear and Failure
Signs of timing belt wear and failure include visible cracks, fraying, and missing teeth on the belt, along with unusual engine noises such as ticking or squealing. Engine misfires, rough idling, and difficulty starting the vehicle often indicate timing belt issues, as a worn or broken timing belt can disrupt engine synchronization. Regular inspection is critical since timing belt failure can cause severe engine damage, including bent valves or piston damage.
Common Symptoms of Serpentine Belt Issues
Common symptoms of serpentine belt issues include squealing noises from the engine, visible cracks or fraying on the belt surface, and difficulty steering or malfunctioning power accessories like the alternator and air conditioning. A worn or slipping serpentine belt can cause overheating and battery charging problems due to its role in driving multiple critical engine components. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the serpentine belt are vital to prevent breakdowns and maintain optimal engine performance.
Maintenance Schedule for Timing Belts
Timing belts require replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles depending on the vehicle manufacturer's specifications to prevent engine damage. Unlike serpentine belts, which typically last 50,000 to 70,000 miles and show visible wear, timing belts operate internally and can fail silently, making strict adherence to the maintenance schedule critical. Regular inspection and timely replacement of the timing belt maintain engine performance and avoid costly repairs associated with belt failure.
How Often Should You Replace Your Serpentine Belt?
Serpentine belts typically require replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle manufacturer's recommendations and driving conditions. Inspect the belt regularly for signs of wear such as cracks, fraying, or glazing to prevent unexpected failure. Timely replacement ensures optimal performance of engine accessories like the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor.
Cost Comparison: Timing Belt vs Serpentine Belt Replacement
Timing belt replacement typically costs between $500 and $900 due to labor intensity and the need for engine disassembly, while serpentine belt replacement ranges from $50 to $200 because of its simpler installation. Timing belts usually require replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, making their higher cost periodic but necessary for engine health. Serpentine belts last longer, around 75,000 to 150,000 miles, contributing to lower maintenance expenses over time.
DIY Inspection Tips for Timing and Serpentine Belts
DIY inspection of timing and serpentine belts involves checking for cracks, fraying, or glazing on the belt surface to detect early signs of wear. Use a flashlight to closely examine the belt's tension by pressing down and observing its give, ensuring it is neither too tight nor too loose. Regularly inspecting belts every 30,000 to 60,000 miles can prevent engine damage and improve vehicle reliability.
Consequences of Ignoring Belt Maintenance in Cars
Ignoring timing belt maintenance can cause severe engine damage, including valve and piston collisions that lead to costly repairs or complete engine failure. Neglected serpentine belts risk accessory system breakdowns, affecting power steering, alternators, and air conditioning, potentially leaving drivers stranded. Regular inspections and timely replacements of both belts are critical to ensure vehicle reliability and prevent extensive mechanical damage.
Timing belt vs serpentine belt Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com