Petrol engines typically offer smoother performance and higher RPMs, making them ideal for lighter vehicles and city driving. Diesel engines provide greater fuel efficiency and torque, which benefits heavy-duty vehicles and long-distance travel. Choosing between petrol and diesel depends on driving habits, vehicle type, and fuel economy priorities.
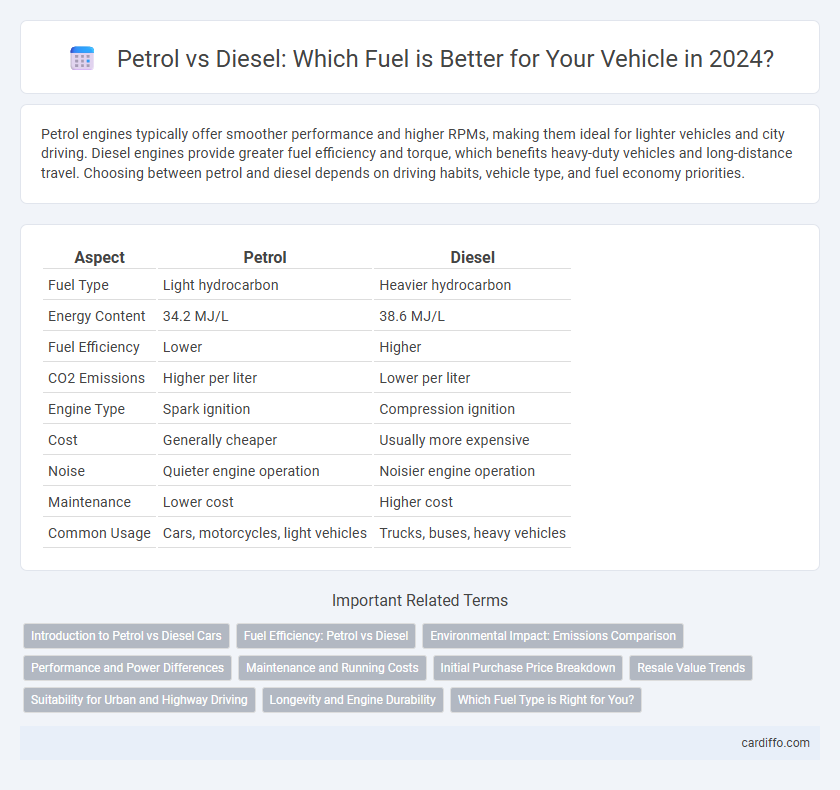
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Petrol | Diesel |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Light hydrocarbon | Heavier hydrocarbon |
| Energy Content | 34.2 MJ/L | 38.6 MJ/L |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| CO2 Emissions | Higher per liter | Lower per liter |
| Engine Type | Spark ignition | Compression ignition |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Usually more expensive |
| Noise | Quieter engine operation | Noisier engine operation |
| Maintenance | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Usage | Cars, motorcycles, light vehicles | Trucks, buses, heavy vehicles |
Introduction to Petrol vs Diesel Cars
Petrol cars use gasoline as fuel, offering higher engine speeds and smoother acceleration, making them ideal for city driving. Diesel cars run on diesel fuel, known for greater fuel efficiency and torque, which enhances performance in heavy vehicles and long-distance travel. The choice between petrol and diesel engines depends on factors like driving habits, fuel economy, and emission regulations.
Fuel Efficiency: Petrol vs Diesel
Diesel fuel offers higher fuel efficiency than petrol due to its greater energy density and more efficient combustion process, resulting in improved mileage and lower fuel consumption per kilometer. Petrol engines typically have lower thermal efficiency, leading to increased fuel usage but smoother and quieter operations. Diesel's efficiency advantage is especially noticeable in heavy-duty vehicles and long-distance driving scenarios, making it the preferred choice for fuel economy.
Environmental Impact: Emissions Comparison
Petrol engines typically emit higher levels of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, contributing to smog formation and air pollution. Diesel engines, while producing less carbon monoxide, release greater quantities of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are linked to respiratory problems and environmental degradation. Advances in emission control technologies like particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction are crucial in reducing the environmental impact of both fuel types.
Performance and Power Differences
Petrol engines typically deliver higher RPMs and smoother acceleration, making them ideal for sporty performance and lighter vehicles. Diesel engines generate greater torque at lower RPMs, providing superior pulling power and fuel efficiency, particularly beneficial for heavy-duty applications. The combustion process in diesel fuels results in higher energy density, which contributes to enhanced power output and durability in tough driving conditions.
Maintenance and Running Costs
Diesel engines generally incur higher initial maintenance costs due to more complex fuel injection systems and turbochargers, but offer better fuel efficiency and durability, reducing long-term running expenses. Petrol engines require less specialized maintenance and have lower repair costs but tend to consume more fuel, increasing overall operational costs over time. Choosing between petrol and diesel depends on mileage expectations and usage patterns, with diesel favored for heavy, long-distance driving and petrol for lighter, urban use.
Initial Purchase Price Breakdown
Petrol vehicles generally have a lower initial purchase price compared to diesel vehicles due to less complex engine technology and manufacturing costs. Diesel engines require robust components to handle higher compression ratios, increasing the cost of production and, consequently, the vehicle price. Price differences can vary between 5% to 20% depending on make and model, influencing buyer decisions based on upfront investment.
Resale Value Trends
Diesel vehicles generally maintain higher resale values due to better fuel efficiency and durability, attracting buyers looking for long-term savings. Petrol vehicles, while often cheaper upfront, tend to depreciate faster because of higher fuel consumption and increased maintenance costs. Market demand for diesel engines in commercial and heavy-duty sectors further supports stronger resale value trends.
Suitability for Urban and Highway Driving
Petrol engines excel in urban driving due to their smoother acceleration and quieter operation, making them ideal for stop-and-go traffic conditions. Diesel engines offer superior fuel efficiency and torque, which provides better performance and cost-effectiveness on highways during long-distance driving. Choosing between petrol and diesel depends on driving patterns, with petrol favoring city commutes and diesel supporting extensive highway use.
Longevity and Engine Durability
Diesel engines generally offer superior longevity and engine durability compared to petrol engines due to their robust construction designed to withstand higher compression ratios and increased thermal efficiency. The slower combustion process in diesel reduces engine wear, contributing to longer service intervals and overall engine lifespan. Petrol engines, while smoother and quieter, typically experience more frequent maintenance needs and shorter engine life under similar usage conditions.
Which Fuel Type is Right for You?
Choosing between petrol and diesel depends on your driving habits, vehicle type, and fuel efficiency needs. Petrol engines typically offer smoother performance and lower upfront costs, making them ideal for city driving and shorter distances. Diesel engines provide better fuel economy and torque, suited for long-distance travel and heavy-duty vehicles, but they often come with higher maintenance expenses.
Petrol vs Diesel Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com