Gel cell batteries offer superior vibration resistance and maintenance-free operation compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for long-term use in battery pets. Their sealed design prevents acid leakage and allows for safer handling and transport. While lead-acid batteries provide a lower upfront cost, gel cells deliver enhanced durability and longer lifespan under demanding conditions.
Table of Comparison
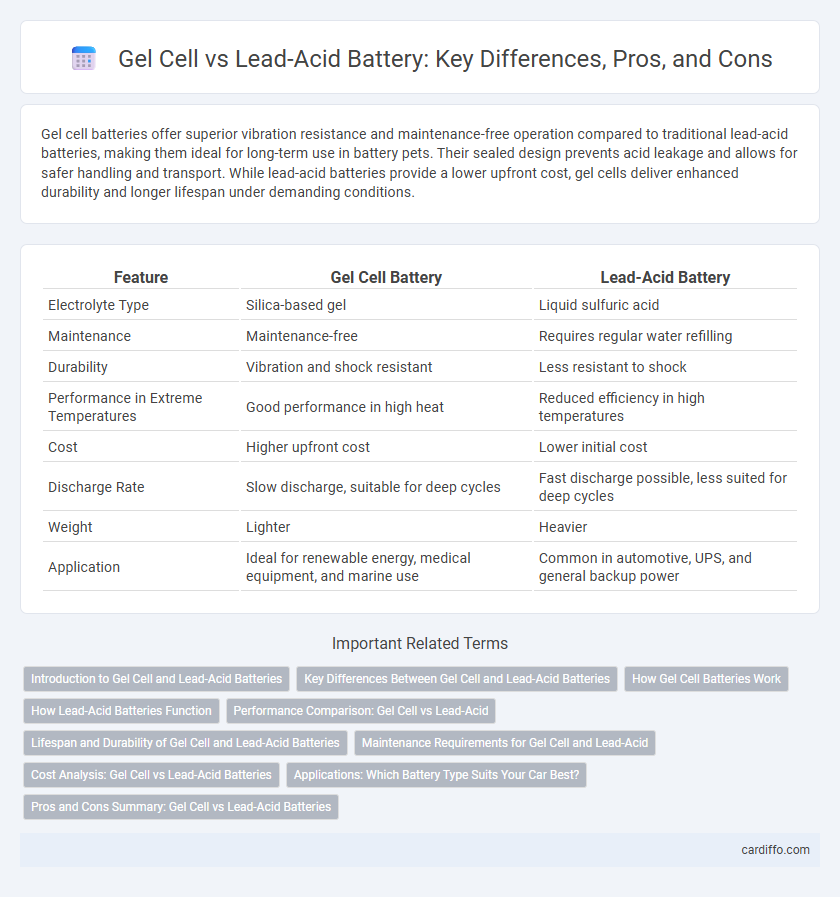
| Feature | Gel Cell Battery | Lead-Acid Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Type | Silica-based gel | Liquid sulfuric acid |
| Maintenance | Maintenance-free | Requires regular water refilling |
| Durability | Vibration and shock resistant | Less resistant to shock |
| Performance in Extreme Temperatures | Good performance in high heat | Reduced efficiency in high temperatures |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Discharge Rate | Slow discharge, suitable for deep cycles | Fast discharge possible, less suited for deep cycles |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Application | Ideal for renewable energy, medical equipment, and marine use | Common in automotive, UPS, and general backup power |
Introduction to Gel Cell and Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel cell batteries use a silica-based gel electrolyte, which reduces spillage and enhances safety, making them ideal for deep-cycle applications. Lead-acid batteries contain a liquid sulfuric acid electrolyte, offering high surge currents suitable for automotive starters and backup power systems. Both types provide reliable energy storage, but gel cells are preferred for vibration resistance and maintenance-free operation.
Key Differences Between Gel Cell and Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel cell batteries utilize a silica-based gel electrolyte that prevents acid stratification and enhances vibration resistance, making them ideal for deep cycle applications. Lead-acid batteries contain a liquid electrolyte, which can lead to acid stratification and require regular maintenance, but they generally offer higher initial power output and lower cost. Gel cell batteries are more resistant to temperature extremes and spillage, while lead-acid batteries tend to perform better in high-rate discharge scenarios.
How Gel Cell Batteries Work
Gel cell batteries utilize a silica-based gel electrolyte that immobilizes the sulfuric acid, preventing leakage and improving safety compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. The gel electrolyte allows for efficient ion movement between the lead dioxide cathode and sponge lead anode, enabling stable electrochemical reactions and consistent power delivery. This design enhances deep discharge capabilities and extends battery lifespan in applications such as renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
How Lead-Acid Batteries Function
Lead-acid batteries function through a chemical reaction between lead dioxide (PbO2) at the positive plate and sponge lead (Pb) at the negative plate, immersed in a sulfuric acid electrolyte. During discharge, lead dioxide and sponge lead react with sulfuric acid to produce lead sulfate (PbSO4), water, and electrical energy, enabling current flow. This reversible electrochemical process allows lead-acid batteries to be recharged by applying an external voltage that converts lead sulfate back to lead dioxide and sponge lead.
Performance Comparison: Gel Cell vs Lead-Acid
Gel cell batteries offer superior deep discharge recovery and longer cycle life compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent power delivery and durability. Their sealed construction prevents acid leakage and reduces maintenance, while lead-acid batteries provide higher initial current output but suffer from faster degradation under repeated deep discharges. Temperature tolerance is also enhanced in gel cells, maintaining performance in extreme conditions where lead-acid batteries may experience efficiency loss.
Lifespan and Durability of Gel Cell and Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel cell batteries typically offer a longer lifespan of around 3 to 5 years due to their sealed design, which reduces electrolyte evaporation and maintenance needs. Lead-acid batteries generally last 2 to 4 years but are more prone to sulfation and require regular maintenance to ensure durability. The enhanced durability of gel cell batteries makes them ideal for deep-cycle applications and environments with vibration or temperature fluctuations.
Maintenance Requirements for Gel Cell and Lead-Acid
Gel cell batteries require minimal maintenance due to their sealed, valve-regulated design that prevents electrolyte evaporation and reduces the need for water refilling. Lead-acid batteries demand regular maintenance, including checking electrolyte levels, topping off distilled water, and cleaning terminals to prevent corrosion. Proper maintenance practices directly impact the lifespan and performance of both gel cell and lead-acid batteries.
Cost Analysis: Gel Cell vs Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel cell batteries generally have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional lead-acid batteries due to their advanced electrolyte suspension technology and enhanced durability. Lead-acid batteries offer lower initial investment but typically require more frequent replacement and maintenance, which can increase long-term expenses. Cost analysis shows gel cell batteries provide better value in applications demanding deep cycling and extended lifespan, reducing overall lifecycle cost despite the premium price.
Applications: Which Battery Type Suits Your Car Best?
Gel cell batteries excel in deep cycle applications and off-road vehicles due to their superior vibration resistance and low maintenance requirements. Lead-acid batteries suit standard passenger cars, offering reliable cold starting power and cost-effectiveness for daily driving conditions. Choosing between gel cell and lead-acid depends on your vehicle's usage intensity, terrain, and maintenance preferences.
Pros and Cons Summary: Gel Cell vs Lead-Acid Batteries
Gel cell batteries offer superior resistance to vibration and deep discharge cycles, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and maintenance-free operation. Lead-acid batteries are more cost-effective with higher surge currents but require regular maintenance and are prone to acid stratification. The choice depends on factors such as budget, application environment, and maintenance capabilities.
Gel Cell vs Lead-Acid Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com